One of the most consequential and visible spectrum auctions ever is over, and it will have a significant impact on broadcasters, wireless carriers, and the future competitive landscape of the wireless industry.
The world’s first “incentive auction” paid television stations to voluntarily vacate or move their assigned channels to make room for the wireless industry’s desire for more spectrum to power wireless data services. Up for bid was 70MHz of spectrum currently used by UHF television stations. A total of 50 winning wireless bidders collectively agreed to pay $19.8 billion to acquire that space. The biggest winner was T-Mobile USA, which is paying almost half the amount of total proceeds to acquire 45% of the spectrum available in the current auction. T-Mobile managed to acquire enough spectrum to cover 100% of the United States and Puerto Rico with an average of 31MHz of available spectrum nationwide, quadrupling its current inventory of important “low-band” spectrum, which is excellent for covering rural areas and inside buildings.
Consumers are likely to benefit as early as later this year when T-Mobile begins lighting up cellular service utilizing the newly available spectrum. Unfortunately, customers will have to buy new devices compatible with the new bands of frequencies.
Having the spectrum alone is not enough to beef up T-Mobile’s network. The company will have to invest in a large number of new cell sites, particularly in outlying areas, to eventually rival the coverage of AT&T and Verizon Wireless. But with an ample supply of 600MHz spectrum, T-Mobile could soon challenge AT&T and Verizon Wireless’ perceived network and coverage superiority. After this auction, AT&T continues to hold the largest portfolio of <1GHz spectrum — 70.5MHz. Verizon is second with 46.2MHz and T-Mobile has moved up in its third place position with 41.1MHz.
 Although the FCC claims the current auction was among the highest grossing ever conducted by the FCC, industry observers claim companies got the new frequencies at a bargain price. A 2015 spectrum auction attracted $44.9 billion in bids, more than double the amount bid this year. The average price wireless companies paid per megahertz per person this year was just shy of 90¢, compared with $2.72 in 2015.
Although the FCC claims the current auction was among the highest grossing ever conducted by the FCC, industry observers claim companies got the new frequencies at a bargain price. A 2015 spectrum auction attracted $44.9 billion in bids, more than double the amount bid this year. The average price wireless companies paid per megahertz per person this year was just shy of 90¢, compared with $2.72 in 2015.
Where bargains are to be had, Charles Ergen and his Dish Network satellite company are sure to follow.
Few companies have as much unused wireless spectrum in their portfolio as Dish. Ergen loves to bid in auctions and has also picked up excess spectrum available on the cheap from other satellite companies that have since gone dark or bankrupt. Dish spent $6.2 billion on spectrum during the latest auction, puzzling investors who drove Dish’s share price down wondering what the company intends to do with the frequencies.
Investors were hoping Dish would eventually sell its spectrum portfolio at a profit, something that could still happen if other wireless carriers see a deal to be made. But some Wall Street analysts fear Dish might actually build a large wireless network of its own to offer wireless broadband service. Wall Street dislikes big spending projects and the competition it could bring to the marketplace, potentially driving down prices.
The other possibility is that Dish is making itself look more attractive to a possible buyer like Verizon, which could acquire the satellite company to win cheaper cable programming prices for its FiOS TV and an attractive amount of wireless spectrum for Verizon Wireless. The nation’s biggest wireless carrier notably did not participate in this spectrum auction.
Another unusual bidder was Comcast. Craig Moffett from Wall Street firm MoffettNathanson called Comcast’s $1.7 billion bid “half-hearted” and said it was unlikely to be enough spectrum for the company to begin offering its own wireless service. Comcast plans to rely on Verizon Wireless to power its wireless service, at least initially.
Comcast targeted its bids only in cities where it already provides cable service, which also nixes the theory Comcast and Charter might have been working together to form a cellular joint venture. Moffett expected Comcast would seek at least 20MHz of spectrum across most of the country. It ended up with 10MHz and only in select cities. Moffett thinks that may signal Comcast’s interest in buying an existing wireless carrier is still on the table.


