America’s most costly large cable internet service provider is Sparklight, formerly known as Cable One. Its internet plans are usually data-capped and it barely offers new customers a pricing break before high regular prices apply. Sparklight primarily services small cities and towns, many income-challenged, in the middle of the country. Customers do not have much to rave about, because Sparklight puts its own profits far ahead of its customers. The cable operator was among the first to slap on data caps and was the nation’s most aggressive at getting rid of costly cable television channels.
America’s most costly large cable internet service provider is Sparklight, formerly known as Cable One. Its internet plans are usually data-capped and it barely offers new customers a pricing break before high regular prices apply. Sparklight primarily services small cities and towns, many income-challenged, in the middle of the country. Customers do not have much to rave about, because Sparklight puts its own profits far ahead of its customers. The cable operator was among the first to slap on data caps and was the nation’s most aggressive at getting rid of costly cable television channels.
About the only thing that does move Sparklight’s pricing is the presence of a formidable competitor. In Meridian and Garden City, Ida., TDS Fiber (formerly TDS Telecom) has been bringing gigabit fiber to the home service to area residents at prices low enough to motivate Sparklight customers to abandon the cable company. That motivated Sparklight to improve their plans and lower prices.
First, let’s examine the internet rate card for ordinary Sparklight customers typically stuck choosing either the cable company or DSL from Frontier, AT&T, or Windstream:
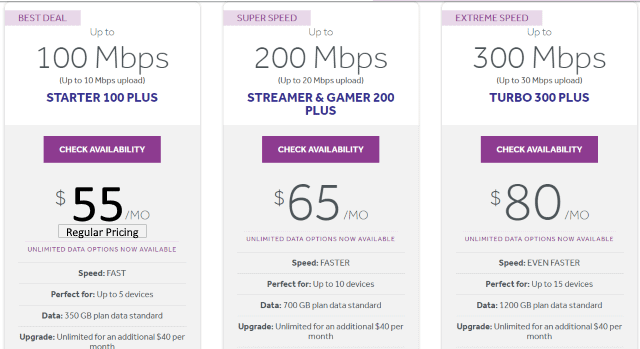
Sparklight regular pricing nationwide
Notice the entry-level internet plan (100/10 Mbps) costs $55 a month, does not mention the $10.50/mo modem rental fee (required if you choose the company’s Wi-Fi service), an internet service surcharge of $2.75/mo (not charged in all areas), and a stingy data cap of just 350 GB, which is at least 100 GB less than what the average U.S. broadband household now consumes each month. Internet overlimit fees are $10 for each additional block of 100GB of data in excess of your allowance, up to a maximum of $50 a month. Unlimited service costs an extra $40 a month.
When you add it all up: for an unlimited (100/10 Mbps) internet service plan with in-home Wi-Fi, Sparklight charges $108.25 a month.
If you happen to live in a competitive service area, such as Meridian and Garden City, Ida., speeds are faster, prices are lower, and data caps are nowhere to be found:
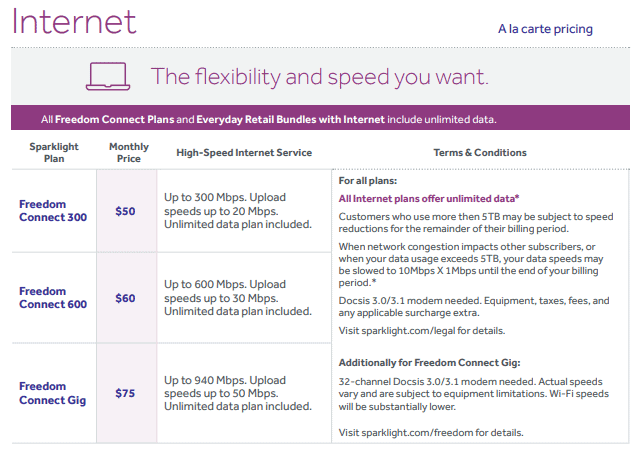
Pricing for Sparklight in Meridian and Garden City, Ida.
Customers still face a $10.50/mo charge to lease a cable modem, and that $2.75/mo internet surcharge fee might also apply.
The prospect of competition could cut dramatically into company profits, which is one reason telecom companies are fiercely lobbying the Biden Administration not to fund municipal broadband projects or supply funds to a new competitor as part of the 2021 Infrastructure Plan.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Comcast on Wednesday said it will
Comcast on Wednesday said it will  AT&T has
AT&T has 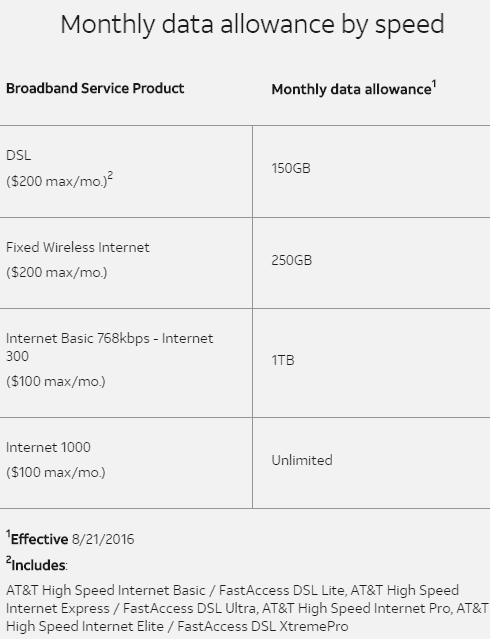
 Cox will return to data capping its broadband customers on Wednesday, July 1 but with a bigger usage allowance from now on.
Cox will return to data capping its broadband customers on Wednesday, July 1 but with a bigger usage allowance from now on.