
GIVE us more money and TAKE what we offer you.
Bloomberg News is reporting what many of you already know — it is getting tougher to get a better deal from your cable or phone company.
As Stop the Cap! has documented since the completion of the Time Warner Cable/Bright House/Charter Spectrum merger in 2016, companies are pulling back on promotions, taking advantage of a lack of competition and offering best pricing only to new customers.
Charter Spectrum and Cable One (soon to be Sparklight) are the most notorious for implementing “take it or leave it” pricing. In fact, one of Charter CEO Thomas Rutledge’s chief complaints about Time Warner Cable was its “Turkish Bazaar” mentality about pricing. Rutledge claimed Time Warner Cable had as many as 90,000 different promotions running at the same time, typically targeted on what other companies were theoretically providing service and how serious the representative felt you were about canceling service. Time Warner Cable had basic retention plans available for regular representatives to offer, better plans for retention specialists to pitch, and the best plans of all to customers complaining on the “executive customer service” line or after filing complaints with the Better Business Bureau. There were plans for complaining over the phone and different plans for complaining at the cable store. Rutledge was horrified, because customers were now well-trained on how to extract a better deal every year when promotions ran out.
Last month, Rutledge said he was indifferent about cash-strapped consumers that cannot afford a runaway cable TV bill on a retired/fixed income or the urban poor who can’t imagine paying $65 a month for basic broadband service. To those customers, pointing to the exit is now perfectly acceptable. In fact, companies make more profit than ever when you drop cable television service and upgrade your broadband connection to a faster speed. That is because there is up to a 90% margin on internet service — provisioned over a network paid off decades ago and designed for much less space efficient analog television. Charging you $20 more for faster internet service is nearly 100% profit and costs most companies next to nothing to offer, and Time Warner Cable executives once laughed off the financial impact of so-called “heavy users,” calling data transport costs mere “rounding errors.”
Even with a much tougher attitude about discounting service, Charter and Comcast are still adding new broadband customers every month, usually at the expense of phone companies still peddling DSL. So if you cancel, there are probably two new customers ready to replace you, at least for now.
Cable One redefines rapacious pricing. The company specializes in markets where the incumbent phone company is likely to offer low-speed DSL, if anything at all. As a result, they have a comfortable monopoly in many areas and price their service accordingly. Cable One’s basic 200 Mbps plan, with a 600 GB data cap, costs $65 a month, not including the $10.50/mo modem fee, and $2.75 monthly internet service surcharge. To ditch the cap, you will pay another $40 a month — $118.25 total for unlimited internet.
 In fact, Cable One charges so much money for internet, they even have Wall Street concerned they are overcharging!
In fact, Cable One charges so much money for internet, they even have Wall Street concerned they are overcharging!
When Joshua May tried calling Spectrum to deal with the 29% more it wanted (around $40 a month) after his promotion expired, the customer service representative told him to go pound salt.
“I expected they’d at least offer free HBO or Showtime,” May, 34, of Springfield, Ohio, told Bloomberg News. “They did nothing.”
He did something. He cut the cord. The representative could have cared less.
The product mix cable and phone companies offer has not really changed, but the era of shoving a triple play bundle of internet, TV, and phone service sure has. Charter and Comcast now treat cable television as a nice extra, not the start of a bundle offer. Broadband is the key item, and the most profitable element, of today’s cable package. Beleaguered phone service gets no respect either. Time Warner Cable used to sell its triple play bundle including a phone line for less money than their double play bundle that omitted it. Today, it’s a simple $9.99/mo extra, given as much attention as a menu offering premium movie channels.
Comcast differs from Charter by offering a plethora of options to their customers. If you don’t want to spend a lot for high speed internet, spend a little less for low speed internet. Their television packages also vary in price and channel selection, often maddeningly including a “must-have” channel in a higher-priced package. Like Spectrum, their phone line is now an afterthought.
