
How low can AT&T go? Customers retaining “unlimited data plans” that were discontinued in 2010 were throttled to as little as 127 kbps after using just 2 GB a month.
AT&T’s lawyers are asking a judge to accept media coverage exposing the company’s allegedly “secret” speed throttling policy for some of its wireless customers as a valid defense in a 2015 class action case that seeks to compensate some AT&T customers for misrepresenting its “unlimited data plan.”
AT&T last month asked the judge to have the long-running case thrown out, claiming AT&T well publicized its new speed throttling policy it imposed on a legacy unlimited data plan the wireless company stopped selling in 2010, but allowed existing customers to keep. By 2011, some customers still subscribed to the grandfathered unlimited plan started noticing data speeds plummeting to near dial-up if they used a lot of data. At first, AT&T appeared to impose a speed throttle on customers using over 10 GB of data per month, but by 2012, AT&T was accused of speed throttling unlimited customers after they used as little as 2 GB of data during a billing period.
The resulting class action lawsuit, filed in California, alleged that AT&T misrepresented its unlimited data plan as ‘unlimited,’ when in fact in practical terms it was not. The plaintiffs are seeking damages from AT&T to discourage the company from engaging in false advertising in the future, and to compensate customers that paid for an unlimited data plan that eventually became almost useless after customers used just over 2 GB a month.
AT&T’s defense partly relies on the company’s claim it extensively publicized changes to its legacy unlimited data plan as early as 2011, and the plaintiffs should have been aware of it. The Federal Communications Commission was aware of AT&T’s actions and just a month before the class action case was filed, the regulatory agency issued a notice of apparent liability to AT&T proposing a $100 million fine for unwarranted speed throttling.
AT&T’s attorneys have worked hard to stop the lawsuit over the last five years. In addition to claiming customers were notified of their excessive data usage through text messages and billing notices, AT&T last month sought to introduce a dozen media reports covering its speed throttling policy into the court record to convince U.S. District Judge Edward Milton Chen the plaintiffs don’t have a case and to get the lawsuit dismissed.
One of the news articles cited in AT&T’s May 14 filing was written by former DSL Reports’ author Karl Bode, who has been roundly critical of AT&T’s data caps for over a decade. Ironically, AT&T’s defense team is arguing Bode’s report, “AT&T Wages Quiet War on Grandfathered Unlimited Users” offers proof AT&T was not keeping its speed throttling policy “secret,” as at least one plaintiff claimed. Bode suggested AT&T had engineered its speed throttling plan to push grandfathered unlimited data plan customers off the plan in favor of more profitable plans offering a specified data allowance and overlimit fees.

Bode
“In other words, pay $30 for “unlimited” service where you’re actually only getting 2 GB of data before your phone becomes useless, or sign up for a 3 GB tier for the same price so you’re in line to get socked with the usage overages of tomorrow,” Bode wrote at the time.
His views have not changed in 2020.
“For nearly a decade AT&T has tap danced around the fact it misleadingly sold an ‘unlimited’ data plan packed with confusing limits. No amount of legal maneuvering can hide the fact that AT&T lied repeatedly to its customers about the kind of connection they were buying,” Bode told Stop the Cap! “Instead of owning its mistake, learning from it, and moving forward, AT&T’s now trying to point to critical news coverage from the era to falsely suggest consumers should have known better. It’s utterly nonsensical and speaks volumes about the lack of ethical leadership at a company that routinely sees some of the lowest customer satisfaction ratings in American industry.”
AT&T’s lawyers are not prepared to concede, however. Since the lawsuit was filed, AT&T’s legal team attempted to force the case into arbitration in 2016. That effort was successful until a 2017 California Supreme Court decision in another case gave the plaintiffs ammunition to claim that it was against California law to force consumers into arbitration. The Ninth Circuit court agreed, and the case reverted to district court, where AT&T immediately began efforts to have the case dismissed outright.
AT&T is not alone throttling so-called “heavy users” that have either legacy or current unlimited data plans. All major cellular companies enforce fine print policies that allow speed throttling after customers consume as little as 20 GB of wireless data during a billing cycle. The fact companies still advertise such plans as “unlimited” irks Bode.
“An unlimited data connection should come with no limits. If giant wireless carriers can’t respect the dictionary, they should stop using the word entirely,” Bode told us.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Leichtman Research Group reports that most customers are looking for stable and reliably fast internet service, and phone company DSL delivers neither. Having a speedy and dependable connection has become crucial as tens of millions of Americans work from home to avoid contracting the illness. Sharing that internet connection with kids staying home from school quickly caused a spike in upgrade orders.
