 Two months after a late July thunderstorm interrupted phone and internet service for some CenturyLink customers in parts of Albemarle County, Va, some are still waiting for the phone company to restore service.
Two months after a late July thunderstorm interrupted phone and internet service for some CenturyLink customers in parts of Albemarle County, Va, some are still waiting for the phone company to restore service.
Multiple CenturyLink customers around the area told The Daily Progress about the extended outage, and the company’s lack of responsiveness in restoring service. Many report their service appointments are unilaterally canceled or a repair technician just never shows up. Others are receiving messages the repairs are complete, but they still have no service.
Mobile phone service is spotty in this part of central Virginia, so many customers keep their landlines to reach emergency services. With service out for nearly two months, making emergency calls or accessing the internet has been difficult.
In August, CenturyLink employee Derek Kelly told attendees at a Albemarle Broadband Authority meeting that at storm brought down almost a mile of CenturyLink’s legacy copper wire network, which has been in place for decades. Kelly noted CenturyLink intended to replace the damaged copper wiring with more copper wiring, instead of upgrading to fiber optics, and because of supply chain issues, customers have been left waiting.
“We ran into logistical issues of being able to find that length of copper,” Kelly said. “I think between COVID and everything else, supplies are limited, so it took us longer than we typically hope for to get the copper in place and get it in town and get it hung back up and spliced in.”
So far, customers are still being billed for service they do not have, and the company has refused to issue automatic credits for customers left without service. Some customers want CenturyLink to compensate them extra for interrupted service as well as for the company wasting their time on unfulfilled service calls and being left on hold, sometimes for an hour, trying to resolve the problem.

Firefly is a service of municipal/co-op power companies in central Virginia.
Albemarle County Supervisor Donna Price has been hearing complaints from local residents for weeks and she is also well aware CenturyLink is in the process of selling a large part of its legacy local phone operations in 20 states to Apollo Global Management, a private equity firm. The phone company will keep its most profitable customers in 16 states — many already served by fiber optics, under its Lumen brand. As that sale waits to close, Price believes CenturyLink has already walked away from their soon-to-be ex-customers.
“I believe that corporate CenturyLink has basically given up and has abandoned their responsibility, which leaves it all upon the individual consumers to either seek some sort of collective relief or basically just suffer until a new provider comes in,” Price told the newspaper. “I think CenturyLink has failed in customer service, in the delivery of service and, I’ll be a little more generous, in the recovery from the storm, because those are really difficult situations.”
Some customers in nearby Fluvanna County who have also experienced multi-month service interruptions from CenturyLink were lucky enough to have a choice of broadband providers, and many have switched to Firefly Fiber Broadband, which also supplies landline phone service. Firefly is owned and operated by a partnership subsidiary that includes the Central Virginia Electric Cooperative. That fiber to the home network has survived serious storms in the past without lengthy service interruptions. The member-owned cooperative has also invested heavily in fiber broadband and communications services its members demand, and if something goes wrong, local repairmen answerable to local supervisors are on hand to manage any issues.
Firefly Fiber is currently looking to expand its operations within its central Virginia service area, which includes the counties of Albemarle, Appomattox, Buckingham, Cumberland, Fluvanna, Goochland, Greene, Louisa, and Powhatan.
![]() Charter Communications this week reduced prices on multi-line unlimited data plans.
Charter Communications this week reduced prices on multi-line unlimited data plans.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Two months after a late July thunderstorm interrupted phone and internet service for some CenturyLink customers in parts of Albemarle County, Va, some are still waiting for the phone company to restore service.
Two months after a late July thunderstorm interrupted phone and internet service for some CenturyLink customers in parts of Albemarle County, Va, some are still waiting for the phone company to restore service.
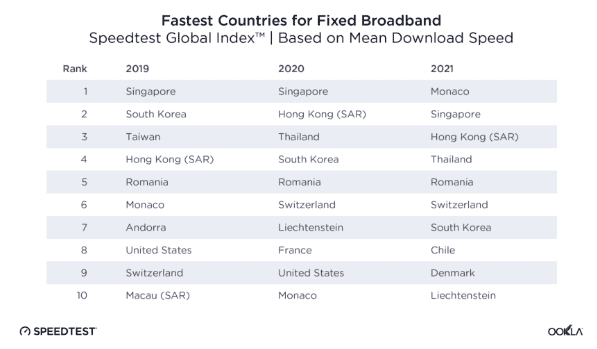
 “South Korea and the United Arab Emirates stood out with mean mobile download speeds that were more than 240% faster than the global average and fixed broadband downloads that were more than 70% faster than the global average,”
“South Korea and the United Arab Emirates stood out with mean mobile download speeds that were more than 240% faster than the global average and fixed broadband downloads that were more than 70% faster than the global average,”  After weeks of tense negotiations to secure bipartisan support for the Biden Administration’s $1 trillion infrastructure stimulus measure, the White House appears to have largely capitulated to Republican efforts to water down funding to expand broadband service into a $65 billion package that will doubtless be a financial bonanza to the country’s largest phone and cable operators.
After weeks of tense negotiations to secure bipartisan support for the Biden Administration’s $1 trillion infrastructure stimulus measure, the White House appears to have largely capitulated to Republican efforts to water down funding to expand broadband service into a $65 billion package that will doubtless be a financial bonanza to the country’s largest phone and cable operators. The latest proposal’s idea of solving the broadband affordability issue is to admit there is a problem and declare the need for some kind of low-cost broadband option, but apparently does not specify pricing, who is qualified to get cheaper service, and who will oversee that such programs remain affordable. That allows providers to keep writing the rules of their own token, voluntary efforts to offer discounted internet, like those that disqualify current customers and requires enrollees to jump through various qualification hoops to sign up. The stimulus program will also spend billions of dollars effectively paying a portion of disadvantaged Americans’ internet bills, at the current high prices many ISP’s charge. That is a direct subsidy to big cable and phone companies that can continue charging whatever they please for access, knowing the government will now pay $30-50 of the bill.
The latest proposal’s idea of solving the broadband affordability issue is to admit there is a problem and declare the need for some kind of low-cost broadband option, but apparently does not specify pricing, who is qualified to get cheaper service, and who will oversee that such programs remain affordable. That allows providers to keep writing the rules of their own token, voluntary efforts to offer discounted internet, like those that disqualify current customers and requires enrollees to jump through various qualification hoops to sign up. The stimulus program will also spend billions of dollars effectively paying a portion of disadvantaged Americans’ internet bills, at the current high prices many ISP’s charge. That is a direct subsidy to big cable and phone companies that can continue charging whatever they please for access, knowing the government will now pay $30-50 of the bill.
 “While a telecommunications giant like Verizon may be able to absorb such a loss, others may not,” Judge Hurley wrote in his order.
“While a telecommunications giant like Verizon may be able to absorb such a loss, others may not,” Judge Hurley wrote in his order.