 As part of its investigation of cable and satellite television companies, the U.S. Senate Permanent Subcommittee on Investigations found large discrepancies in how five of America’s largest cable and satellite companies—Charter Communications, Comcast, Time Warner Cable, DirecTV, and Dish—identify and correct overcharges caused by company billing errors.
As part of its investigation of cable and satellite television companies, the U.S. Senate Permanent Subcommittee on Investigations found large discrepancies in how five of America’s largest cable and satellite companies—Charter Communications, Comcast, Time Warner Cable, DirecTV, and Dish—identify and correct overcharges caused by company billing errors.
The subcommittee released its report to coincide with today’s hearings on customer service and billing practices in the cable and satellite television industry. The Senate subcommittee focused its attention primarily on billing errors associated with rented set-top boxes and receivers, not programming packages or add-on services. The bipartisan report found satellite TV company Dish was probably the least prone to billing errors associated with satellite equipment and Time Warner Cable was the worst at identifying equipment billing discrepancies. Even when it did find instances of overbilling, the company refused to give customers automatic full refunds as a matter of “efficiency.”
That “efficiency” is expected to be very profitable for Time Warner Cable, which is likely to collect $1,919,844 from overbilling this year alone. Time Warner Cable estimates that, in 2015, it overbilled 40,193 Ohio customers a total of $430,393 and 4,232 Missouri customers a total of $44,152. Time Warner Cable also told the subcommittee that, during the first five months of 2016, it overbilled customers in Ohio for 11,049 pieces of equipment, totaling $108,221.
Charter Communications only did marginally better, mostly because it is a much smaller cable company. Charter estimates that it has overcharged approximately 5,897 Missouri customers a total of $494,000. Charter, along with Time Warner Cable, made no effort to trace equipment overcharges to their origin unless customers specifically asked them to and did not provide notice or refunds to customers.
Let’s review how the five companies compare:
Time Warner Cable
 Time Warner Cable is notorious for its “no refunds unless asked” policy, which often leaves customers uncompensated for service outages and other problems. That policy also extends to equipment-related billing errors. During the 6.5 year time period covered by the subcommittee investigation, Time Warner Cable never automatically refunded or credited customer for equipment overcharges discovered by the company. Instead, Time Warner’s “Revenue Assurance” team quietly identified and corrected billing errors without any notification or explanation to customers, which may explain why your Time Warner Cable bill can change even when you are locked in with a promotion.
Time Warner Cable is notorious for its “no refunds unless asked” policy, which often leaves customers uncompensated for service outages and other problems. That policy also extends to equipment-related billing errors. During the 6.5 year time period covered by the subcommittee investigation, Time Warner Cable never automatically refunded or credited customer for equipment overcharges discovered by the company. Instead, Time Warner’s “Revenue Assurance” team quietly identified and corrected billing errors without any notification or explanation to customers, which may explain why your Time Warner Cable bill can change even when you are locked in with a promotion.
The subcommittee discovered Time Warner Cable still relies on two entirely different billing systems. One, “Integrated Communications Operations Management System”, otherwise known as ICOMS, is especially troublesome to navigate at Time Warner because the company does not use standardized coding across the entire company. Placing an order for Internet service in the Northeast Division of Time Warner Cable is completely different from ordering the same product in a city like Kansas City or the west coast. Employees have complained about ICOMS for years, noting it can take up to 30 separate codes entered correctly in the system to add just one product, like High-Speed Internet. A simple data entry error can mess up an order and generate a billing error (or a lost order or service request that is never processed). But Time Warner Cable also relies on a different platform developed by CSG to manage some of its billing. Some of Time Warner Cable’s acquisitions, like Insight Communications, have operated under the Time Warner Cable brand for several years, but still use some of the billing platforms that were in place before Time Warner took over.
The subcommittee found strong evidence ICOMS is a big problem for Time Warner Cable. Attempts to audit the platform often crash, as it did in May of this year, preventing Time Warner Cable from identifying billing issues. At best, the company only aims for an 80% correction rate using its auditing tools.
