 DirecTV Now customers will soon be introduced to AT&T TV Now as the streaming service rebrands with new apps and prepares for the launch of WarnerMedia’s HBO Max streaming service early next year.
DirecTV Now customers will soon be introduced to AT&T TV Now as the streaming service rebrands with new apps and prepares for the launch of WarnerMedia’s HBO Max streaming service early next year.
The streaming service, originally branded as part of the DirecTV platform, has suffered major subscriber losses (168,000 in the last three months alone) after reducing the size of its TV packages and raising prices twice in the last year. To date, more than 26% of DirecTV Now’s subscriber base has defected to other streaming services, with no end to those losses in sight. AT&T’s DirecTV satellite and U-verse TV have also turned in stunning reductions in the number of subscribers, losing at least two million customers in the last year, with 778,000 departing during the second quarter of 2019.
AT&T has stopped offering deep promotional discounts to most customers threatening to cancel over rate hikes, and subscribers are making good on their threats to leave. The company is also embroiled in two major retransmission consent disputes that have left customers in several cities facing a blackout of as many as three network affiliated local TV stations. With higher prices for fewer channels, and plenty of alternatives, customers are turning to other providers.
AT&T’s 2015 purchase of DirecTV, in retrospect, appears to have been a major business mistake, according to some Wall Street analysts. Originally intended to help AT&T manage the spiraling costs of video for its U-verse TV service by winning more generous volume discounts from programmers, the DirecTV acquisition came just before the phenomenon of cord-cutting took off, leaving all of AT&T’s video services vulnerable to customer losses. DirecTV Now initially benefited from cord-cutters attracted to its generous package of channels at a low price, but an executive decision to reduce the channel lineup while raising prices drove off what executives characterized as ‘undesirable customers only looking for deals.’

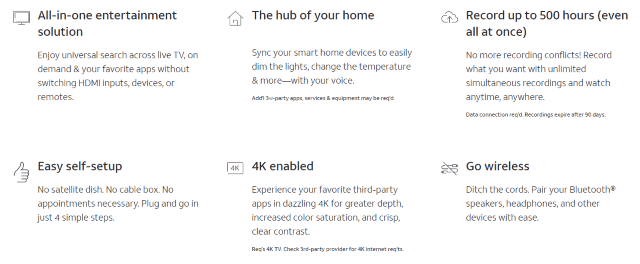
AT&T has also been experimenting with a separate streaming service that will likely eventually replace the satellite-based DirecTV. Beta testers have been providing feedback to AT&T about a new set top streaming box intended to work with this service, now to be called AT&T TV. AT&T is also reducing the number of apps required to access its myriad of video services. AT&T TV and AT&T TV Now customers will download the same app, only the channel lineups will be different. The company is targeting AT&T TV Now on cord-cutters looking for a cheaper and smaller video package, while AT&T TV will include a range of packages likely identical or very similar to DirecTV’s current satellite lineup.
If AT&T TV is successful, AT&T can cut costs incurred installing and maintaining satellite dishes and also eventually decommission DirecTV’s satellite fleet. Rural satellite TV customers without access to broadband may be in a difficult position if that happens, and the country has still not resolved the rural broadband challenge.
Even with these changes, AT&T customers are faced with a large menu of potentially confusing video options. AT&T sells traditional live cable TV services through AT&T TV, AT&T TV Now, DirecTV, and U-verse. It also offers a stripped down WatchTV package offering 35 channels for $15 a month or less. Premium customers still trying to tell the difference between HBO Go and HBO Now will soon also contend with HBO Max. Cinemax has its own similar offerings for cable TV customers and direct to consumer subscribers.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Comcast has put its proverbial finger to the wind to define an “appropriate” data cap it declares “generous,” regardless of how subjectively random that cap happens to be. Although 1,000 GB — a terabyte — usage allowance represents a lot of internet traffic, more and more customers are finding they are flirting with exceeding that cap, and Comcast has never been proactive about regularly adjusting it to reflect the reality of rapidly growing internet traffic. That means customers must protect themselves by checking their usage and take steps if they are nearing the 1 TB limit.
Comcast has put its proverbial finger to the wind to define an “appropriate” data cap it declares “generous,” regardless of how subjectively random that cap happens to be. Although 1,000 GB — a terabyte — usage allowance represents a lot of internet traffic, more and more customers are finding they are flirting with exceeding that cap, and Comcast has never been proactive about regularly adjusting it to reflect the reality of rapidly growing internet traffic. That means customers must protect themselves by checking their usage and take steps if they are nearing the 1 TB limit.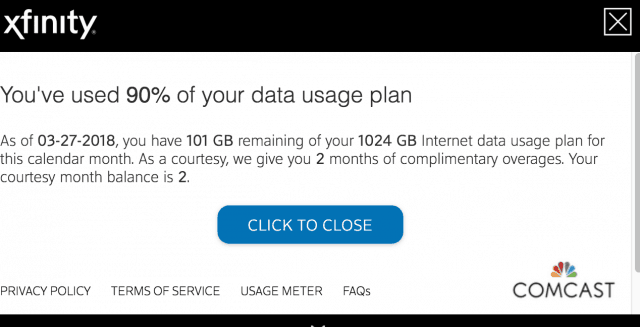 Video Games Consoles/PCs
Video Games Consoles/PCs AT&T/WarnerMedia’s new streaming service due to debut in Spring 2020 will be called HBO Max and bundle original and classic content from AT&T-owned networks and studios, including Warner Bros., New Line, DC Entertainment, CNN, TNT, TBS, truTV, CW, Turner Classic Movies, Cartoon Network, Adult Swim, Crunchyroll, Rooster Teeth, and Looney Tunes.
AT&T/WarnerMedia’s new streaming service due to debut in Spring 2020 will be called HBO Max and bundle original and classic content from AT&T-owned networks and studios, including Warner Bros., New Line, DC Entertainment, CNN, TNT, TBS, truTV, CW, Turner Classic Movies, Cartoon Network, Adult Swim, Crunchyroll, Rooster Teeth, and Looney Tunes. As some Netflix shareholders grumble about
As some Netflix shareholders grumble about 
 WarnerMedia’s forthcoming streaming service will showcase HBO and Cinemax at the heart of a one-size-fits-all streaming package priced at $16-17 a month, featuring premium movies and Warner Bros. vast movie and TV show collection. We wanted to enjoy those streams.
WarnerMedia’s forthcoming streaming service will showcase HBO and Cinemax at the heart of a one-size-fits-all streaming package priced at $16-17 a month, featuring premium movies and Warner Bros. vast movie and TV show collection. We wanted to enjoy those streams. 
