 Large media companies and streaming services are on to many of you.
Large media companies and streaming services are on to many of you.
If you are among the two-thirds of subscribers that have reportedly shared your Netflix, HBO GO, Hulu, or Disney+ password with friends and family, your provider probably already knows about it.
A recent report from HUB Entertainment Research found that at least 64% of 13-24-year-olds have shared a password to a streaming service with someone else, with 31% of consumers admitting they are sharing passwords with people outside of their home.
The reason many people share passwords is to save money on the cost of signing up for multiple streaming services. Many trade a Netflix password in return for a Hulu password, or hand over an HBO GO password in exchange for access to your Disney+ account. Research firm Park Associates claims that streamers lost an estimated $9.1 billion in revenue from password sharing, and can expect to lose nearly $12.5 billion by 2024 if password sharing is not curtailed.
Oddly, most streaming services are well aware of password sharing and the lost revenue that results from sharing accounts, and most care little, at least for now.
Marketplace notes a lot of the complaints about password sharing are coming from cable industry executives, shareholders, and Wall Street analysts, but for now most streaming services are just monitoring the situation instead of controlling it.
 “I think we continue to monitor it,” said Gregory K. Peters, Netflix’s chief product officer, on the 2019 third quarter earnings call. “We’ll see those consumer-friendly ways to push on the edges of that, but I think we’ve got no big plans to announce at this point in time in terms of doing something differently there.”
“I think we continue to monitor it,” said Gregory K. Peters, Netflix’s chief product officer, on the 2019 third quarter earnings call. “We’ll see those consumer-friendly ways to push on the edges of that, but I think we’ve got no big plans to announce at this point in time in terms of doing something differently there.”
Netflix sells different tiers of service that limit the number of concurrent streams to one, two, or four streams at a time. The company believes that if customers that share accounts bump into the stream limits, many will upgrade to a higher level of service which will result in more revenue.
Newcomer Disney+ not only recognizes password sharing is going on, it almost embraces it.
“We’re setting up a service that is very family friendly. We expect families to consume it,” Disney CEO Bob Iger said in an interview with CNBC. “We will be monitoring [password sharing] with the various tools that we have.”
The biggest tool Disney has to monitor account sharing is Charter Spectrum, which is aggressively encouraging streaming services to crack down hard on password sharing. Spectrum internet customers who watch Disney+ are now tracked by Spectrum, recording each IP address that accesses Disney+ content over Spectrum’s broadband service. When multiple people at different IP addresses access Disney+ content on a single account at the same time, Spectrum can flag those customers as potential password sharers.
Synamedia, a streaming provider security firm, uses geolocation tools to determine who is watching streaming services from where. If someone is watching one stream from one address and another person is watching from another city at the same time, password sharing is the likely culprit. For now, most companies are quietly collecting data to learn just how big a problem password sharing is and are not using that information to crack down on customers.
 Streaming providers are more interested in stopping the pervasive sale of stolen account credentials on services like eBay and shutting down stolen accounts used to harvest content for unauthorized resale. But as sharing grows, so will calls from stakeholders to curtail the practice. Those in favor of vigorous crackdowns on password sharing argue billions of dollars of lost revenue will be lost. If a service like Netflix blocked password sharing, that could lead to dramatic increases in account sign-ups. But less established brands like Disney+ seem more concerned about losing the unofficial extra viewers that are watching and buzzing about shows on its new streaming platform. Find the best residential proxies to access the streaming content that is not available in your location.
Streaming providers are more interested in stopping the pervasive sale of stolen account credentials on services like eBay and shutting down stolen accounts used to harvest content for unauthorized resale. But as sharing grows, so will calls from stakeholders to curtail the practice. Those in favor of vigorous crackdowns on password sharing argue billions of dollars of lost revenue will be lost. If a service like Netflix blocked password sharing, that could lead to dramatic increases in account sign-ups. But less established brands like Disney+ seem more concerned about losing the unofficial extra viewers that are watching and buzzing about shows on its new streaming platform. Find the best residential proxies to access the streaming content that is not available in your location.
Cable companies are frustrated about losing scores of cable TV customers to competitors that may be effectively giving away service for free. That has raised tempers at companies like Charter Communications.
“Pricing and lack of security continue to be the main problems contributing to the challenges of paid video growth,” Charter CEO Thomas Rutledge said in recent prepared remarks with Wall Street analysts. “The traditional bundle … is very expensive, and the actual unit rate of that product continues to rise, and that’s priced a lot of people out of the market. And it’s free to a lot of consumers who have friends with passwords. So our ability to sell that product is ultimately constrained by our relationship with content [companies], and we have to manage that in terms of the kinds of power that the content companies have.”
Charter’s power comes from its willingness to distribute cable networks like The Disney Channel to tens of millions of homes around the country. That forces Disney to listen to Charter’s concerns about piracy and password sharing and the issue is even documented in the latest carriage contract between the two companies.
Cable industry executives believe a crackdown on password sharing is inevitable, eventually. Just as the cable industry was forced to combat cable pirates during its formative years, streaming providers that welcome extra viewers today may lament the lost revenue those subscribers don’t bring to the table tomorrow.
Marketplace reports on the growing issue of streaming service password sharing. (2:19)


 Subscribe
Subscribe AT&T was unhappy with the low internet speed score the FCC was about to give the telecom giant, so it made a few phone calls and got the government regulator to effectively rig the results in its favor.
AT&T was unhappy with the low internet speed score the FCC was about to give the telecom giant, so it made a few phone calls and got the government regulator to effectively rig the results in its favor. An FCC spokesman told the Journal the program has a transparent process and that the agency will continue to enable it “to improve, evolve, and provide meaningful results as we move forward.”