One audit uncovered 18,000 customers in the Carolinas, Midwest, and Northeast that were being overbilled for modem and CableCARD equipment. Although Time Warner Cable was going to remove the erroneous charges going forward, it had no plans to automatically refund customers it identified as overcharged unless customers somehow realized that themselves and called in to request retroactive credit.

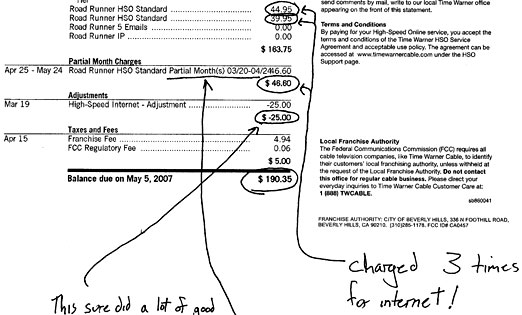
Time Warner Cable once erroneously billed one of its own employees for three Internet accounts.
The subcommittee found if an audit showed that a customer had not been billed for equipment or services that the customer had received, the company treats those inconsistencies as undercharges and adds the charge to the customer’s bill going forward. Time Warner Cable does not attempt to retroactively charge the customer for previous months where that customer was undercharged.
If the audit shows that a customer has been billed for equipment or services that he or she does not have, the story is more complicated. In some cases, customers agree to pay for equipment they do not actually have so that they can receive a cheaper package price—for example, a consumer who wants only Internet service might decide the cheapest option is a promotional package including both Internet and cable television. By participating in the promotion, the customer agrees to pay a monthly rental fee for a set-top box but may instruct the company not to provide a set-top box. In such a case, the customer’s billing records will show a charge for a set-top box, but the customer’s equipment records will show that he or she does not physically have a set-top box. In April 2016, for example, Time Warner Cable identified 49,132 pieces of equipment associated with overcharges; of those 37,653 (approximately 77 percent) were not “correctable” overcharges because they were associated with accounts participating in promotional offers.
Time Warner Cable does not attempt to trace billing errors to their origin. Instead, it only provides a partial credit for the month during which the error was discovered. The company will not notify you of the error or for how long it has been on your bill. Unless you call and demand full credit for the overbilling, you will not receive it.
The cable company defends its policy on the ground that it is “efficient.” Going through months of customer bills to identify overcharges would be costly and time consuming, the company argues. The company also claims that the customer is best positioned to notice an overcharge and bring it to Time Warner Cable’s attention.
After reviewing policies at several different companies, the subcommittee cast doubt on Time Warner’s assertions, noting other companies had no problems returning overbilled amounts to customers without a request to do so.
Charter Communications
Unfortunately for customers, not included on the list of companies willing and able to automatically refund overbilling is Charter Communications, which recently acquired Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks.
 The subcommittee called Charter’s process of identifying and correct overbilling “substandard.”
The subcommittee called Charter’s process of identifying and correct overbilling “substandard.”
According to Charter, prior to August 2015, the company did not run any systematic audits to reconcile its billing records with equipment records. Charter’s failure to perform regular audits means that overcharged customers could not receive a prospective correction of their bill unless they noticed the problem themselves and contacted Charter. Beginning in August 2015, however, Charter began taking steps to identify equipment overcharges now on its system. Charter will complete that process in June 2016.
Charter recently upgraded some of its systems to make sure that when an employee adds or deletes services and/or equipment, an update to the customer’s billing record occurs automatically. Charter has 21 employees working for its Billing Quality Assurance department. The employees randomly sample bills to check their accuracy and when Charter changes its bill format or presentation, the team is supposed to review the bills to make certain any billing changes do not introduce mass errors. The subcommittee found these auditing methods were unlikely to discover common “one-off” errors, such as when customers are overbilled for equipment or programming on their specific account.
Charter’s alternate methods of identifying discrepancies quickly become more convoluted and less useful after that.
For example, beginning in August 2015, Charter undertook what it called a “controller reconciliation,” in which the company began to reconcile its billing records with equipment data from its 35 “controllers” throughout the country. These “controllers” are designed to manage box authorizations and “from the office” service connection and disconnection so that a truck roll is unnecessary. These systems can also be useful in identifying unauthorized equipment installed at locations where they were never registered or if the box was authorized for channels a customer was not paying to receive. A controller reconciliation allowed Charter to identify anomalies like in Missouri, where almost 6,000 customers were being billed for set-top boxes they were not using.
