Frontier’s office in Charleston, W.V.
Conditions within many Frontier Communications service areas are in a state of dangerous disrepair, with a growing number of disruptions to 911 services and a long wait for urgent repairs of Frontier’s deteriorating landline network that can now take over a month.
A growing number of states are documenting unprecedented service problems at Frontier Communications, the independent phone company providing phone and internet services to homes and businesses in 29 states. News reports predict that the company will be in bankruptcy court as early as March, hoping to discharge or refinance its staggering debts. But until then, some Frontier customers have been unable to reach 911 or rely on their rural landline service for remote medical monitoring, potentially putting their lives at risk.
One of the latest states to report serious deficiencies with Frontier’s service is Wisconsin. At a Dec. 20 public meeting in Mondovi to discuss the quality of service at Frontier, the city administrator heard harrowing tales of rural Wisconsin residents who frantically tried to call 911 and got nothing but a strange busy signal.
The Wisconsin State Journal reported that after Mike Wright’s shed collapsed on him under the weight of multiple feet of snow, his wife’s attempts to reach 911 from their Mondovi home failed again and again. A Frontier technician later admitted 911 was out of service for about eight hours that day. Frontier apparently did not notify customers or the media about the outage.
James Rud, a volunteer firefighter and the town’s street superintendent, told the meeting that was not an unusual situation. A few years earlier, a local dentist’s office repeatedly tried to reach 911 after a disabled girl choked on a piece of dental equipment. There was no answer.
“Everybody’s frantic because they’ve called five times and got a busy signal on 911,” Rud told the meeting, noting that when people call 911 and “nobody picks up, your anxiety level goes from a bad situation to a (really) bad situation.”
That day, 911 operators were waiting to take emergency calls. The calls failed to connect because of network problems at Frontier. Based on a review of state regulator complaints, the problems are growing in size and scope across multiple states served by Frontier. In Wisconsin alone, at least 93 serious complaints were filed with the state’s telecom regulator. The Department of Agriculture, Trade, and Consumer Protection received 405 pages of complaints between January 2019 through January 2020, mostly about poor quality phone and internet service in rural Wisconsin and very long wait times for often ineffective repairs. One complaint from Barneveld even included a physician’s letter emphasizing the urgent need for reliable landline service for a patient in poor medical condition.
There are indications Frontier satisfactorily handled some complaints… eventually, but many customers had to take extraordinary action to get the phone company’s attention about problems the company allegedly ignored for months.

One complainant turned out to be Marathon County IT director Gerald Klein, responsible for maintaining the county’s 911 system. He couldn’t get Frontier to respond to him either, eventually reaching out to Wisconsin state officials as a last resort. Klein complained Frontier was unresponsive “for months” to his county’s request to upgrade a crucial trunk line necessary to activate a new and improved 911 system. He had no idea who to appeal to next.
“Our 911 system is maintained by Frontier but the equipment is long since past end‐of‐life,” Klein wrote in a letter to the Wisconsin Public Service Commission on Dec. 27. “Can I file a complaint with the Wisconsin PSC or can you give me other advice on how to get Frontier’s attention? Is this something that should be given to the FCC?”

Lane
In West Virginia, perhaps the epicenter of Frontier’s epic problems, Public Service Commission chairperson Charlotte Lane, a former Kanawha County delegate, considers Frontier’s performance in her state to be unacceptable.
“Frontier has over 300,000 customers in our state,” Lane said, noting that for many West Virginians Frontier is their sole provider. “In 2019, we received nearly 2,000 complaints from Frontier customers about the company’s phone and internet service. We spend a lot of time responding to these complaints.”
Other media reports count the number of complaints regarding Frontier exceeding 4,000 “over the last couple of years.”
Lane is especially worried about the growing number of 911 outage incidents reported across West Virginia. There were at least a half-dozen high profile outages in 2019 that attracted media attention and scrutiny from local, county, and state legislators.
In July 2019, the PSC commissioned Schumaker and Company to perform an extensive management audit of Frontier Communications. Lane said the audit was critical because Frontier’s performance has been questionable since the company acquired Verizon Communications-owned landlines in the state back in 2010. Lane said Frontier has been cutting staff and maintenance workers in the state, but wanted a definitive report on the company so the PSC can intelligently oversee Frontier’s performance. That report is due to be released on March 19.
West Virginia “has a lot of power and we will exercise it,” Lane said.
The same may not be true in Wisconsin, where a well-funded deregulation campaign by AT&T and other phone companies in Wisconsin won bipartisan favor in 2011, with the full endorsement of then Gov. Scott Walker. One Republican state senator even promised that the new law would result in more than 50,000 new jobs and inspire telecom companies to invest in the state. In fact, AT&T, Frontier, and other phone companies have cut jobs over the last nine years and Frontier has invested little in upgrading its Wisconsin network to more reliable fiber optic technology. Telecom companies also claim deregulation frees them from having to deliver traditional copper-based landline service where most people are now using cell phones, and consumers can always exercise their choice by switching from a disappointing phone company to the local cable operator.
But rural residents in Wisconsin complain they often do not have the option of switching to cell phone or cable service, because there is no reliable cell coverage or local cable operator in many of the areas Frontier services. That has left them vulnerable to the consequences of ending universal landline service and a telecom industry that is investing in upgrades almost exclusively in urban areas.
Even Frontier officials now admit serving rural areas is becoming an unsustainable proposition for the phone company.

