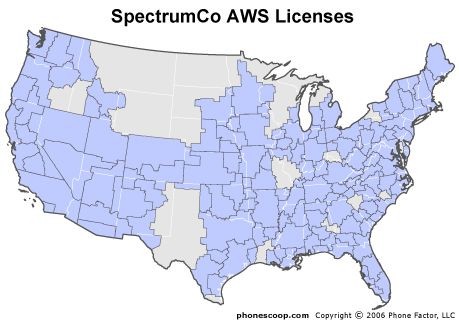
Comcast, Time Warner Cable, and Bright House Networks sold AWS spectrum in areas shown here to Verizon Wireless, virtually guaranteeing the cable industry will not compete in the wireless phone business.
Two years ago, Cox Communications was hungry to get into the wireless phone business. It announced it was launching “unbelievably fair” wireless — an oasis in a wireless desert of tricks and traps on offer from competing wireless companies. No more expiring minutes, the option of affordable flat rate service, and no hidden fees or surcharges were all supposed to be part of the deal.
“Our research found that value and transparency are very important to consumers when choosing a wireless service plan, but they are not finding these qualities in the wireless plans offered today,” Stephen Bye, vice president of wireless said back in 2010, introducing the service. “Total loss of unused minutes as well as unforeseen overage charges on bills are just two examples of what our customers have told us is just unfair.”
Those same issues still exist for wireless customers today, but Cox won’t be a part of the solution. The company announced this past May it was exiting the competitive arena of wireless and would simply resell Sprint service instead. Last month, it announced it wouldn’t even bother with that, and will transition its remaining wireless customers directly to Sprint.
What changed Cox’s mind? The cost of building and operating a wireless network to compete with much larger national companies. It simply no longer made sense to build a small regional wireless carrier and rent the rest of your national coverage area from other providers, who set wholesale prices at a level high enough to protect them from would-be competitors.
The lesson Cox learned first has now been taught to America’s largest cable operators Comcast and Time Warner Cable (and its sidekick Bright House Networks).
All three cable operators have effectively signed a non-aggression treaty with Verizon Wireless, agreeing to sell their unused wireless spectrum acquired by auction in 2006 at a 50% markup to Big Red. In return, Verizon will market cable service to wireless customers. It’s the ultimate non-compete clause so wide-reaching, Verizon stores will soon be selling Time Warner Cable right next to Verizon FiOS, something unheard of in the telecommunications marketplace.
It’s a win for Verizon Wireless, which accumulates additional wireless spectrum and peace of mind knowing the cable industry will not enter the wireless communications business. Cable companies get to profit from their purchase of the public airwaves and see the potential of a dramatic reduction in customer poaching, as cable and phone companies stop fighting each other for customers. Ultimately, it means customers could eventually pay the cable or phone company for all of their telecommunications services from television and broadband to wired and wireless phone service. What consumers enjoy in one-bill-convenience may eventually come with higher rates made possible from reduced competition.
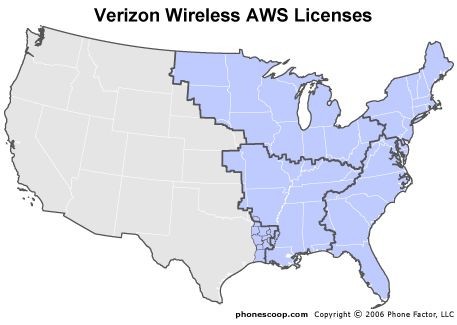
Verizon Wireless' currently unused AWS spectrum favor the east coast, but not for long.
Verizon will pay $3.6 billion to Comcast, Time Warner and Bright House Networks for the spectrum. The deal has stockholders cheering because that payment represents a tidy profit for cable operators who did absolutely nothing with the spectrum they purchased five years ago. It also makes AT&T even more intent on completing its own spectrum merger with T-Mobile USA.
The agreement has concerned consumer advocates because it seems to signal Verizon is content making money primarily from its wireless business, and will repay the favor from the cable industry by pitching phone customers on cable service. That could ultimately spell big trouble for Verizon’s stalled FiOS fiber-to-the-home network. Verizon may find it easier and cheaper to end its aggressive entry into Big Cable’s territory by simply reselling traditional cable television products. It can still market wireless products and services to cable subscribers and not endanger the new atmosphere of goodwill. Rural broadband, where cable never competes, could be served through wireless spectrum, for example.
For now, Verizon says it intends to continue competing with its FiOS network, but the company stopped deploying the service in new areas nearly two years ago.
The deal will go before regulators at the Justice Department and the Federal Communications Commission for review. What will likely concern them the most is the appearance of collusion between the cable companies and Verizon.
“A flag is raised when two rival networks move to start selling each other’s services,” a person familiar with the concerns of federal antitrust officials told the Washington Post. “They lose their desire, impetus, to compete. That is a big antitrust flag.”
Mark Cooper, the director of research for the Consumer Federation of America, expressed serious concern as well.
“Verizon was supposed to be the great competitor for Comcast in the video space, while Comcast has been looking for a wireless play to match the Verizon bundle,” he said. “The deal signals bad news for consumers, who can expect higher prices for video, fewer choices and higher prices for wireless.”

Who owns what
Four years into the deal, consumers may not know what company they are dealing with, as cable operators will be able to market Verizon Wireless service under their own respective cable brand names.
The deal is also trouble for lagging Clearwire, which had been providing wireless broadband service to both Comcast and Time Warner Cable. Under the agreement, both cable companies will end their relationship with Clearwire, which is particularly bad news for the wireless company because of its ongoing financial distress. Sprint, which has heavily invested in Clearwire, may ultimately find itself with an investment gone sour, troubling news for the third largest wireless company manning the barricades against a nearly-complete duopoly in wireless service between AT&T and Verizon Wireless.
Cable stock cheerleader Craig Moffett from Sanford Bernstein seems thrilled with the prospect. In a research note to his Wall Street clients, Moffett says AT&T could benefit from the Verizon pact with Big Cable by ending up in a “more duopolistic industry structure without paying for it.” If the FCC approves the non-aggression pact, the deal “would amount to an unmistakable step towards the duopolization of the U.S. wireless market, inasmuch it would leave T-Mobile, once again, stranded without a 4G strategy.”
Cable investors, he adds, are likely to be excited the cable industry won’t spend billions of dollars in capital building a wireless venture, and instead has agreed to work with competitors to cross-sell products and services. With little competitive pressure, prices won’t be falling anytime soon.
That’s great news for investors, even if it is “unbelievably unfair” for consumers.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Bloomberg Verizon to Buy Wireless Spectrum for 3-6 Billion 12-2-11.flv[/flv]
Bloomberg News explains the deal and its implications in the wireless industry spectrum battle. (2 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe