 CenturyLink’s stock is being pummeled after the company announced a cut in divided payouts to shareholders earlier this year, preferring to keep the money in-house to reduce debt and increase spending on necessary broadband upgrades.
CenturyLink’s stock is being pummeled after the company announced a cut in divided payouts to shareholders earlier this year, preferring to keep the money in-house to reduce debt and increase spending on necessary broadband upgrades.
Last fall, CenturyLink stock was trading for over $23 a share. By January, rumors that CenturyLink was going to cut its dividend put the stock on a downward trajectory, falling to an all-time-low below $11 this month. Company officials argued that with tightening credit opportunities and increasing interest rates, the company needed to devote money normally paid back to shareholders towards paying down its $35.5 billion long-term debt and provide better service to its customers.
A half billion dollars of that money will also be spent on upgrading CenturyLink’s broadband service, particularly in rural areas where the company is receiving Connect America Fund (CAF) dollars from the federal government.
“Our plan for 2019 includes investing to improve the trajectory of the business increasing CapEx by roughly $500 million,” Jeff Storey, president and CEO of CenturyLink said on a January analyst conference call. “As I mentioned earlier those investments include expanding the fiber network, adding new buildings throughout our footprint, enhancing our enterprise product portfolio, continuing our investments in CAF-II, and transforming our customer and employee experience.”
 Investors were not impressed with those plans, and CenturyLink’s share price cratered.
Investors were not impressed with those plans, and CenturyLink’s share price cratered.
Independent phone companies have traditionally attracted investors with handsome dividend payouts, but the realities of their aging infrastructure and the inability to compete effectively with cable companies on lucrative broadband services have left companies like CenturyLink, Windstream, and Frontier Communications in a quandary. Shareholders do not perceive value investing in fiber optic network upgrades and punish companies that announce dramatic increases in network investments. Customers left on slow-speed ADSL networks are increasingly dissatisfied with their internet experience and seek alternative providers — usually the local cable company. As Frontier Communications has discovered, attempting to win back ex-customers has been exceedingly difficult, often only possible with lucrative promotional offers that undercut the cable company. But such offers attract customers with above-average price sensitivity, making it difficult to extract increased revenue from them going forward.
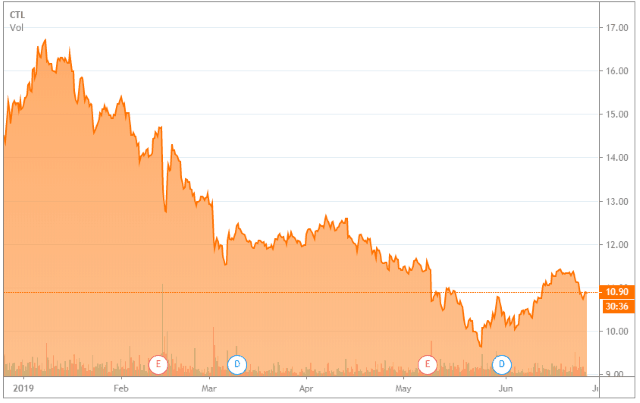
CenturyLink’s stock price has dropped to an all-time low over the last six months.
Investors are also increasingly concerned about the financial viability of investor-owned phone companies that are stuck between leveraging their old networks and facing down shareholders when upgrades become essential. AT&T and Verizon have wireless units responsible for much of the revenue earned by those two Baby Bells. Traditional phone companies have had less luck trying to sell ancillary support services like Frontier’s “Peace of Mind” technical support service, or bundling satellite TV service into packages.
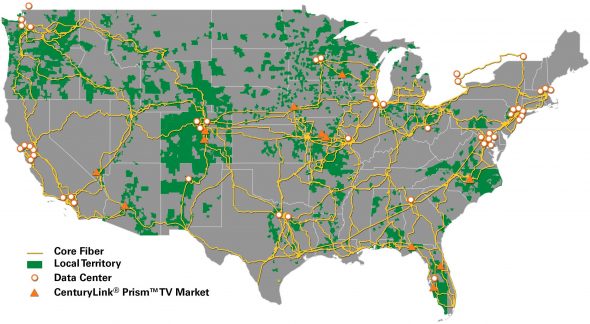
CenturyLink’s Local Service Territory (Source: CenturyLink)
CenturyLink is increasingly depending on its enterprise and wholesale businesses to earn revenue. That fact has prompted some shareholders to ask why the company hasn’t spun off or sold off its traditional landline network and consumer businesses, which currently account for only 25% of its revenue. In May, CenturyLink seemed determined to placate those investors with an announcement it was exploring “strategic options” for its consumer business. Investors theorize that CenturyLink could “unlock value” from its legacy landline networks in such a sale or spinoff that would benefit shareholder value. It would also be much cheaper than investing in that network to upgrade it.