 AT&T and Verizon have their own approaches to deal with reluctant customers. Verizon FiOS customers face steep price hikes when their promotions expire, but the opportunity to score a better deal is still there, if Verizon is in the mood that quarter. Verizon remains sensitive about their subscriber numbers and growth, so when a quarter looks like it will be difficult, the promotions turn up. AT&T prefers to play a shell game with their customers. Most recently, the company has given a cold shoulder to its U-verse product, treating it like yesterday’s news and best forgotten. AT&T literally markets its own customers to abandon U-verse in favor of AT&T Fiber. Verizon and AT&T treat their DSL customers like they are doing them a favor just by offering any service. All the best deals go to their fiber customers.
AT&T and Verizon have their own approaches to deal with reluctant customers. Verizon FiOS customers face steep price hikes when their promotions expire, but the opportunity to score a better deal is still there, if Verizon is in the mood that quarter. Verizon remains sensitive about their subscriber numbers and growth, so when a quarter looks like it will be difficult, the promotions turn up. AT&T prefers to play a shell game with their customers. Most recently, the company has given a cold shoulder to its U-verse product, treating it like yesterday’s news and best forgotten. AT&T literally markets its own customers to abandon U-verse in favor of AT&T Fiber. Verizon and AT&T treat their DSL customers like they are doing them a favor just by offering any service. All the best deals go to their fiber customers.
AT&T Randall Stephenson is a recent convert to the “who cares about video customers” movement. Services like DirecTV Now were originally channel-rich bargains, but now they are a place for rate hikes and channel deletions. Over a half-million streaming customers have already canceled after the most recent price hikes, but Stephenson claims he does not mind, because those bargain-chasers are low-quality customers worthy of purging. AT&T’s dream customer is one who appreciates whatever AT&T gives them and does not mind a parade of rate hikes.
Comcast’s chief financial officer Mike Cavanagh said it more succinctly: seeking subscribers that “really value video and our bundle despite the increases in prices,” and has “the wallet for a fuller video experience.”
Customers who decide to take their business to a streaming competitor are already learning the industry still has the last laugh. As package prices head north of $50/month, that is not too far off from the pricing offered by cable and phone companies for base video packages. In fact, Spectrum has begun undercutting most streaming providers, offering $15-25 packages of local and/or popular cable channels with a Cloud DVR option for around $5 more a month.
 A New York bankruptcy judge cleared the way for Windstream Holdings to pay its top executives up to $24 million in special retention bonuses to convince them to stay at Windstream while the company continues restructuring under Chapter 11 bankruptcy.
A New York bankruptcy judge cleared the way for Windstream Holdings to pay its top executives up to $24 million in special retention bonuses to convince them to stay at Windstream while the company continues restructuring under Chapter 11 bankruptcy.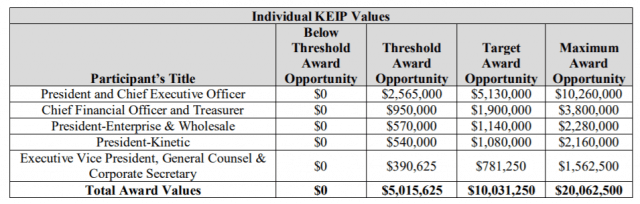


 Subscribe
Subscribe AT&T claims it is willing to play hardball to force cell tower owners to reduce the cost of leasing space for AT&T’s wireless services. If tower owners won’t lower their prices, AT&T is threatening to find someone else willing to build a new, cheaper tower nearby.
AT&T claims it is willing to play hardball to force cell tower owners to reduce the cost of leasing space for AT&T’s wireless services. If tower owners won’t lower their prices, AT&T is threatening to find someone else willing to build a new, cheaper tower nearby. WarnerMedia’s forthcoming streaming service will showcase HBO and Cinemax at the heart of a one-size-fits-all streaming package priced at $16-17 a month, featuring premium movies and Warner Bros. vast movie and TV show collection. We wanted to enjoy those streams.