A statement from Frontier’s Javier Mendoza.
“Frontier serves only about ten percent of the state voice lines in its service area—and falling—but has 100 percent of the universal service obligation to serve the most rural and high-cost areas,” Frontier spokesperson Javier Mendoza said in a statement about its business in West Virginia in July 2019. “Our customer base continues to decline, while the cost of service per line has increased dramatically. This has resulted in an unsustainable model for providing service in rural and high-cost areas, manifesting in increased numbers of service complaints. We plan to reach out to the state’s leaders to collaboratively find solutions to this difficult challenge.”

West Virginia’s Public Service Commission is undertaking a comprehensive audit of Frontier Communications.
Deregulation in states like Wisconsin has allowed Frontier to escape some of the harsher consequences from regulators held responsible for ensuring customers have reliable access to basic phone service. That leaves many rural customers vulnerable to whatever goodwill exists at private telecommunications companies to continue offering service.
Observers suggest Chapter 11 bankruptcy will allow Frontier to shed its punishing level of debt many believe is responsible for Frontier’s ongoing lack of investment in network upgrades. But others believe Frontier is more likely to seek a sale of its rural service areas to focus on its more profitable urban service areas, especially in California, Texas, and Florida. Frontier has already announced a sale of its landline network in the Pacific Northwest to a regional telecommunications company promising to scrap much of Frontier’s copper wire infrastructure in favor of fiber optics.
In the meantime, problems at Frontier’s operations are ongoing. Last week, a “massive phone outage” in Cabell County, W.V. took down phone service across large parts of the county.
Earlier this month, Frontier officials were called to a meeting to address complaints about poor service in Tennessee. In attendance were Cumberland County Mayor Allen Foster, Crossville City Mayor James Mayberry, Senator Paul Bailey and U.S. Representative John Rose. The complaints were called “severe” by the public officials and dangerous to public safety.
“Frontier officials appeared to have no definitive answer to the complaints,” reported 3B Media.
Plumas County, Calif. officials are alarmed about reports of Frontier’s possible bankruptcy. District 2 Supervisor Kevin Goss said he is a Frontier customer that has experienced firsthand the issues he says all Indian Valley residents experience: paying for high speeds and experiencing low speeds in return. Goss said Frontier’s broadband service often works only intermittently for a few hours at a time. Incoming residents often cannot subscribe to broadband service at all, after Frontier allegedly placed a moratorium on adding new DSL customers in the area in 2018. Koss claims he has seen no evidence Frontier plans to invest in service expansion and the DSL moratorium remains in place two years later.
In Minnesota, the state’s Public Utility Commission recently reached a settlement with Frontier over its poor quality landline and broadband service, particularly in rural areas. But now the Minnesota Department of Commerce is launching a new investigation focusing on Frontier’s billing and customer service practices.
“We are concerned about Frontier’s practices when customers are signing up for service and the prospect that Minnesotans are being overcharged for their phone service,” said Commerce Commissioner Steve Kelley.

A broken Frontier telephone pole. (Left) Frontier phone cables left stretched against a tree (Right) Images: PUCO
The Minnesota Department of Commerce has just launched another investigation into Frontier Communications, focusing on the company’s billing and customer service practices. The primary issues under investigation include whether Frontier failed to inform customers of their service options and whether Frontier enrolled customers in long distance service plans that customers did not want or use.
“We are concerned about Frontier’s practices when customers are signing up for service and the prospect that Minnesotans are being overcharged for their phone service,” said Commerce Commissioner Steve Kelley.
In Ohio, state regulators are tangling with Frontier over network and infrastructure upkeep practices. The Ohio Department of Transportation (ODOT) is taking issue with Frontier’s attempts to ‘pass the buck’ on pole and infrastructure maintenance. Patricia Binkiewicz says her family is collateral damage in that battle, after her husband’s car was struck by a falling branch hanging over Route 43 in Carroll County — a branch Frontier should have dealt with over a year ago.
“If you drive, especially around here, you’re going to see these trees hanging over lines and they don’t realize no one is claiming responsibility, accountability, any liability or damages if a tree should fall down,” Binkiewicz said. Attempts to have Frontier Communications deal with overgrown trees and brush fell on deaf ears. The company claimed that was the responsibility of ODOT. No so fast, ODOT responds.