The chorus for a sale increased after Frontier Communications announced it was spinning off its landline territories in the Pacific Northwest to a company specializing in upgrading legacy networks to support better broadband. Frontier, mired in debt and facing a concerning due date for some of its bonds, made the sale to give a boost to its balance sheet. Frontier had also been facing increasing scrutiny about a potential Chapter 11 bankruptcy filing. Windstream declared bankruptcy earlier this year, reminding investors that a trip to bankruptcy court could quickly wipe out all shareholder value.
MoffettNathanson, a Wall Street analyst firm that specializes in telecommunications, finds little to like about CenturyLink shedding its own landline operations. Frontier’s sale benefited from the fact a significant part of its Pacific Northwest territory was built from an acquisition from Verizon, which had already installed its FiOS fiber to the home network in parts of Washington and Oregon. About 30% of the territory Frontier is selling is fiber-enabled. In comparison, CenturyLink has installed fiber to the home service in only about 10% of its territory, dramatically reducing any potential sale price. Much of CenturyLink’s core fiber network powers its enterprise and wholesale operations — businesses CenturyLink would likely keep for itself.
MoffettNathanson also sees little value from the proposition a buyer could leverage CenturyLink’s network to provide backhaul fiber capacity for future 5G services, because CenturyLink provides service mostly in smaller communities likely to be bypassed by 5G, at least for the near term.
Wall Street’s idea of a win-win strategy for CenturyLink is to keep its consumer business and expand its broadband service footprint and capability, if the federal government offers to cover much of the cost through more rounds of CAF subsidies. Taxpayers would subsidize broadband expansion while CenturyLink and shareholders share all the profits.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Dish Network Corporation is in the final stages of talks to acquire assets that include valuable wireless spectrum and Sprint’s Boost Mobile brand for an estimated $6 billion, according to a report quoting anonymous sources
Dish Network Corporation is in the final stages of talks to acquire assets that include valuable wireless spectrum and Sprint’s Boost Mobile brand for an estimated $6 billion, according to a report quoting anonymous sources  Wall Street analyst MoffettNathanson remains skeptical about the T-Mobile/Sprint merger and is even more puzzled by Dish’s reported involvement. The analyst firm released a research note to its clients warning the future of Boost may be bleak:
Wall Street analyst MoffettNathanson remains skeptical about the T-Mobile/Sprint merger and is even more puzzled by Dish’s reported involvement. The analyst firm released a research note to its clients warning the future of Boost may be bleak: AT&T claims it is willing to play hardball to force cell tower owners to reduce the cost of leasing space for AT&T’s wireless services. If tower owners won’t lower their prices, AT&T is threatening to find someone else willing to build a new, cheaper tower nearby.
AT&T claims it is willing to play hardball to force cell tower owners to reduce the cost of leasing space for AT&T’s wireless services. If tower owners won’t lower their prices, AT&T is threatening to find someone else willing to build a new, cheaper tower nearby. WarnerMedia’s forthcoming streaming service will showcase HBO and Cinemax at the heart of a one-size-fits-all streaming package priced at $16-17 a month, featuring premium movies and Warner Bros. vast movie and TV show collection. We wanted to enjoy those streams.
WarnerMedia’s forthcoming streaming service will showcase HBO and Cinemax at the heart of a one-size-fits-all streaming package priced at $16-17 a month, featuring premium movies and Warner Bros. vast movie and TV show collection. We wanted to enjoy those streams. 

 In fact, Cable One charges so much money for internet, they
In fact, Cable One charges so much money for internet, they  AT&T and Verizon have their own approaches to deal with reluctant customers. Verizon FiOS customers face steep price hikes when their promotions expire, but the opportunity to score a better deal is still there, if Verizon is in the mood that quarter. Verizon remains sensitive about their subscriber numbers and growth, so when a quarter looks like it will be difficult, the promotions turn up. AT&T prefers to play a shell game with their customers. Most recently, the company has given a cold shoulder to its U-verse product, treating it like yesterday’s news and best forgotten. AT&T literally markets its own customers to abandon U-verse in favor of AT&T Fiber. Verizon and AT&T treat their DSL customers like they are doing them a favor just by offering any service. All the best deals go to their fiber customers.
AT&T and Verizon have their own approaches to deal with reluctant customers. Verizon FiOS customers face steep price hikes when their promotions expire, but the opportunity to score a better deal is still there, if Verizon is in the mood that quarter. Verizon remains sensitive about their subscriber numbers and growth, so when a quarter looks like it will be difficult, the promotions turn up. AT&T prefers to play a shell game with their customers. Most recently, the company has given a cold shoulder to its U-verse product, treating it like yesterday’s news and best forgotten. AT&T literally markets its own customers to abandon U-verse in favor of AT&T Fiber. Verizon and AT&T treat their DSL customers like they are doing them a favor just by offering any service. All the best deals go to their fiber customers.