 Charter Communications has set the stage for a Wall Street-pleasing boost in average revenue per user (ARPU) with a major broadband rate hike planned for this fall.
Charter Communications has set the stage for a Wall Street-pleasing boost in average revenue per user (ARPU) with a major broadband rate hike planned for this fall.
The rate of U.S. broadband subscriber growth slowed significantly in the second quarter of 2019, as the marketplace for internet access remains saturated and current customers are largely staying with the provider they know.
A MoffettNathanson report to investors shared by Light Reading reported subscriber growth is down from 3% during the first three months of 2019 to 2.8% over the late spring and early summer. In total, cable and phone companies added 438,000 new broadband customers in the second quarter, a significant drop from the 570,000 they added at the same time last year.
The number of new household formations continues to decline in the United States, presumably because younger Americans saddled with student loan debt are having a tougher time buying property or justifying high rent payments. Providers also believe the ongoing shift away from copper telco DSL service to cable broadband has slowed to a trickle, with those still loyal to DSL not concerned about internet speed, are happy with lower cost service, or do not have any other option. Craig Moffett, chief analyst for MoffettNathanson believes much of the growth in cable broadband at this point is coming from customers switching from services like AT&T U-verse, which still offers top speeds of under 30 Mbps in some areas. Other phone companies still relying on fiber-to-the-neighborhood service are likely also seeing customer departures triggered by recent discontinuation of video service. In most areas, cable operators are still the largest beneficiaries of provider changes. Phone companies relying on DSL continue to report broadband subscriber losses. Last year during the second quarter, phone companies lost 127,000 subscribers (a 1.1% decline). This summer, they lost 172,000 subscribers (a 1.3% decline).
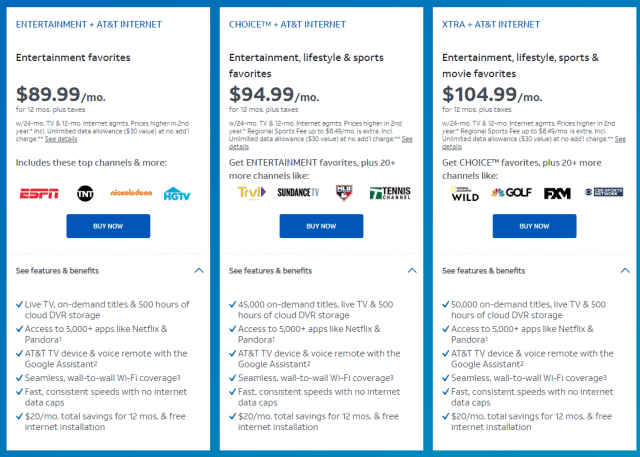
With slowing cable broadband growth, companies are still under pressure to report positive quarterly results to shareholders. Without a significant number of new customers, Moffett believes operators will raise broadband prices to deliver higher revenue, especially in light of ongoing video cord-cutting. Moffett points to Charter Communications’ Spectrum in particular. Spectrum has one of the cable industry’s lowest ARPU numbers, because it does not impose cable modem rental fees or usage caps. That may explain the company’s plans to hike general internet pricing 6% starting in October, soon collecting $69.99 for Standard 100 (or 200 Mbps) service and $75.99 a month for customers bundling Standard Internet with Wi-Fi.
“The broadband increases alone would suggest significant upside to Charter ARPU estimates,” Moffett said. He also noted Charter’s plan to dramatically increase video pricing also “underscores their recent pivot towards ‘letting’ video customers leave if they want, and repricing those who remain for profitability.”
That means customers outraged by Spectrum’s cable TV rate hikes will not get much sympathy from customer retention agents. Moffett believes customers will be invited to cancel cable television service, because Charter does not make as much profit on the service as it used to, and customers will probably still keep their Spectrum internet service, which is enormously profitable for the cable operator. Customers will also pay an even higher price for standalone internet service once they stop bundling television service, increasing Charter’s profits even more.
Ironically, the more Spectrum customers drop cable TV packages, the more profit Charter can report to shareholders. Those keeping cable television won’t hurt Charter’s bottom line either. Customers that readily agree to pay more with each cable TV rate hike are statistically the least likely to complain or cancel.


