 Frontier Communications is preparing a detailed plan for bondholders explaining how the company hopes to cut its $17 billion in debt before it faces the possibility of bankruptcy.
Frontier Communications is preparing a detailed plan for bondholders explaining how the company hopes to cut its $17 billion in debt before it faces the possibility of bankruptcy.
The Wall Street Journal reports Frontier is ready to begin formal negotiations with those holding its debt to create a new payback plan before it faces the first of several repayment deadlines for bonds running into the billions, starting in 2022. But the strategy is risky because if any of the company’s major bondholders disagree, it could put Frontier on a fast track to Chapter 11 bankruptcy reorganization.
Frontier’s debt problems are a consequence of its decision to expand its wireline footprint through acquisitions of castoff copper landline networks being sold primarily by Verizon Communications and AT&T. Critics have repeatedly called out Frontier for bungling network transitions with extended service outages, billing problems, and other customer service-related failures that left customers and some state regulators frustrated and alienated. The company is still facing regulatory review in states like Connecticut, where it failed to properly manage a customer cutover from AT&T’s systems to its own, and in Utah, West Virginia, California, and Florida where similar cutovers from Verizon Communications left more than a few customers without service and months of billing problems.
As a result, Frontier lost many of the customers it acquired, with many unwilling to consider doing business with the phone company ever again.
Although Frontier’s latest acquisitions of Verizon landline customers in California, Texas, and Florida included large Verizon FiOS fiber to the home territories, Frontier customers continue to disconnect service at a greater pace than the phone company’s chief cable competitors — Comcast and Charter Spectrum. Customer defections are even worse in large sections of Frontier’s stagnant “legacy” markets — service areas that have been managed by Frontier or its predecessor Citizens Communications for decades. That is because almost all of those legacy markets are still serviced by decades-old copper wire networks, many capable only of providing low speed DSL internet access.
Frontier’s large debt load is cited as the principal reason the company cannot embark on upgrade efforts to replace existing copper wiring with optical fiber. In fact, virtually all of Frontier’s fiber service areas have been acquired from AT&T or Verizon. Frontier executives have attempted to placate shareholders by promising to aggressively manage costs. But promises of dramatic savings have proved elusive and frequent media reports have emerged covering extensive service outages, poor network maintenance, ongoing billing and customer service issues, and inadequate staffing to address a growing number of service outages and problems. In several states, repeated 911 outages have triggered regulator investigations with the prospect of stiff fines.
Three Frontier insiders have privately shared their insights with Stop the Cap! about ongoing frustrations with the company and the most recent developments.
“Upper management has no comprehension that in many of our markets, customers have choices and they abandon us when all we can sell is DSL service at speeds often less than 12 Mbps,” one senior regional executive told us. “Our retention efforts are so poor these days, representatives are not really expected to rescue accounts because in most cases there is no legitimate reason to do business with us. In some states where there are high mandated surcharges, we cost more than our cable competitors.”
Another mid-level executive in one of Frontier’s largest legacy markets — Rochester, N.Y., said morale is low and a growing number of colleagues believe the days to bankruptcy are short.
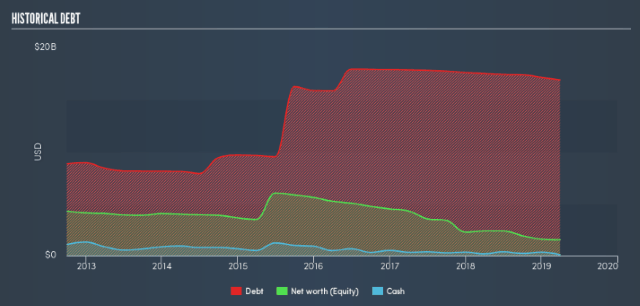
Frontier Communications debt load.
“Our loyal customers are literally dying off, as their adult children disconnect decades-old landline accounts,” said an executive who wished to remain anonymous because they were not authorized to speak with the media. “The customer numbers have been ugly for a long time and are getting worse. Our recently retired customers who have had DSL and voice service with us since the 1990s are disconnecting because some have gone with Spectrum and others are moving out of the area. Some of these customers hate Spectrum and won’t do business with them no matter the price, but we are losing their business anyway when they move out of state.”
The Rochester executive noted Frontier has an impossible job trying to sell its internet and voice products against Charter Spectrum.
“Their offers are $40 a month for 100 Mbps internet and $10 for unlimited local and long-distance calls,” the executive noted. “Ours costs nearly $30 just for the phone line after taxes and fees, and how can you sell someone DSL that delivers less than 6 Mbps to many parts of a market still served by copper trunk lines to a central office several miles away? They also find out they have to lease our modem at an additional fee and there are other fees in the contract many customers have learned to look for. Answer: you can’t.”
