 Charter Spectrum’s broadband-only customers run up more than double the amount of broadband usage average customers subscribing to both cable TV and broadband use, and that consumption is growing fast.
Charter Spectrum’s broadband-only customers run up more than double the amount of broadband usage average customers subscribing to both cable TV and broadband use, and that consumption is growing fast.
“Data usage by residential internet customers is rising rapidly and monthly median data usage is over 200 GB per customer,” Charter CEO Thomas Rutledge said on a morning quarterly results conference call. “When you look at average monthly usage for customers that don’t subscribe to our traditional video product, usage climbs to over 400 GB per month.”
Last week, Comcast reported its average broadband customer also used over 200 GB a month, but did not break out the difference between those subscribing to cable TV and those who do not. If Comcast’s broadband-only customers are consuming a comparable amount of data, they could be nearing half of their monthly usage allowance (1 TB), in markets where Comcast caps its customers’ usage. But because that is only an average, it means many more Comcast customers are likely nearing or now exceeding Comcast’s data cap, exposing them to hefty overlimit penalties.
Spectrum does not impose any data allowances on its customers — all usage is unlimited.
Charter officials also reported their average mobile customers use “well under 10 GB a month.” The fact Charter did not get more specific about mobile usage is important because the new product is getting scrutiny from some on Wall Street concerned it will have a hard time becoming profitable because of its wholesale agreement with Verizon Wireless, which provides the 4G LTE service for Spectrum Mobile.
Subscribers have been primarily drawn to the $14/GB plan, which includes unlimited talk and texting, because it offers a very low entry price for a full-function wireless plan. But a customer only needs to use more than 3 GB of service per month to find their bill higher than what they would pay subscribing to Spectrum Mobile’s $45 unlimited usage plan. If Charter executives said the average mobile user consumed 5 GB of data, analysts could deduce what the average customer bill probably looked like. To maximize profits, Charter needs customers to select an unlimited data plan and keep data usage low to assure it can cover the wholesale costs Verizon Wireless charges the cable company for wireless connectivity.

Rutledge
Rutledge stressed he expects Spectrum Mobile to be profitable with the current Verizon Wireless MVNO contract in place — the service simply needs a larger user base to overcome its current losses.
Rutledge also announced Spectrum Mobile was testing dual SIM technology, which could allow it to eventually offload more of its 4G LTE traffic to its own (cheaper) network, which could eventually include mid-band wireless spectrum and the CBRS spectrum the company is already testing for fixed wireless service for rural areas. Spectrum could also follow Comcast with its own in-home network of publicly available Wi-Fi or innovate with unlicensed wireless mobile spectrum using small cells or external antennas.
Charter executives noted that customer data demands were pushing many to upgrade to higher speed internet products.
“Over 80% of our internet customers are now in packages that deliver 100 Mbps of speed or more and 30% of our customers are getting 200 Mbps or more,” Rutledge said. “We’re also seeing strong demand for our Ultra product, which delivers 400 Mbps, and we have gigabit service available everywhere.”
The costs to continue upgrading service for broadband customers are negligible on the company’s current platform, Rutledge admits. In the future, Charter Spectrum is considering offering 10 Gbps and 25 Gbps symmetrical service to customers, and it can scale up upgrades very quickly.
“For example, in only 14 months we launched DOCSIS 3.1, which took our speeds up to 1 Gbps across our entire footprint at a cost of just $9 per passing,” Rutledge said.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Virginia officials cannot get broadband providers to reveal full details about their actual service areas, so the state now believes cable and phone companies will be more forthcoming if they can quietly share that information with each other, keeping the state government in the dark.
Virginia officials cannot get broadband providers to reveal full details about their actual service areas, so the state now believes cable and phone companies will be more forthcoming if they can quietly share that information with each other, keeping the state government in the dark.
 The average Comcast broadband customer
The average Comcast broadband customer 
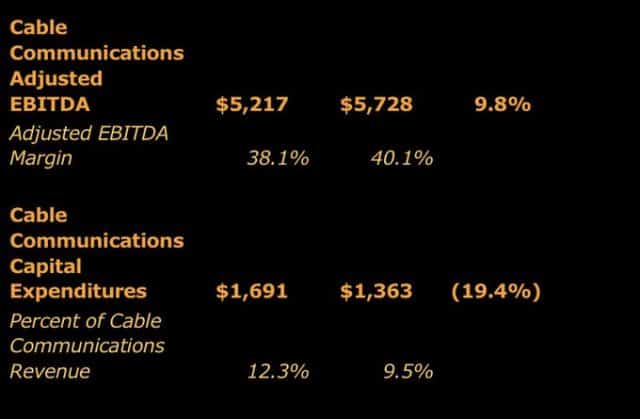
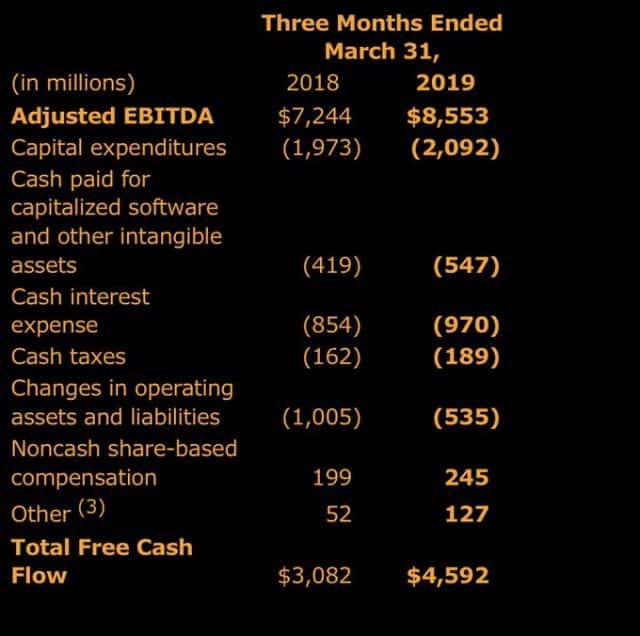
 Verizon Communications has indefinitely suspended plans to charge customers an extra $10 a month for access to Verizon’s extremely spotty and uneven 5G service, which launched earlier this month in Chicago and Minneapolis.
Verizon Communications has indefinitely suspended plans to charge customers an extra $10 a month for access to Verizon’s extremely spotty and uneven 5G service, which launched earlier this month in Chicago and Minneapolis.