The subcommittee was unhappy neither Time Warner Cable or Charter seem willing to use “brute manpower to identify how long a customer has been overcharged and automatically grant a refund or credit,” as well as do more to minimize equipment and programming mismatches with billing records.

Comcast has bigger problems than overbilling.
Comcast
Comcast relies on a very similar auditing process in use at Time Warner Cable to identify billing discrepancies, except once Comcast finds one it identifies how long a customer was overcharged, notifies the customer and automatically credits the customer’s account. Starting late last year, Comcast began running audits weekly to improve billing accuracy. Comcast claims just a 0.3% error rate.
Comcast has more than 60 employees nationwide on the east and west coasts examining billing issues and, when needed, individually investigates each case to identify applicable refunds.
DirecTV
DirecTV doesn’t do regular audits, instead relying on a program called SAS Enterprise Miner to search for billing errors before bills are generated. It can also use the same tools to identify and correct past billing errors. The satellite provider goes as far back as necessary to correct past mistakes, and pointed to instances where credits of thousands of dollars were issued to affected customers. DirecTV’s Revenue Assurance department can also reach out and communicate with employees at all levels of the company to investigate billing issues and prevent future ones. What will change as a result of AT&T’s ownership of the company isn’t known.
Dish Network
 Dish was cited by the subcommittee report as having the billing system least likely to generate billing errors. Dish links its equipment and billing systems together, which means any change on one system automatically updates the other.
Dish was cited by the subcommittee report as having the billing system least likely to generate billing errors. Dish links its equipment and billing systems together, which means any change on one system automatically updates the other.
According to Dish, it is impossible to add or remove equipment without altering the customer’s billing records. Dish provides each customer with one free “receiver”—Dish’s term for the equivalent of a set-top box—and charges $7.00 to $15.00 per month for each additional receiver a customer has. That is the only equipment charge. Dish’s system will only send a television signal to receivers that have been “activated,” which happens as part of the installation process. Once a receiver has been activated, the customer’s billing information is automatically updated to reflect that addition. That system ensures that no receiver is added to a customer’s account unless it has been activated.
Dish customers return their receivers by mail. Dish provides a packaging label so that it can track the receiver once it has been mailed. When the receiver returns to the Dish warehouse, an employee scans the barcode on the receiver, which removes the receiver from the customer’s provisioning records and, in turn, from the customer’s bill.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Senate Cable Billing Practices 6-23-16.mp4[/flv]
Hearing: Customer Service and Billing Practices in the Cable and Satellite Television Industry
Permanent Subcommittee on Investigations, June 23, 2016 10:00AM ET
(Video starts at 19:55) (2:18:54)
 First credit cards were tied to your credit score, then auto insurance, and now how much you pay for cable television and what kind of support you receive from customer service may also depend on your creditworthiness, at least at Cable One.
First credit cards were tied to your credit score, then auto insurance, and now how much you pay for cable television and what kind of support you receive from customer service may also depend on your creditworthiness, at least at Cable One. Cable One has even stopped direct marketing its cable service, even though it was winning nine percent of new customer sign-ups. The customers Cable One attracted were so low quality, Might claims the company didn’t make a penny from the marketing effort.
Cable One has even stopped direct marketing its cable service, even though it was winning nine percent of new customer sign-ups. The customers Cable One attracted were so low quality, Might claims the company didn’t make a penny from the marketing effort.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Despite vociferous denials to New York regulators that Altice’s unique way of cost-cutting expenses in Europe would mean the same in the United States, a Suddenlink employee in the Appalachians found herself visiting a nearby Kroger supermarket recently to pick up some “forever” postage stamps after the office’s postage meter machine stopped working.