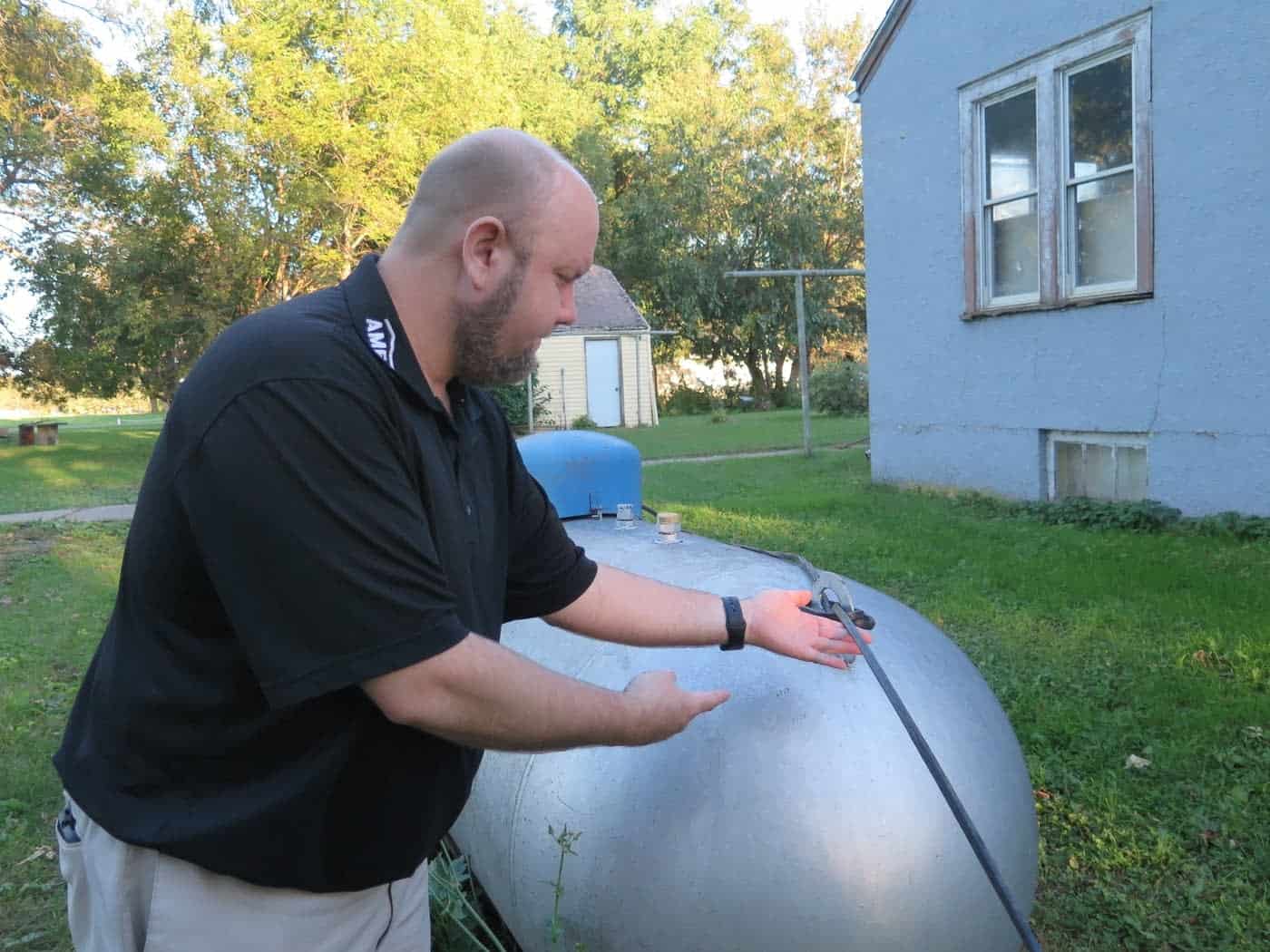
A Frontier installer draped a new line across this customer’s residential propane tank, and then left. (Image courtesy: Mark Steil, MPR News)
“Utilities that run in the state’s right of way are to be maintained by the utility company,” ODOT spokesperson Lauren Borell said. “So, what that means is if there’re trees there, the utility company is responsible for those trees.”
When the story made the local news, ODOT removed the offending tree, but there is no word how many other trees represent accidents waiting to happen. Local officials claim Frontier has shown a lack of interest in investment.
That lack of investment is also apparent in the state of Utah, where the Utah Public Service Commission is continuing its investigation into Frontier Communications as a result of complaints from Castle Valley and the nearby area that the company failed to provide reliable service to customers. Julie Price, a spokesperson for Utah’s Division of Public Utilities, said her agency is concerned about the “company’s level of investment in Utah.”
The consequences of deregulation of phone service in rural areas dependent on landlines may eventually include unnecessary deaths from an inability to reach emergency services due to a service outage or network problem. Observers note that cell phone service remains spotty, especially indoors, in large sections of rural America. Some wireless carriers like T-Mobile and Sprint barely provide any direct coverage in states like West Virginia, and AT&T and Verizon offer solid service primarily in larger cities.
It remains unlikely rural cell service will ever be ubiquitous in many rural areas, because there will not be enough customers to make such investments profitable. Instead, for over a century consumers have traditionally relied on universally available landline telephone service. But as deregulation efforts weaken or eliminate universal service requirements, local phone companies may eventually cease offering landline service. AT&T is already experimenting with eliminating legacy phone lines in favor of wireless service, with mixed results. An effort by Verizon to replace deteriorating rural landlines with a wireless landline replacement proved unpopular and unreliable.
What compelled local phone companies to provide universal, high quality landline service for decades was strong regulatory enforcement with stiff fines for non-compliance. Repairs were expected to be made in most cases within a day or two, not four to nine weeks. Public safety from overgrown trees and brush near telephone company-owned utility poles is also a growing and relatively recent problem. In some cases, deregulation has left regulators unable to police the condition of utility poles that present a safety risk, and that task has now fallen on local media that can embarrass a company into fixing problems.
Public policy advocates recommend Frontier be held accountable for the quality of their service and states should strongly consider rolling back deregulation, especially in rural areas.