An FCC spokesman told the Journal the program has a transparent process and that the agency will continue to enable it “to improve, evolve, and provide meaningful results as we move forward.” Cox also managed to find an innovative way out of its poor score for internet speed consistency, which the FCC initially rated a rock bottom 37% of what Cox advertises. Cox claimed its speed test results were faulty because SamKnows’ tests sent traffic through an overcongested internet link yet to be upgraded. That ‘unfairly lowered Cox’s ratings’ for many of its Arizona customers, the company successfully argued, and the FCC put Cox’s poor speed consistency rating in a fine print footnote, which included both the 37% rating and a predicted/estimated reliability rating of 85%, assuming Cox properly routed its internet traffic.
Cox also managed to find an innovative way out of its poor score for internet speed consistency, which the FCC initially rated a rock bottom 37% of what Cox advertises. Cox claimed its speed test results were faulty because SamKnows’ tests sent traffic through an overcongested internet link yet to be upgraded. That ‘unfairly lowered Cox’s ratings’ for many of its Arizona customers, the company successfully argued, and the FCC put Cox’s poor speed consistency rating in a fine print footnote, which included both the 37% rating and a predicted/estimated reliability rating of 85%, assuming Cox properly routed its internet traffic.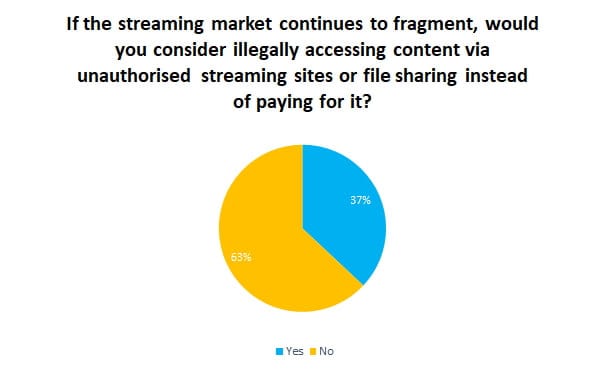 As more paid streaming services debut, consumers have signaled they are increasingly willing to pirate their favorite shows and movies to save money.
As more paid streaming services debut, consumers have signaled they are increasingly willing to pirate their favorite shows and movies to save money.
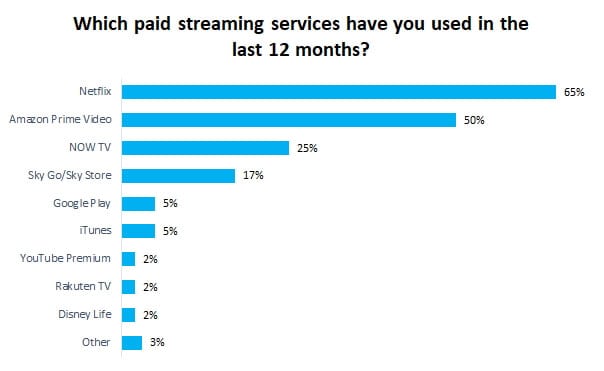
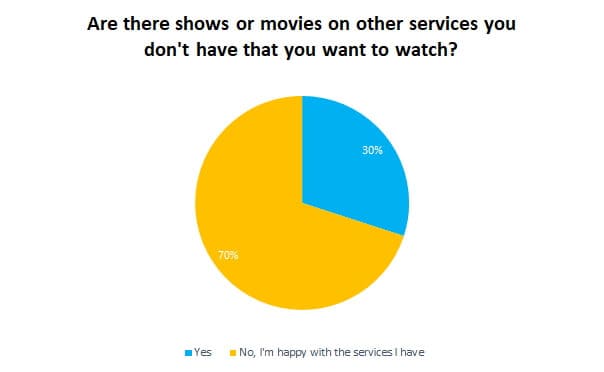
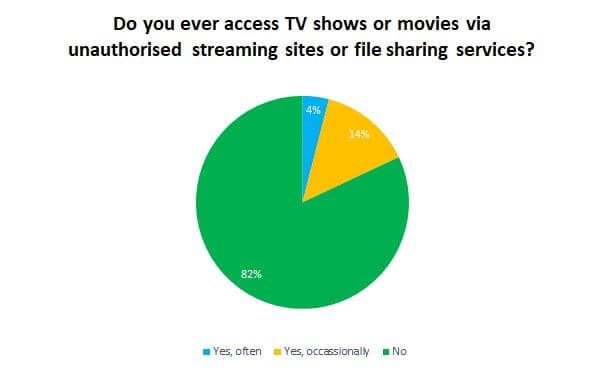
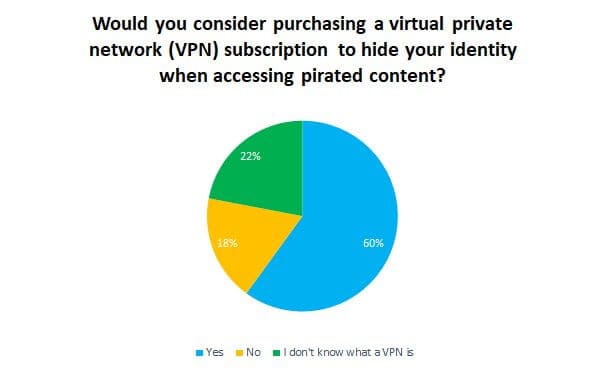
 Netflix stock lost over 11% of its value late today after the company
Netflix stock lost over 11% of its value late today after the company