 Verizon Wireless has sued the City of Rochester, N.Y. in a potentially precedent-setting case, for demanding excessive and discriminatory fees to use public rights-of-way to deploy a fiber backhaul network and hundreds of small cells to support the introduction of 5G wireless service in the community.
Verizon Wireless has sued the City of Rochester, N.Y. in a potentially precedent-setting case, for demanding excessive and discriminatory fees to use public rights-of-way to deploy a fiber backhaul network and hundreds of small cells to support the introduction of 5G wireless service in the community.
The lawsuit, Cellco Partnership (d/b/a Verizon Wireless) v. City of Rochester seeks a declaratory judgment acknowledging that local laws regarding the use of rights-of-way by telecommunications companies have been largely overridden by the Trump Administration’s Federal Communications Commission. Under FCC guidelines, the maximum compensation rate a city can generally collect is $270 annually for each small cell site, far less than what the City of Rochester hopes to collect from telecommunications companies planning to dig up streets and place hundreds of small cell antennas on utility and light poles across the city.
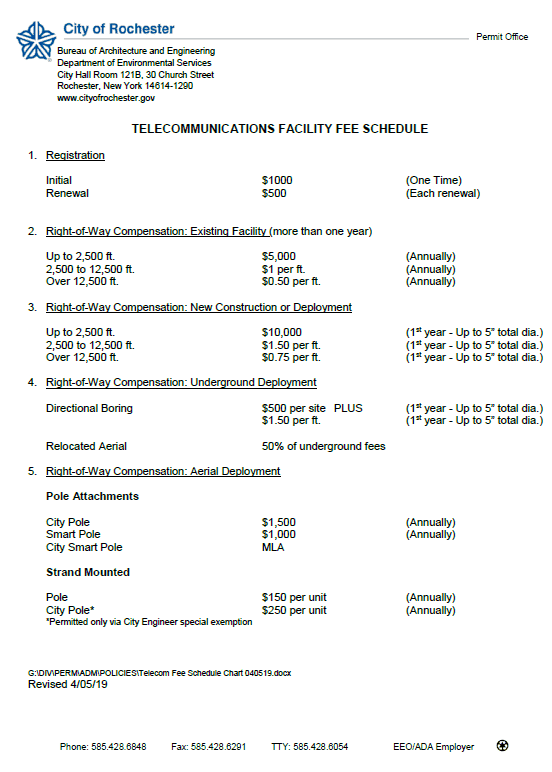
The two parties are far apart on what defines fair and just compensation. In early 2019, the City of Rochester introduced a new fee schedule that seeks $1,500 annually for the use of each publicly owned utility or light pole, and $1,000 per standalone “smart pole” erected by a wireless company to support a small cell. Verizon Wireless wants to pay no more than $270 annually for either type.
 The City also wants compensation to cover “administrative costs for retaining and managing documents and records,” “costs for managing, coordinating and responding to public concerns and complaints,” and “the costs of the City’s self-insurance.” Verizon Wireless’ attorneys argue that the FCC’s “presumptive limit” of $270 annually is all-inclusive, and therefore the fees requested are inherently unreasonable.
The City also wants compensation to cover “administrative costs for retaining and managing documents and records,” “costs for managing, coordinating and responding to public concerns and complaints,” and “the costs of the City’s self-insurance.” Verizon Wireless’ attorneys argue that the FCC’s “presumptive limit” of $270 annually is all-inclusive, and therefore the fees requested are inherently unreasonable.
The City ordinance is also designed to discourage providers from installing cables on existing utility poles, preferring underground installation.
“Aerial installation of fiber or other telecommunications facilities and accessory equipment strung between poles, buildings, or other facilities, is strongly discouraged due to area weather, safety concerns, limited capacity, and aesthetic disturbances,” the ordinance reads. But Verizon Wireless argues the extra fees demanded by the City for underground burial of fiber optic cable are illegal under federal law.
“The Code’s ‘underground’ fee structure is not a reasonable approximation of actual cost, is not objectively determined, and is discriminatory,” Verizon Wireless argues.
The City’s fees for fiber optic cable installation are significant. Verizon Wireless’ lawsuit notes fees start at $10,000 for up to 2,500 linear feet of installed fiber optic cable, plus an additional $1.50 for each additional foot from 2,500-12,500 feet and $0.75 for each additional foot above 12,500 feet. After the first year, fees continue at $5,000 annually for up to 2,500 feet, $1 for each additional foot from 2,500-12,500 feet, and $0.50 for each additional foot above 12,500 feet. Somewhat lower fees apply if Verizon places its fiber cables in an existing conduit with other cables, or if it uses directional boring to place conduit and wiring without disturbing lawns, roads, or sidewalks.