WarnerMedia’s forthcoming streaming service will showcase HBO and Cinemax at the heart of a one-size-fits-all streaming package priced at $16-17 a month, featuring premium movies and Warner Bros. vast movie and TV show collection. We wanted to enjoy those streams. 

 Charter Spectrum sold its merger with Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks partly on its argument that modem fees would no longer be charged. Despite that, many former Time Warner Cable and Bright House customers still use their own modems, which has been a problem for a company that raised the standard internet speed available to residential customers from 15 Mbps to 100 Mbps (200 Mbps in some markets, mostly those also served by AT&T). Older modems often cannot achieve those speeds. Spectrum notifies affected customers in periodic campaigns, offering to replace their obsolete equipment, but many customers suspect hidden fees may be lurking in such offers and discard them.
Charter Spectrum sold its merger with Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks partly on its argument that modem fees would no longer be charged. Despite that, many former Time Warner Cable and Bright House customers still use their own modems, which has been a problem for a company that raised the standard internet speed available to residential customers from 15 Mbps to 100 Mbps (200 Mbps in some markets, mostly those also served by AT&T). Older modems often cannot achieve those speeds. Spectrum notifies affected customers in periodic campaigns, offering to replace their obsolete equipment, but many customers suspect hidden fees may be lurking in such offers and discard them. Cox is also in a similar predicament. It runs seasonal checks on its network to identify customers using older DOCSIS modems, often DOCSIS 3.0 4×4 modems, which can only support four download channels. When it finds customers eligible for an upgrade, it mails postcards offering a “free modem upgrade,” usually supplying a SB6183 or SB8200 modem that can arrive in 24-48 hours. But many Cox customers suspect trickery from Cox as well, or run into poorly trained customer service representatives that reject the postcards, claiming the customer is ineligible.
Cox is also in a similar predicament. It runs seasonal checks on its network to identify customers using older DOCSIS modems, often DOCSIS 3.0 4×4 modems, which can only support four download channels. When it finds customers eligible for an upgrade, it mails postcards offering a “free modem upgrade,” usually supplying a SB6183 or SB8200 modem that can arrive in 24-48 hours. But many Cox customers suspect trickery from Cox as well, or run into poorly trained customer service representatives that reject the postcards, claiming the customer is ineligible. In fact, most modem upgrade offers from your provider are likely genuine, but customers need to pay attention to any fine print.
In fact, most modem upgrade offers from your provider are likely genuine, but customers need to pay attention to any fine print.
 In fact, Cable One charges so much money for internet, they
In fact, Cable One charges so much money for internet, they  AT&T and Verizon have their own approaches to deal with reluctant customers. Verizon FiOS customers face steep price hikes when their promotions expire, but the opportunity to score a better deal is still there, if Verizon is in the mood that quarter. Verizon remains sensitive about their subscriber numbers and growth, so when a quarter looks like it will be difficult, the promotions turn up. AT&T prefers to play a shell game with their customers. Most recently, the company has given a cold shoulder to its U-verse product, treating it like yesterday’s news and best forgotten. AT&T literally markets its own customers to abandon U-verse in favor of AT&T Fiber. Verizon and AT&T treat their DSL customers like they are doing them a favor just by offering any service. All the best deals go to their fiber customers.
AT&T and Verizon have their own approaches to deal with reluctant customers. Verizon FiOS customers face steep price hikes when their promotions expire, but the opportunity to score a better deal is still there, if Verizon is in the mood that quarter. Verizon remains sensitive about their subscriber numbers and growth, so when a quarter looks like it will be difficult, the promotions turn up. AT&T prefers to play a shell game with their customers. Most recently, the company has given a cold shoulder to its U-verse product, treating it like yesterday’s news and best forgotten. AT&T literally markets its own customers to abandon U-verse in favor of AT&T Fiber. Verizon and AT&T treat their DSL customers like they are doing them a favor just by offering any service. All the best deals go to their fiber customers.