A Frontier executive in Ohio shared a similar story.
“We hold our own in our rural markets where we can offer a customer better than dial-up internet, and our service is very good if you live in an area where we expanded broadband thanks to FCC subsidies. Some of these new areas are even served by fiber,” the executive explained. “The problem with this is fewer people live in rural areas and these places cost a lot more to maintain when we dispatch service crews or have to run new cable. For Frontier to be truly successful, we have to get better internet service into our larger older markets, but that means pulling copper off poles and putting up fiber and there is just no interest from the higher ups to spend the money to do this. So instead the company bought new territories to keep revenue numbers up, but we are also quickly losing many of those customers to cable too. I really don’t know what we will do when wireless companies offer 5G internet.”
Some Frontier bondholders recognize Frontier must reduce its debt to have the financial resources to expand fiber service. Others want the company to shed its legacy copper service areas (while keeping FiOS/U-verse enabled markets) either to regional companies willing to invest in upgrades or to hedge funds that would likely ring whatever remaining value still exists out of these abandoned service areas. Some suspect these hedge funds would also load up the spinoff companies with even greater debt to facilitate dividend payouts and other investor-friendly rewards.
It will be up to state and federal regulators to protect Frontier’s customers as the two emerging groups of conflicting bondholders angle to protect their investments, perhaps at the risk of reliable phone and internet service.
The Wall Street Journal:
One, including Elliott Management and Franklin Resources, pushed for an exchange of their bonds at a discount to their face value for new secured debt that would be paid before unsecured debt in a potential bankruptcy.
Still, bondholders including GoldenTree Asset Management have warned the company against doing such a swap since 2018, arguing it violated the terms of their bonds.
The company this week reached out to Houlihan Lokey, which represents a group of bondholders that includes GoldenTree—as well as JPMorgan Chase & Co., Oaktree Capital Management and Brigade Capital Management—to sign up to view a confidential restructuring proposal, a person familiar with the matter said. That group has yet to gather enough holders to form a majority, people familiar with the matter said.

 A modem rental fee may also apply in most states, unless you use your own cable modem. Outside of New York and New Jersey, most legacy ELP customers have already experienced several gradual rate increases on this plan, which was originally sold nationwide for $14.99/mo. The first rate increase took most customers to $19.99/mo, followed by a rate increase last fall to $24.99/mo. Now Charter Spectrum has notified customers of another $3/mo rate hike, bringing the monthly rate to $27.99.
A modem rental fee may also apply in most states, unless you use your own cable modem. Outside of New York and New Jersey, most legacy ELP customers have already experienced several gradual rate increases on this plan, which was originally sold nationwide for $14.99/mo. The first rate increase took most customers to $19.99/mo, followed by a rate increase last fall to $24.99/mo. Now Charter Spectrum has notified customers of another $3/mo rate hike, bringing the monthly rate to $27.99.

 Subscribe
Subscribe Frontier Communications is preparing a detailed plan for bondholders explaining how the company hopes to cut its $17 billion in debt before it faces the possibility of bankruptcy.
Frontier Communications is preparing a detailed plan for bondholders explaining how the company hopes to cut its $17 billion in debt before it faces the possibility of bankruptcy.
 After learning from the experiences of providing a wireless 5G home broadband alternative in a handful of U.S. cities, Verizon is preparing to launch a refreshed 5G Home fixed wireless product in all 30 cities where it intends to provide mobile 5G service this year.
After learning from the experiences of providing a wireless 5G home broadband alternative in a handful of U.S. cities, Verizon is preparing to launch a refreshed 5G Home fixed wireless product in all 30 cities where it intends to provide mobile 5G service this year. Verizon uses its tool to assure “qualified” customers are well inside the radius of its 5G coverage area. An analysis found Verizon’s millimeter wave network, which operates in the 28 GHz band, has a limited range. Although Verizon predicted its network could reach 1,000 feet from each small cell location, the website only qualified those in Sacramento living within around 500 feet of each small cell. Verizon is also heavily reliant on using light poles for smart cells, and these were not always suitable for the widest coverage.
Verizon uses its tool to assure “qualified” customers are well inside the radius of its 5G coverage area. An analysis found Verizon’s millimeter wave network, which operates in the 28 GHz band, has a limited range. Although Verizon predicted its network could reach 1,000 feet from each small cell location, the website only qualified those in Sacramento living within around 500 feet of each small cell. Verizon is also heavily reliant on using light poles for smart cells, and these were not always suitable for the widest coverage.
 Altice
Altice  Spectrum customers in Southern California are gradually getting a free upgrade to 200 Mbps — twice the usual Standard speed, starting with new customers.
Spectrum customers in Southern California are gradually getting a free upgrade to 200 Mbps — twice the usual Standard speed, starting with new customers.