Curtin
Verizon Wireless’ attorneys argue the fees cannot possibly reflect the City’s true costs because the charges are the same regardless if Verizon installed three feet or 2,000 feet of fiber optic cable.
But City Corporation Counsel Tim Curtin told the Democrat & Chronicle the city’s new fee schedule is comparable to what other cities are charging, and the City is planning more restrictions to keep providers from repeatedly digging up streets and yards to place new cable and equipment.
“This is a serious problem with people digging up the same right of way every other day and not repairing it,” Curtin told the newspaper.
The City is also exploring passing a new “dig once” policy that would incentivize providers to coordinate fiber installation to place wiring and equipment in a single shared conduit in return for lower fees. But providers like Verizon Wireless consider it in their competitive advantage to wire cities like Rochester before their competitors do.
“To better serve its customers and the City and to begin to serve new customers and provide new services, Verizon Wireless seeks to extend, densify, and upgrade its wireless network infrastructure [in Rochester], including to install additional Small Wireless Facilities to support the provision of current and next-generation telecommunications services such as 5G and to deploy fiber to connect these facilities. To successfully do this, Verizon Wireless requires new approvals from [the City of Rochester] to access City property,” Verizon’s lawsuit states. Because of the City’s fees and policies, “Verizon Wireless has been, and will continue to be, damaged and irreparably harmed, […] [including] an effective prohibition on Verizon Wireless’s ability to provide telecommunications services in the affected area of the City.”
In short, Verizon Wireless is threatening not to deploy 5G service in the area if the City successfully defends its fees and requirements.
Curtin argues Verizon Wireless is the only provider unwilling to comply with the City’s requirements, while others are moving forward under the new ordinance. One provider likely covered by Curtin’s claim is residential fiber overbuilder Greenlight Networks, which has installed fiber to the home service across several city neighborhoods for the past several years. But in 2019, Greenlight began focusing on installations in suburbs west of Rochester, and several city neighborhoods proposed for service have languished for years with “easements required” status, which could reflect Greenlight’s reluctance or ability to pay the City’s new fees.
Verizon has been the most aggressive wireless provider in Western and Central New York with respect to the proposed 5G service expansion. In addition to being the incumbent local telephone company in several New York cities (excluding Rochester), it has also offered spotty FiOS fiber to the home service in several suburbs of Buffalo and Syracuse.
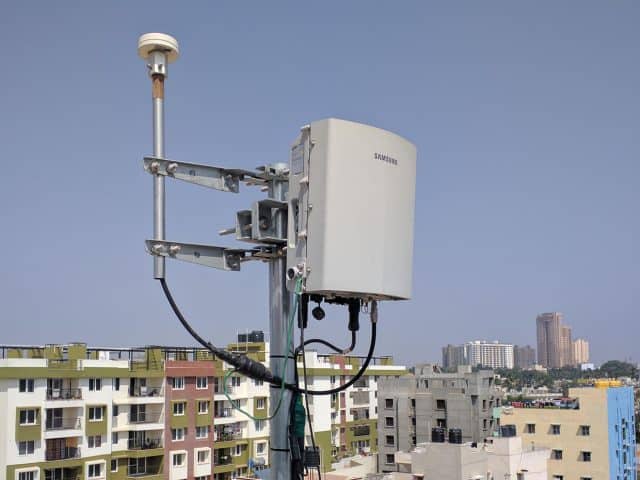

A small cell
In contrast with Rochester, the City of Syracuse decided to effectively “partner” with Verizon Wireless to deploy 5G small cells to be considered America’s “first fully 5G city.” To win Verizon over, the City mothballed its existing fee policy in 2019 that charged $950 per small cell tower, resetting the rate to match the FCC’s presumed maximum of $270 annually. In return, Verizon has tentatively agreed to place up to 600 smart cell poles around the city, paying $162,000 a year. Verizon also agreed to pay a $500 application fee for each pole project (covering up to a maximum of five poles per project). Nobody is certain whether 600 smart cells are enough to saturate the city with 5G coverage, where exactly Verizon will ultimately place the small cells, or exactly when.
Ken Schmidt, president of Steel in the Air, a consultant to public and private landowners and municipalities on matters related to wireless infrastructure valuation, offered to advise the City of Syracuse for free about its agreement with Verizon Wireless, but the City never returned his calls, despite his direct experience working with other cities that negotiated with Verizon Wireless over 5G smart cells, pole attachment fees, and antenna placement rules.
“Syracuse seems to have bent over backward for Verizon,” Schmidt argues on his blog. “Make no mistake, there are benefits to becoming a 5G city, but this agreement does no more for Syracuse than it does for other cities where Verizon promised the same thing. At least some of the other cities didn’t enter into such a one-sided agreement. For example, Sacramento, San Diego and San Jose negotiated better terms and conditions than Syracuse did, and will have a similarly robust small cell deployment.”
Many consultants recommend that cities consider whether Verizon’s threats not to deploy 5G service are real, especially considering the company’s PR claims that moving forward with 5G is essential to Verizon’s network expansion.

