Time Warner Cable’s summer was “horrible,” to quote one analyst, after three percent of customers left over programming disputes and increasing prices for broadband and telephone service, with more likely to follow as price promotions expire and rates increase further.
Time Warner Cable’s summer was “horrible,” to quote one analyst, after three percent of customers left over programming disputes and increasing prices for broadband and telephone service, with more likely to follow as price promotions expire and rates increase further.
Cable analysts were shocked Time Warner Cable lost 308,000 customers in the last three months, most leaving over interruptions of CBS and Showtime over a contract dispute. But customers were also ready to leave over increasing modem rental fees, rate increases, and the company’s growing pullback on promotional pricing. Time Warner Cable’s poor results have ironically caused its stock price to increase this morning, but only because investors suspect a shareholder value-boosting merger with Charter Communications could come within months.
“Just horrible,” MoffetNathanson analyst Craig Moffett wrote in a note to investor clients this morning. “The CBS dispute apparently took a much larger toll than anyone would have imagined, and this colored all the results.”
Sources have told Reuters that cable billionaire John Malone has approached Time Warner Cable about a full takeover by Charter Communications, but has been rebuffed by Britt so far. But with Britt exiting and Time Warner Cable’s underperformance, shareholder pressure for a deal with Charter will only increase.
“This enhances Malone’s appeal to Time Warner Cable shareholders that they would be better off with another management team,” Brean Capital analyst Todd Mitchell told Reuters.
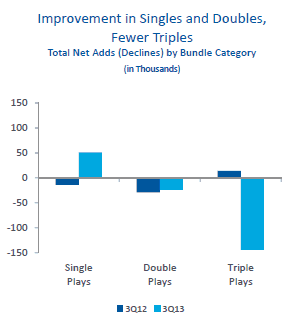
When promotional prices end, a growing percentage of TWC customers drop services or take their business elsewhere.
The subscriber losses pushed profits down 34 percent at the cable company, to $532 million. The triple play tragedy saw subscriber losses for all the company’s residential services. At a time when other cable companies cannot process High Speed Internet sign ups fast enough, at least 24,000 Time Warner Cable broadband customers left over rate hikes and equipment fees. Analysts had expected the company to pick up more than 46,000 broadband customers during the last three months, not lose them. The company’s phone service is also in decline. Only rate increases and customers upgrading to higher speed tiers delivered a slight revenue boost.
Outgoing CEO Glenn Britt set the stage for the current forced retreat on its revenue forecast for the year:
- Time Warner Cable executives made the decision at the end of 2012 to stop heavily discounting service and cut back on promotions. Their theory was the company would attract a larger base of stable customers willing to pay non-promotional rates and tolerate rate increases;
- Executives announced as Time Warner’s phone service was brought “in-house,” the company would stop aggressively pricing triple play bundles that included phone service. That turned out to be a bad decision for growth because customers, already prone to landline cord-cutting, downgraded their bundle or left when promotions expired and ditched the phone line;
- A year of broadband price increases and the introduction of a modem rental fee rubbed customers the wrong way. “We have raised prices recently in the form of modem rental fees, but it’s really just broadband price increase,” again admitted Britt this morning. Future rate increases on modem rentals will give broadband customers another push to shop around for a better deal. At least 24,000 did that over the summer and left, mostly for AT&T U-verse in the midwest and Verizon FiOS in the east.
The lengthy dispute between Time Warner and CBS did the most damage and not just to customers directly affected by channel losses. A major increase in call volumes from alienated customers overwhelmed national call centers, creating long hold times for everyone calling in.
Time Warner expects 40 percent of the cable company’s service area will be overlapped by major competitors AT&T U-verse (now 27%) and Verizon FiOS (now 13%). That represents one million more homes than last year.
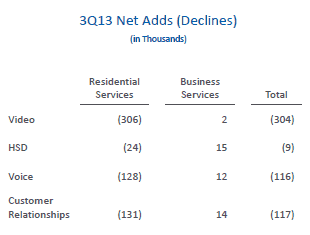
Bye Bye: Time Warner Cable lost residential customers for all of its services during the third quarter.
Incoming CEO Robert Marcus said he was dissatisfied with subscriber results from current promotions and rates. New Time Warner Cable customers, Marcus noted, are paying higher prices for fewer or less robust services as part of current promotional packages. Although that has driven a “dramatic improvement in recurring revenue” among customers actually signing up, many choose the lower-priced competition instead.
Marcus also noted customers are taking fewer services and are resistant to upgrading to double or triple play packages, reducing the potential average revenue per customer (ARPU).
“To a great extent, these are expected outcomes of our pricing and packaging strategy and the trade-off between ARPU and volume, but I’m confident we can do better on volume without giving up the ARPU benefits we’ve been achieving,” Marcus told analysts on a morning conference call.
Instead of getting more aggressive on pricing, the company plans to trot out free gifts and pitch discounted slow speed Internet to attract price-resistant DSL customers.
“Next week, we’ll launch our holiday offer, which includes a free Samsung tablet loaded with all of our apps, including TWC TV, with the purchase of higher-end packages,” Marcus said. “I think this will generate lots of interest and really highlight TWC TV and the value it adds to our service offerings.”
Marcus called it inconceivable and unacceptable that at least 4.5 million people are still subscribed to telephone company DSL in Time Warner Cable service areas. The company plans an advertising blitz to steal customers away from companies like AT&T, Verizon, Frontier, CenturyLink, Windstream and FairPoint.
At the center of that effort is the recently announced 2/1Mbps Lite package, which will sell at the everyday price of $14.95 a month. Marcus wants at least 500,000 DSL customers switched to Time Warner over the next 18 months.
“Over time, as these customers’ speed and capacity needs increase, we’ll be well positioned to sell them higher-end product,” Marcus said.
Or they will switch back to the phone company if Time Warner increases the price.


 Subscribe
Subscribe the worst-rated cable operator in the United States, claims it needs usage caps and consumption billing to force heavy users to pay for needed upgrades. But that isn’t what Mediacom’s executives are telling investors and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
the worst-rated cable operator in the United States, claims it needs usage caps and consumption billing to force heavy users to pay for needed upgrades. But that isn’t what Mediacom’s executives are telling investors and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). “
“
 Other customers incensed about the new usage limits have called to cancel service only to be threatened with steep early termination fees.
Other customers incensed about the new usage limits have called to cancel service only to be threatened with steep early termination fees.
 Time Warner Cable has chosen a gradual transition to IP video for cable television service. Subscribers can expect about a dozen channels per year to be removed from analog service until the cable system offers a completely digital television package. In Maine and New York City, that digital transition is already complete.
Time Warner Cable has chosen a gradual transition to IP video for cable television service. Subscribers can expect about a dozen channels per year to be removed from analog service until the cable system offers a completely digital television package. In Maine and New York City, that digital transition is already complete.