 Subscribe
Subscribe






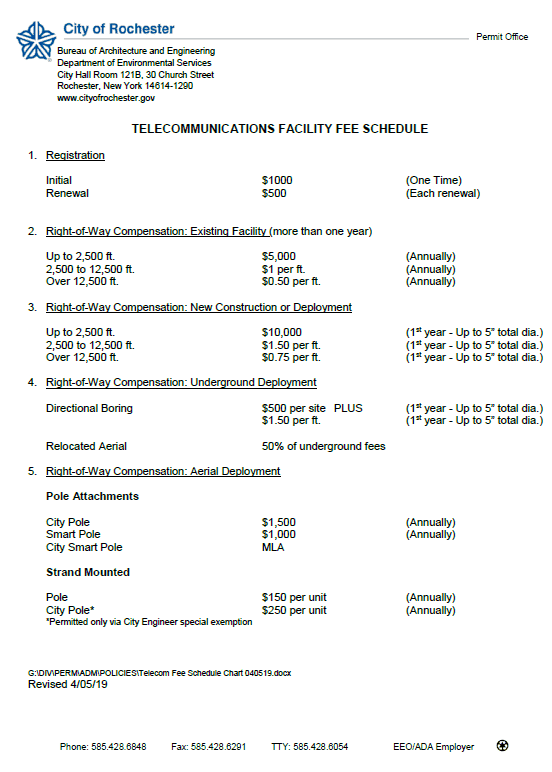
 Verizon Wireless has sued the City of Rochester, N.Y. in a potentially precedent-setting case, for demanding excessive and discriminatory fees to use public rights-of-way to deploy a fiber backhaul network and hundreds of small cells to support the introduction of 5G wireless service in the community.
Verizon Wireless has sued the City of Rochester, N.Y. in a potentially precedent-setting case, for demanding excessive and discriminatory fees to use public rights-of-way to deploy a fiber backhaul network and hundreds of small cells to support the introduction of 5G wireless service in the community. The City also wants compensation to cover “administrative costs for retaining and managing documents and records,” “costs for managing, coordinating and responding to public concerns and complaints,” and “the costs of the City’s self-insurance.” Verizon Wireless’ attorneys argue that the FCC’s “presumptive limit” of $270 annually is all-inclusive, and therefore the fees requested are inherently unreasonable.
The City also wants compensation to cover “administrative costs for retaining and managing documents and records,” “costs for managing, coordinating and responding to public concerns and complaints,” and “the costs of the City’s self-insurance.” Verizon Wireless’ attorneys argue that the FCC’s “presumptive limit” of $270 annually is all-inclusive, and therefore the fees requested are inherently unreasonable.



 The cut cable was located at Griffin’s home where AT&T’s network interface box connected the overhead line with the home’s inside wiring. AT&T crews sought to replace the overhead drop line from the utility pole to Griffin’s home, which initially caused Quinones to object because the utility pole serving her home is behind his. After the dispute attracted coverage from Cleveland’s ABC affiliate, Quinones relented.
The cut cable was located at Griffin’s home where AT&T’s network interface box connected the overhead line with the home’s inside wiring. AT&T crews sought to replace the overhead drop line from the utility pole to Griffin’s home, which initially caused Quinones to object because the utility pole serving her home is behind his. After the dispute attracted coverage from Cleveland’s ABC affiliate, Quinones relented.