Schmidt
Schmidt acknowledges the current FCC has a vested interest in helping large wireless companies deploy 5G infrastructure with a minimum of interference or fees from local governments.
“While the City could have negotiated a higher amount for the pole access rights or permit fees, it would have had to demonstrate that its actual costs in reviewing small cell applications and maintaining the rights-of-way were higher than the nominal fees allowed by the FCC,” Schmidt said.
Verizon’s lawyers appeared to outmaneuver the City’s attorneys by winning a number of concessions for Verizon that Syracuse will have to live with for up to 45 years. Schmidt’s recommendations may be useful to other cities, including Rochester, wrestling with these issues.
Schmidt:
Syracuse granted rights to Verizon for upward of 45 years when it didn’t have to. The city signed a master license agreement for 20 years, which allows Verizon to install poles under individual pole licenses that run up to 25 years from the date the pole was installed. Thus, if a pole is installed in year 20, it will be there for another 25 years. In short, the city is entering a possible 45-year agreement even though there is no legal requirement to do so by the FCC or any other agency. While Verizon surely prefers a much longer agreement, other cities are entering much shorter, 10-year agreements with Verizon. Verizon retained the right to terminate “at any time for any reason or no reason by written notice to the city,” but the city does not have the same right. So, the city is now committed to this specific agreement legally, regardless of what happens with technology in the future.
The agreement entered into by the city concedes unnecessary rights to Verizon under contract law. The agreement is substantially the same as other agreements proposed by Verizon to other cities. It attempts to incorporate many of the standards from the FCC Order into the license agreement. From a legal perspective, these clauses did not need to be in the license agreement. If Verizon felt the city was not adhering to the FCC order, Verizon by default has the option of requesting relief from the FCC or filing in federal court for injunction or damages. However, by adding the language in the license agreement, Verizon can now file in state court on a civil claim if Verizon believes the city is in breach of the agreement and collect monetary damages. This is absolutely of no benefit to Syracuse.
Other cities have received additional compensation in the form of public safety or “internet of things” monitoring and services, and higher fees to help pay for additional staff to review small cells applications. Syracuse received nothing. In fairness, the other cities are bigger and more important to Verizon than Syracuse. Nonetheless, the only concession Verizon appears to have made to Syracuse is the requirement for Verizon to monitor a limited set of small cells for compliance with applicable radio frequency emission standards. Verizon did not commit to deploying a certain number of small cells by any date. It is not required to deploy in the poorer areas of the city. And it did not commit to smart city initiatives or research on how 5G can benefit the residents of Syracuse.
The agreement gives the city limited rights to terminate, even if health risks are identified and proven. The city, in what appears to be an effort to appease its citizens that small cells are safe, inserted language that requires Verizon to test up to 5% of the small cells annually to confirm that they meet the minimum applicable health, safety and radio frequency regulations. The city could also test on its own, but only to confirm compliance with applicable FCC standards. By agreeing to a long-term license with limited rights to terminate, the city could be legally committed to Verizon small cells in the public right of way even if there is ample evidence that they should be removed, unless the FCC revokes its order.
By agreeing to such a one-sided agreement, the city has condemned itself to agree to similar agreements with any company providing wireless services who want to deploy in the right-of-way. Under the FCC Order and previous case law regarding the Telecommunications Act of 1996, the city may not discriminate between similar providers of wireless services. By agreeing to the terms with Verizon, the city will have a difficult time agreeing to different terms with other providers.