 Subscribe
Subscribe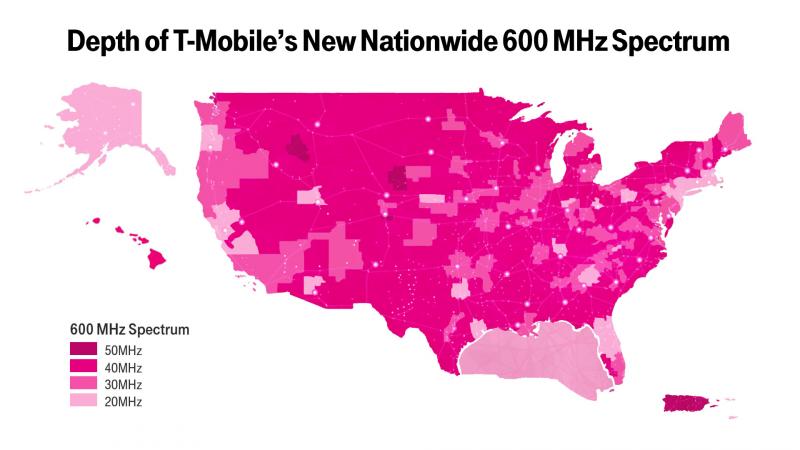


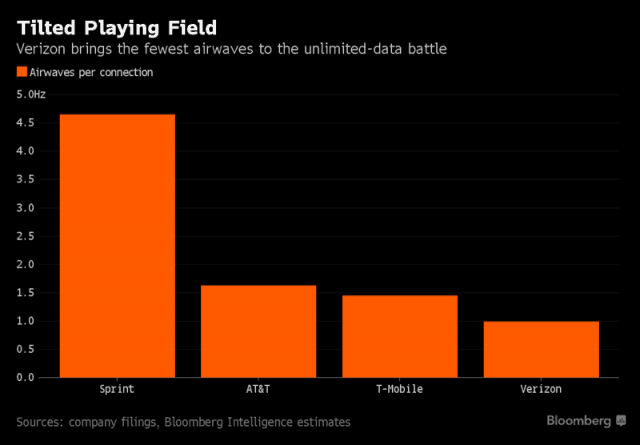 Verizon Wireless’ new unlimited data plan threatens to destroy everything, fear Wall Street analysts in an open panic attack over the prospects of value destruction and network reliability damage.
Verizon Wireless’ new unlimited data plan threatens to destroy everything, fear Wall Street analysts in an open panic attack over the prospects of value destruction and network reliability damage. What also concerns Wall Street is the increasing evidence an all-out price war provoked by T-Mobile and Sprint will threaten to close some doors on network monetization. Charging customers for data consumption has a growth prospect that would have guaranteed increasing average revenue per customer indefinitely. But unlimited plans mean consumers pay one flat price for data no matter how much they consume. Consumers love it. Wall Street analysts generally don’t.
What also concerns Wall Street is the increasing evidence an all-out price war provoked by T-Mobile and Sprint will threaten to close some doors on network monetization. Charging customers for data consumption has a growth prospect that would have guaranteed increasing average revenue per customer indefinitely. But unlimited plans mean consumers pay one flat price for data no matter how much they consume. Consumers love it. Wall Street analysts generally don’t.
 Ten years earlier, Sprint was worth $69 billion and was prepared to dominate the U.S. wireless industry, but drove customers off with very poor customer service and inadequate investment in its network, allowing competitors like AT&T and Verizon Wireless to leap ahead. Sprint also embarked on an executive-inspired fantasy: a disastrous merger with Nextel that preoccupied the company for years. Softbank taking the lead has done little to change customer perceptions, nor those of some Wall Street analysts who fear Sprint is a bottomless money pit that always promises better times and profits are coming, but never seems to get there.
Ten years earlier, Sprint was worth $69 billion and was prepared to dominate the U.S. wireless industry, but drove customers off with very poor customer service and inadequate investment in its network, allowing competitors like AT&T and Verizon Wireless to leap ahead. Sprint also embarked on an executive-inspired fantasy: a disastrous merger with Nextel that preoccupied the company for years. Softbank taking the lead has done little to change customer perceptions, nor those of some Wall Street analysts who fear Sprint is a bottomless money pit that always promises better times and profits are coming, but never seems to get there.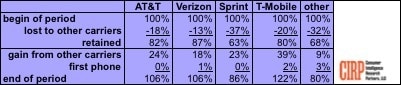
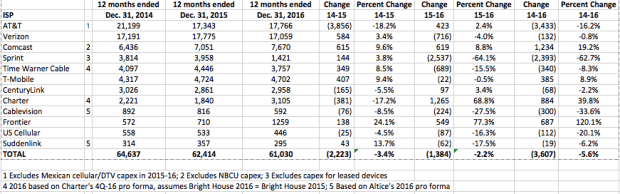
 Son’s argument to the new administration depends on President Trump and FCC Chairman Ajit Pai being more friendly to the idea of less competition than the Obama Administration. Son may have an uphill battle, considering the former Obama Administration’s opposition to earlier mergers, including T-Mobile and AT&T and T-Mobile and Sprint seems to have paid off for consumers in the form of today’s fiercer competition and a price war.
Son’s argument to the new administration depends on President Trump and FCC Chairman Ajit Pai being more friendly to the idea of less competition than the Obama Administration. Son may have an uphill battle, considering the former Obama Administration’s opposition to earlier mergers, including T-Mobile and AT&T and T-Mobile and Sprint seems to have paid off for consumers in the form of today’s fiercer competition and a price war.