Despite vociferous denials to New York regulators that Altice’s unique way of cost-cutting expenses in Europe would mean the same in the United States, a Suddenlink employee in the Appalachians found herself visiting a nearby Kroger supermarket recently to pick up some “forever” postage stamps after the office’s postage meter machine stopped working. When Altice took over Cablevision, employees were stunned when top executives dined in the staff canteen on their first day after the deal closed. That was never the style of former CEO James Dolan and other executives who avoided hobnobbing with anyone too far from the executive suites. Dolan himself often used a helicopter to travel back and forth from the office, occasionally with bodyguards.
When Altice took over Cablevision, employees were stunned when top executives dined in the staff canteen on their first day after the deal closed. That was never the style of former CEO James Dolan and other executives who avoided hobnobbing with anyone too far from the executive suites. Dolan himself often used a helicopter to travel back and forth from the office, occasionally with bodyguards. With a commitment to slash $900 million in expenses out of Cablevision alone during 2016, that’s a lot of discipline. Employees are echoing their French counterparts at Altice’s SFR-Numericable when they call life at Suddenlink and Cablevision “a culture of fear,” watching workers exiting each week without being replaced. Much the same happened in Europe, despite commitments not to engage in job-cutting. In both cases, Altice claims the slow but steady trickle of employee departures are “normal churn,” not layoffs.
With a commitment to slash $900 million in expenses out of Cablevision alone during 2016, that’s a lot of discipline. Employees are echoing their French counterparts at Altice’s SFR-Numericable when they call life at Suddenlink and Cablevision “a culture of fear,” watching workers exiting each week without being replaced. Much the same happened in Europe, despite commitments not to engage in job-cutting. In both cases, Altice claims the slow but steady trickle of employee departures are “normal churn,” not layoffs. Is your cable television service included in your rent or condo “services” fee? Have you ever called another provider and told service was not available at your address even through others outside of your condo neighborhood or apartment complex can sign up for service today? Chances are your landlord or property management company is receiving a kickback to keep competition off the property, while you may be stuck paying for substandard services you neither want or need. Worst of all, chances are it’s all legal and everyone is getting a piece of the action… except you.
Is your cable television service included in your rent or condo “services” fee? Have you ever called another provider and told service was not available at your address even through others outside of your condo neighborhood or apartment complex can sign up for service today? Chances are your landlord or property management company is receiving a kickback to keep competition off the property, while you may be stuck paying for substandard services you neither want or need. Worst of all, chances are it’s all legal and everyone is getting a piece of the action… except you. With the FCC’s 2007 declaration that exclusive contracts between cable companies and property owners were “null and void,” the power of the cable industry to negotiate on their terms was markedly diminished. Although many property owners applauded their new-found freedom to tell the local cable company to take a hike if they did not offer better service to their tenants, many others saw dollar signs in their eyes. With leverage now in the hands of the property owner, if the local cable company wanted to stay, in many cases it had to pay. Only the most brazen property owners kicked uncooperative cable companies off their properties, putting tenants at a serious inconvenience. Instead, many found life more peaceful and lucrative to stick with the existing cable company, signing a new contract for “bulk billing” tenants. On the surface, it seemed like a good deal. Property owners advertised that cable TV was included in the rent (and they paid a deeply discounted price per tenant) and the cable operator had a guaranteed number of customers, whether they wanted the service or not.
With the FCC’s 2007 declaration that exclusive contracts between cable companies and property owners were “null and void,” the power of the cable industry to negotiate on their terms was markedly diminished. Although many property owners applauded their new-found freedom to tell the local cable company to take a hike if they did not offer better service to their tenants, many others saw dollar signs in their eyes. With leverage now in the hands of the property owner, if the local cable company wanted to stay, in many cases it had to pay. Only the most brazen property owners kicked uncooperative cable companies off their properties, putting tenants at a serious inconvenience. Instead, many found life more peaceful and lucrative to stick with the existing cable company, signing a new contract for “bulk billing” tenants. On the surface, it seemed like a good deal. Property owners advertised that cable TV was included in the rent (and they paid a deeply discounted price per tenant) and the cable operator had a guaranteed number of customers, whether they wanted the service or not. If Google Fiber, AT&T U-verse or Verizon FiOS sought to offer service on one of these properties, they would have to overcome the investment insanity of wiring each building with its own infrastructure, including duplicate cables, in separate conduits and spaces not already designated for the exclusive use of the cable company. Verizon in New York City has faced numerous obstacles wiring some buildings, including gaining access to the building itself. Intransigent on site employees, bureaucratic and unresponsive property management companies, and developers have all made life difficult for Verizon’s fiber upgrade.