 Subscribe
Subscribe

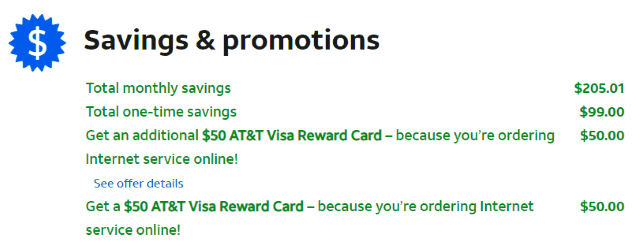

 In fact, Cable One charges so much money for internet, they
In fact, Cable One charges so much money for internet, they  AT&T and Verizon have their own approaches to deal with reluctant customers. Verizon FiOS customers face steep price hikes when their promotions expire, but the opportunity to score a better deal is still there, if Verizon is in the mood that quarter. Verizon remains sensitive about their subscriber numbers and growth, so when a quarter looks like it will be difficult, the promotions turn up. AT&T prefers to play a shell game with their customers. Most recently, the company has given a cold shoulder to its U-verse product, treating it like yesterday’s news and best forgotten. AT&T literally markets its own customers to abandon U-verse in favor of AT&T Fiber. Verizon and AT&T treat their DSL customers like they are doing them a favor just by offering any service. All the best deals go to their fiber customers.
AT&T and Verizon have their own approaches to deal with reluctant customers. Verizon FiOS customers face steep price hikes when their promotions expire, but the opportunity to score a better deal is still there, if Verizon is in the mood that quarter. Verizon remains sensitive about their subscriber numbers and growth, so when a quarter looks like it will be difficult, the promotions turn up. AT&T prefers to play a shell game with their customers. Most recently, the company has given a cold shoulder to its U-verse product, treating it like yesterday’s news and best forgotten. AT&T literally markets its own customers to abandon U-verse in favor of AT&T Fiber. Verizon and AT&T treat their DSL customers like they are doing them a favor just by offering any service. All the best deals go to their fiber customers. The top 10 service providers in the United States collectively lost over 1.25 million paid television customers in the first three months of 2019, providing further evidence that cord-cutting is accelerating.
The top 10 service providers in the United States collectively lost over 1.25 million paid television customers in the first three months of 2019, providing further evidence that cord-cutting is accelerating.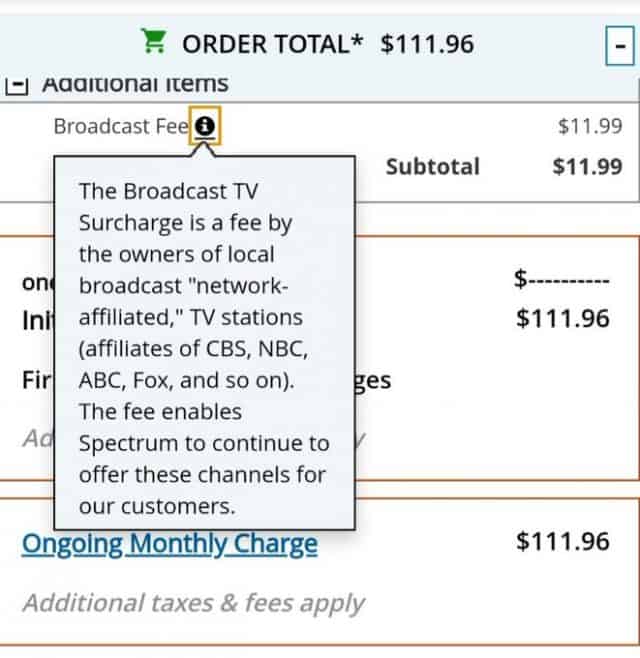 For the last several years, cable subscribers have lamented that the advertised price of service falls short of the real “out-the-door” cost shown on one’s monthly bill.
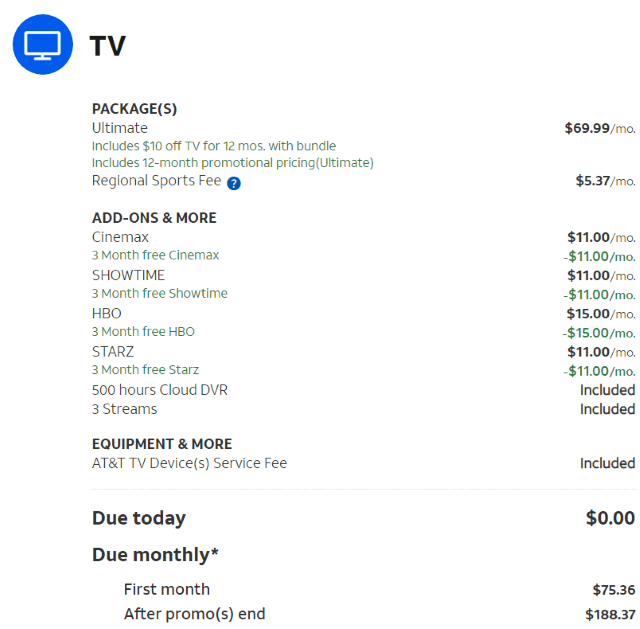
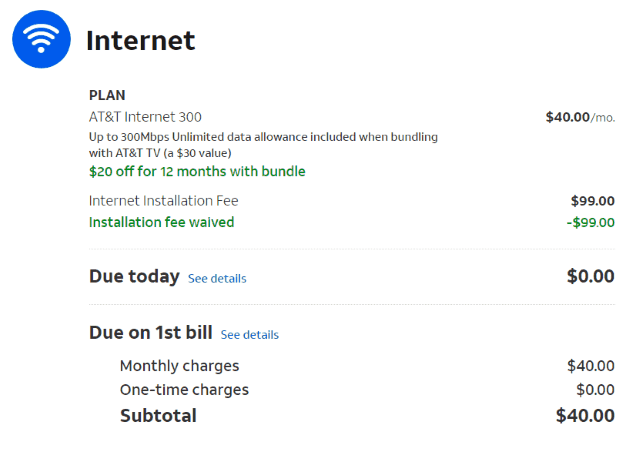
For the last several years, cable subscribers have lamented that the advertised price of service falls short of the real “out-the-door” cost shown on one’s monthly bill.