 A modem rental fee may also apply in most states, unless you use your own cable modem. Outside of New York and New Jersey, most legacy ELP customers have already experienced several gradual rate increases on this plan, which was originally sold nationwide for $14.99/mo. The first rate increase took most customers to $19.99/mo, followed by a rate increase last fall to $24.99/mo. Now Charter Spectrum has notified customers of another $3/mo rate hike, bringing the monthly rate to $27.99.
A modem rental fee may also apply in most states, unless you use your own cable modem. Outside of New York and New Jersey, most legacy ELP customers have already experienced several gradual rate increases on this plan, which was originally sold nationwide for $14.99/mo. The first rate increase took most customers to $19.99/mo, followed by a rate increase last fall to $24.99/mo. Now Charter Spectrum has notified customers of another $3/mo rate hike, bringing the monthly rate to $27.99.

 Subscribe
Subscribe

 Verizon Wireless has sued the City of Rochester, N.Y. in a potentially precedent-setting case, for demanding excessive and discriminatory fees to use public rights-of-way to deploy a fiber backhaul network and hundreds of small cells to support the introduction of 5G wireless service in the community.
Verizon Wireless has sued the City of Rochester, N.Y. in a potentially precedent-setting case, for demanding excessive and discriminatory fees to use public rights-of-way to deploy a fiber backhaul network and hundreds of small cells to support the introduction of 5G wireless service in the community. The City also wants compensation to cover “administrative costs for retaining and managing documents and records,” “costs for managing, coordinating and responding to public concerns and complaints,” and “the costs of the City’s self-insurance.” Verizon Wireless’ attorneys argue that the FCC’s “presumptive limit” of $270 annually is all-inclusive, and therefore the fees requested are inherently unreasonable.
The City also wants compensation to cover “administrative costs for retaining and managing documents and records,” “costs for managing, coordinating and responding to public concerns and complaints,” and “the costs of the City’s self-insurance.” Verizon Wireless’ attorneys argue that the FCC’s “presumptive limit” of $270 annually is all-inclusive, and therefore the fees requested are inherently unreasonable.



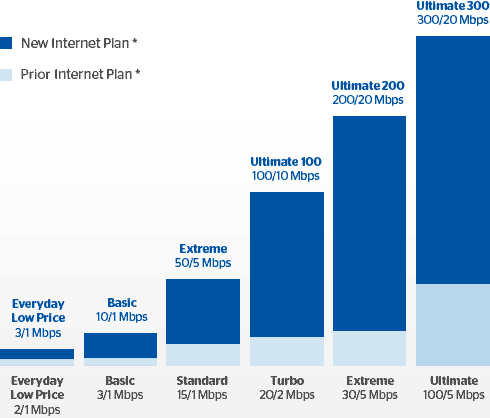
 Charter Communications is not obligated to upgrade New York internet customers to a minimum internet speed of 300 Mbps, according to a letter of clarification directed to Stop the Cap! and received today from the New York State Department of Public Service.
Charter Communications is not obligated to upgrade New York internet customers to a minimum internet speed of 300 Mbps, according to a letter of clarification directed to Stop the Cap! and received today from the New York State Department of Public Service.
 Comcast has put its proverbial finger to the wind to define an “appropriate” data cap it declares “generous,” regardless of how subjectively random that cap happens to be. Although 1,000 GB — a terabyte — usage allowance represents a lot of internet traffic, more and more customers are finding they are flirting with exceeding that cap, and Comcast has never been proactive about regularly adjusting it to reflect the reality of rapidly growing internet traffic. That means customers must protect themselves by checking their usage and take steps if they are nearing the 1 TB limit.
Comcast has put its proverbial finger to the wind to define an “appropriate” data cap it declares “generous,” regardless of how subjectively random that cap happens to be. Although 1,000 GB — a terabyte — usage allowance represents a lot of internet traffic, more and more customers are finding they are flirting with exceeding that cap, and Comcast has never been proactive about regularly adjusting it to reflect the reality of rapidly growing internet traffic. That means customers must protect themselves by checking their usage and take steps if they are nearing the 1 TB limit.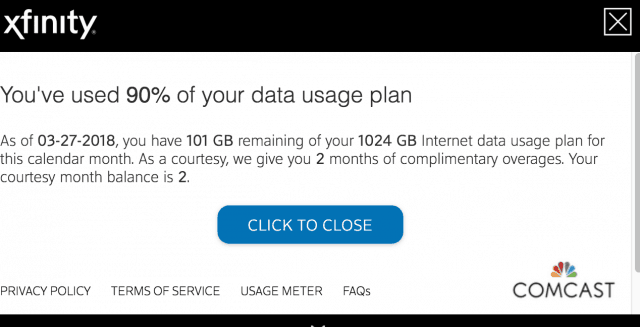 Video Games Consoles/PCs
Video Games Consoles/PCs