
Rep. Marsha Blackburn (R-Tennessee, but mostly AT&T and Comcast)
Rep. Marsha Blackburn (R-Tenn.) is angry that FCC chairman Tom Wheeler is sticking his nose into AT&T, Comcast, and Charter Communications’ private playground — the state of Tennessee.
In an editorial published by The Tennessean, Blackburn throws a fit that an “unelected” bureaucrat not only believes what’s best for her state, but is now openly talking about preempting state laws that ban public broadband networks:
Legislatures are the entities who should be making these decisions. Legislatures govern what municipalities can and cannot do. The principles of federalism and state delegation of power keep government’s power in check. When a state determines that municipalities should be limited in experimenting in the private broadband market, it’s usually because the state had a good reason — to help protect public investments in education and infrastructure or to protect taxpayers from having to bailout an unproven and unsustainable project.
Chairman Wheeler has repeatedly stated that he intends to preempt the states’ sovereign role when it comes to this issue. His statements assume that Washington knows best. However, Washington often forgets that the right answers don’t always come from the top down.
It’s unfortunate Rep. Blackburn’s convictions don’t extend to corporate money and influence in the public dialogue about broadband. The “good reason” states have limited public broadband come in the form of a check, either presented directly to politicians like Blackburn, who has received so many contributions from AT&T she could cross daily exercise off her “things to do” list just running to the bank, or through positive press from front groups, notably the corporate-funded American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC).
According to campaign finance data compiled by the Center for Responsive Politics, three of Blackburn’s largest career donors are employees and PACs affiliated with AT&T, Comcast and Verizon. Blackburn has also taken $56,000 from the National Cable & Telecommunications Association, the lobby for the big telecoms.
Combined, those organizations donated more than $200,000 to Blackburn. In comparison, her largest single donor is a PAC associated with Memphis-based FedEx Corp., which donated $68,500.

Phillip “States’ rights don’t extend to local rights in Blackburn’s ideological world” Dampier
Blackburn’s commentary tests the patience of the reality-based community, particularly when she argues that keeping public broadband out protects investments in education. As her rural constituents already know, 21st century broadband is often unavailable in rural Tennessee, and that includes many schools. Stop the Cap! regularly receives letters from rural Americans who complain they have to drive their kids to a Wi-Fi enabled parking lot at a fast food restaurant, town library, or even hunt for an unintentionally open Wi-Fi connection in a private home, just to complete homework assignments that require a broadband connection.
Blackburn’s favorite telecommunication’s company — AT&T — has petitioned the state legislature to allow it to permanently disconnect DSL and landline service in rural areas of the state, forcing customers to a perilous wireless data experience that doesn’t work as well as AT&T promises. While Blackburn complains about the threat of municipal broadband, she says and does nothing about the very real possibility AT&T will be allowed to make things even worse for rural constituents in her own state.
Who does Blackburn believe will ride to the rescue of rural America? Certainly not AT&T, which doesn’t want the expense of maintaining wired broadband service in less profitable rural areas. Comcast won’t even run cable lines into small communities. In fact, evidence has shown for at least a century, whether it is electricity, telephone, or broadband service, when large corporate entities don’t see profits, they won’t provide the service and communities usually have to do the job themselves. But this time those communities are handcuffed in states that have enacted municipal broadband bans literally written by incumbent phone and cable companies and shepherded into the state legislature through front groups like ALEC.
Chairman Wheeler is in an excellent position to understand the big picture, far better than Blackburn’s limited knowledge largely absorbed from AT&T’s talking points. After all, Wheeler comes from the cable and wireless industry and knows very well how the game is played. Wheeler has never said that Washington knows best, but he has made it clear state and federal legislators who support anti-competitive measures like municipal broadband bans don’t have a monopoly on good ideas either — they just have monopolies.
That isn’t good enough for Congresswoman Blackburn, who sought to strip funding from the FCC to punish the agency for crossing AT&T, Comcast and other telecom companies:

Marsha is an avowed member of the AT&T Fan Club.
In July, I passed an amendment in Congress that would prohibit taxpayer funds from being used by the FCC to pre-empt state municipal broadband laws. My amendment doesn’t prevent Chattanooga or any other city in Tennessee from being able to engage in municipal broadband. It just keeps those decisions at the state level. Tennessee’s state law that allowed Chattanooga and other cities to engage in municipal broadband will continue to exist without any interference from the FCC. Tennessee should be able to adjust its law as it sees fit, instead of Washington dictating to us.
Notice that Blackburn’s ideological fortitude has loopholes that protect a very important success story — EPB Fiber in Chattanooga, one of the first to offer gigabit broadband service. If municipal broadband is such a threat to common sense, why the free pass for EPB? In fact, it is networks like EPB that expose the nonsense on offer from Blackburn and her industry friends that claim public broadband networks are failures and money pits.
In fact, Blackburn’s idea of states’ rights never seems to extend to local communities across Tennessee that would have seen local ordinances gutted by Blackburn’s telecommunications policies and proposed bills. In 2005, Blackburn introduced the ironically named Video Choice Act of 2005 which, among other things:
- Would have granted a nationwide video franchise system that would end all local oversight over rights-of-way for the benefit of incumbent telephone companies, but not for cable or other new competitors like Google Fiber;
- Strips away all local oversight of cable and telephone company operations that allowed local jurisdictions to ensure providers follow local laws and rules;
- Prohibited any mechanism on the local level to collect franchise payments;
- Eliminated any rules forbidding “redlining” — when a provider only chooses select parts of a community to serve.
More recently, Blackburn has been on board favoring legislation restricting local communities from having a full say on the placement of cell towers. Current Tennessee law already imposes restrictions on local communities trying to refuse requests from AT&T, Verizon and others to place new cell towers wherever they like. She is also in favor of highest-bidder wins spectrum auctions that could allow AT&T and Verizon to use their enormous financial resources to snap up new spectrum and find ways to hoard it to keep it away from competitors.
Not everyone in Tennessee appreciated Blackburn’s remarks.
Nashville resident Paul Felton got equal time in the newspaper to refute Blackburn’s claims:
Rep. Marsha Blackburn is on her high horse (Tennessee Voices, Oct. 3) about the idea of the Federal Communications Commission opposing laws against municipal broadband networks, wrapping herself in the mantle of states’ rights. We know that behind all “states’ rights” indignation is “corporate rights” protection.
The last I heard, there was only one Internet, and anyone can log into Amazon or healthcare.gov just as easily from any state. Or any budget.
No, this is about the one Internet being controlled by one corporate giant (or two) in each area, who want to control price and broadband speed, and now want to link the two. They don’t want competition from any pesky municipal providers hellbent on providing the same speed for all users, at a lower price. Check the lobbying efforts against egalitarian ideas to find out which side of an issue Marsha Blackburn always comes down on.
But comments like these don’t deter Rep. Blackburn.
“Congress cannot sit idly by and let a federal agency trample on our states’ rights,” she wrote, but we believe she meant to say ‘AT&T’s rights.’
“Besides, the FCC should be tackling other priorities where political consensus exists, like deploying spectrum into the marketplace, making the Universal Service Fund more effective, protecting consumers, improving emergency communications and other important policies,” Blackburn wrote.
Remarkably, that priority list just so happens to mirror AT&T’s own legislative agenda. Perhaps that is just a coincidence.
 New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo has set a goal that every resident of New York State should have access to at least 100Mbps broadband no later than 2018.
New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo has set a goal that every resident of New York State should have access to at least 100Mbps broadband no later than 2018.
 That must come as a relief for Verizon. The state’s largest phone company has petitioned state officials in the past for a gradual mothballing of New York’s rural landline network in favor of switching customers to wireless voice and broadband over Verizon’s cellular network. Theoretically, taxpayers could end up subsidizing the demise of rural New York landlines and DSL if Verizon seeks money from the rural broadband fund to expand its wireless tower network in rural New York. Time Warner Cable almost certainly will also seek more funding, probably in excess of the average $1,264 paid to the cable company for each of the 4,114 additional connections it agreed to complete during an earlier round of funding.
That must come as a relief for Verizon. The state’s largest phone company has petitioned state officials in the past for a gradual mothballing of New York’s rural landline network in favor of switching customers to wireless voice and broadband over Verizon’s cellular network. Theoretically, taxpayers could end up subsidizing the demise of rural New York landlines and DSL if Verizon seeks money from the rural broadband fund to expand its wireless tower network in rural New York. Time Warner Cable almost certainly will also seek more funding, probably in excess of the average $1,264 paid to the cable company for each of the 4,114 additional connections it agreed to complete during an earlier round of funding.

 Subscribe
Subscribe AT&T CEO Randall Stephenson’s public hissy fit against the Obama Administration’s sudden backbone on Net Neutrality may complicate AT&T’s plans to win approval of its merger with DirecTV. forcing AT&T to retract threats to suspend fiber buildouts if the administration moves forward with its efforts to ban Internet fast lanes.
AT&T CEO Randall Stephenson’s public hissy fit against the Obama Administration’s sudden backbone on Net Neutrality may complicate AT&T’s plans to win approval of its merger with DirecTV. forcing AT&T to retract threats to suspend fiber buildouts if the administration moves forward with its efforts to ban Internet fast lanes.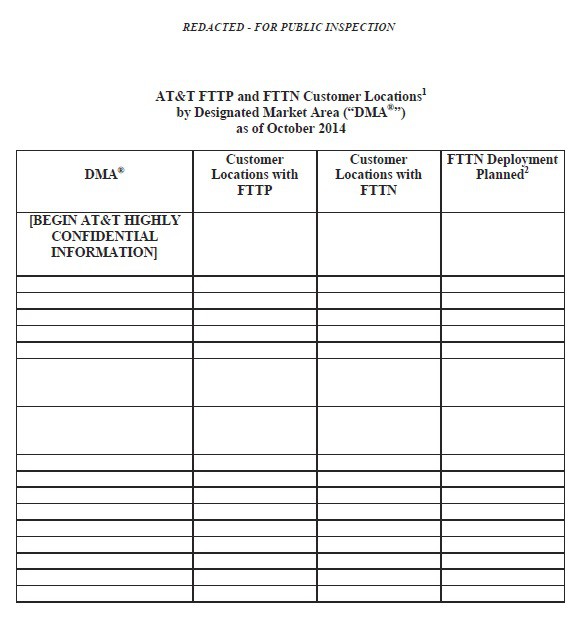


 Comcast: 88% of customers met or exceeded state and federal standards;
Comcast: 88% of customers met or exceeded state and federal standards;



 But some critics contend $664 million is insufficient to wire every building in Ireland for fiber service and suspect the government may try to backtrack and choose fiber to the cabinet or wireless service for the most isolated communities that could prove extremely expensive to reach with fiber.
But some critics contend $664 million is insufficient to wire every building in Ireland for fiber service and suspect the government may try to backtrack and choose fiber to the cabinet or wireless service for the most isolated communities that could prove extremely expensive to reach with fiber.