Leichtman Research Group reports that most customers are looking for stable and reliably fast internet service, and phone company DSL delivers neither. Having a speedy and dependable connection has become crucial as tens of millions of Americans work from home to avoid contracting the illness. Sharing that internet connection with kids staying home from school quickly caused a spike in upgrade orders. Frontier Communications is seeking to slow or block rural broadband funding for tens of thousands of rural Americans that live inside Frontier service areas but cannot subscribe to broadband service because the company does not offer it.
Frontier Communications is seeking to slow or block rural broadband funding for tens of thousands of rural Americans that live inside Frontier service areas but cannot subscribe to broadband service because the company does not offer it. In early April, Frontier
In early April, Frontier 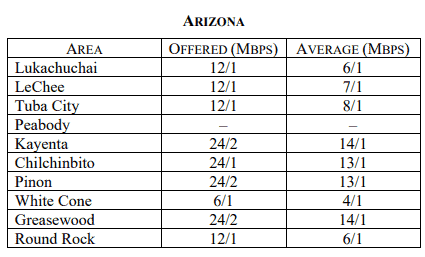

 Even with the threat of COVID-19 and a virtual nationwide work-from-home initiative, the new owners of Frontier Communications’ network in Washington, Oregon, Montana and Idaho are moving rapidly to repair persistent network issues, create a backup network, and lay the foundation to bring fiber to the home service to 85% of its customers over the next three years.
Even with the threat of COVID-19 and a virtual nationwide work-from-home initiative, the new owners of Frontier Communications’ network in Washington, Oregon, Montana and Idaho are moving rapidly to repair persistent network issues, create a backup network, and lay the foundation to bring fiber to the home service to 85% of its customers over the next three years.
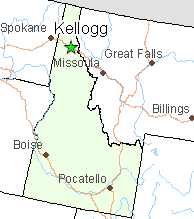 Among the first towns to get fiber service are Kellogg, Moscow, and Coeur d’Alene — all in Idaho. Work has already commenced and is expected to be finished by fall. Ziply wants to keep construction costs as low as possible, so it intends to do aerial deployment of fiber by wrapping the optical cable around existing copper wire telephone cables already on the pole. This process, known as “overlashing” will simplify installation by not requiring additional space to place fiber cables next to existing telephone wiring or going to the effort of removing the existing copper wiring, which raises costs.
Among the first towns to get fiber service are Kellogg, Moscow, and Coeur d’Alene — all in Idaho. Work has already commenced and is expected to be finished by fall. Ziply wants to keep construction costs as low as possible, so it intends to do aerial deployment of fiber by wrapping the optical cable around existing copper wire telephone cables already on the pole. This process, known as “overlashing” will simplify installation by not requiring additional space to place fiber cables next to existing telephone wiring or going to the effort of removing the existing copper wiring, which raises costs. To further speed fiber upgrades, Ziply acquired Wholesail Networks, already contracted to manage fiber network design for Ziply. Company officials quickly identified multiple weak spots in Frontier’s network, particularly relating to its resiliency when fiber cables were cut or copper wiring was stolen. Ziply is building in network redundancy, with each portion of its network served by at least two sets of fiber cabling and identical equipment in each of more than 130 central switching offices. In many markets, Ziply will maintain at least three redundant fiber connections to make certain if one (or two) networks go down, customers can still be served by a third with no interruption in service.
To further speed fiber upgrades, Ziply acquired Wholesail Networks, already contracted to manage fiber network design for Ziply. Company officials quickly identified multiple weak spots in Frontier’s network, particularly relating to its resiliency when fiber cables were cut or copper wiring was stolen. Ziply is building in network redundancy, with each portion of its network served by at least two sets of fiber cabling and identical equipment in each of more than 130 central switching offices. In many markets, Ziply will maintain at least three redundant fiber connections to make certain if one (or two) networks go down, customers can still be served by a third with no interruption in service. Spectrum internet customers in parts of Central Florida and South Texas are getting twice the download speed they used to receive thanks to a series of quiet service upgrades still in progress.
Spectrum internet customers in parts of Central Florida and South Texas are getting twice the download speed they used to receive thanks to a series of quiet service upgrades still in progress. In South Texas, San Benito is one of the communities between Brownsville and McAllen seeing Spectrum’s usual download speed doubled from 100 to 200 Mbps.
In South Texas, San Benito is one of the communities between Brownsville and McAllen seeing Spectrum’s usual download speed doubled from 100 to 200 Mbps.