If Google Fiber, AT&T U-verse or Verizon FiOS sought to offer service on one of these properties, they would have to overcome the investment insanity of wiring each building with its own infrastructure, including duplicate cables, in separate conduits and spaces not already designated for the exclusive use of the cable company. Verizon in New York City has faced numerous obstacles wiring some buildings, including gaining access to the building itself. Intransigent on site employees, bureaucratic and unresponsive property management companies, and developers have all made life difficult for Verizon’s fiber upgrade.



 “I think it’s vital to put our country’s well being ahead of party,” he said in a statement provided by the Clinton campaign. “Hillary Clinton is experienced, qualified, and will make a fine president. The alternative, I fear, would set our nation on a very dark path.”
“I think it’s vital to put our country’s well being ahead of party,” he said in a statement provided by the Clinton campaign. “Hillary Clinton is experienced, qualified, and will make a fine president. The alternative, I fear, would set our nation on a very dark path.” Cicconi would be pleased to see someone like former Tennessee congressman Harold Ford, Jr., take a seat at the FCC under a future Clinton Administration instead. Ford has served as an honorary co-chairman of Broadband for America, an industry-sponsored astroturf operation, for most of Obama’s two terms in office. He remains a close friend of both Bill and Hillary and is never far from the public eye, turning up regularly on MSNBC.
Cicconi would be pleased to see someone like former Tennessee congressman Harold Ford, Jr., take a seat at the FCC under a future Clinton Administration instead. Ford has served as an honorary co-chairman of Broadband for America, an industry-sponsored astroturf operation, for most of Obama’s two terms in office. He remains a close friend of both Bill and Hillary and is never far from the public eye, turning up regularly on MSNBC. As part of its investigation of cable and satellite television companies, the U.S. Senate Permanent Subcommittee on Investigations found large discrepancies in how five of America’s largest cable and satellite companies—Charter Communications, Comcast, Time Warner Cable, DirecTV, and Dish—identify and correct overcharges caused by company billing errors.
As part of its investigation of cable and satellite television companies, the U.S. Senate Permanent Subcommittee on Investigations found large discrepancies in how five of America’s largest cable and satellite companies—Charter Communications, Comcast, Time Warner Cable, DirecTV, and Dish—identify and correct overcharges caused by company billing errors. Time Warner Cable is notorious for its “no refunds unless asked” policy, which often leaves customers uncompensated for service outages and other problems. That policy also extends to equipment-related billing errors. During the 6.5 year time period covered by the subcommittee investigation, Time Warner Cable never automatically refunded or credited customer for equipment overcharges discovered by the company. Instead, Time Warner’s “Revenue Assurance” team quietly identified and corrected billing errors without any notification or explanation to customers, which may explain why your Time Warner Cable bill can change even when you are locked in with a promotion.
Time Warner Cable is notorious for its “no refunds unless asked” policy, which often leaves customers uncompensated for service outages and other problems. That policy also extends to equipment-related billing errors. During the 6.5 year time period covered by the subcommittee investigation, Time Warner Cable never automatically refunded or credited customer for equipment overcharges discovered by the company. Instead, Time Warner’s “Revenue Assurance” team quietly identified and corrected billing errors without any notification or explanation to customers, which may explain why your Time Warner Cable bill can change even when you are locked in with a promotion.

 The subcommittee called Charter’s process of identifying and correct overbilling “substandard.”
The subcommittee called Charter’s process of identifying and correct overbilling “substandard.”
 Dish was cited by the subcommittee report as having the billing system least likely to generate billing errors. Dish links its equipment and billing systems together, which means any change on one system automatically updates the other.
Dish was cited by the subcommittee report as having the billing system least likely to generate billing errors. Dish links its equipment and billing systems together, which means any change on one system automatically updates the other.