
Could this be Comcast’s next target?
As Wall Street continues contemplating mom and dad at the FCC and Department of Justice calling off Comcast’s elopement with Time Warner Cable, some analysts believe Comcast will have to spend the money now burning a hole in its pocket on something.
“Given the strength of Comcast’s balance sheet and an insatiable appetite for acquisitions, we do not believe Comcast would be content with its existing portfolio (no different than after they failed in their 2004 attempt to buy Disney),” wrote Richard Greenfield from BTIG Research.
Greenfield has grown increasingly pessimistic about the Comcast-Time Warner Cable deal since realizing regulators were not going to follow the usual procedure of rubber-stamping approval with mild, short-term conditions to appease politicians. As President Barack Obama highlights telecommunications public policy in his second term, the cable industry (and broadband in particular) has come under unprecedented scrutiny and visibility in the press.
This winter, the FCC redefined broadband speed to mean a connection offering at least 25Mbps. That virtually eliminates DSL as a meaningful competitor, and would hand a combined Comcast/Time Warner Cable over 55% of broadband homes in the United States. The FCC’s approval of Net Neutrality and regulating broadband as a public utility led the audience in attendance to give a standing ovation to Chairman Thomas Wheeler and the two Democratic commissioners voting in favor of the policy change. The public sentiment is clearly against industry deregulation and unfettered deal-making, particularly when it involves Comcast, one of the most-loathed corporations in America.

Greenfield
Greenfield notes momentum is on the side of consumer groups fighting for Net Neutrality, oversight, and an end to cable industry consolidation.
Assuming Comcast’s deal with Time Warner Cable fails, what can Comcast spend its money on without running into a regulator buzzsaw?
Comcast could easily continue a mergers and acquisitions strategy if it avoids attempting to dramatically increase its cable footprint. For instance, Comcast could still choose to sell some of its less important cable systems to Charter Communications — already part of the proposed Time Warner Cable transaction — and make up that subscriber loss by acquiring Cablevision, which provides service in the important suburban New York City market. Of course, the Dolan family is notorious for not selling to anyone, and a considerable number of extended family members are employed as executives in the company.
Cable operators have returned to a strategy of hedging their content costs by spending billions to acquire content producers and sports teams in hopes of moderating their price demands. In the 1980s and early 1990s, large cable operators insisted on owning a piece of nearly every cable network shown on their systems. Today, having an ownership stake in the cable networks one negotiates with at contract renewal time is a helpful advantage.
Comcast has several attractive acquisition targets Greenfield believes it can consider:
 Time Warner (Entertainment): Not affiliated with Time Warner Cable, owning Time Warner (Entertainment) would gain Comcast important cable networks like TNT, HBO, and the Warner Bros. studio.
Time Warner (Entertainment): Not affiliated with Time Warner Cable, owning Time Warner (Entertainment) would gain Comcast important cable networks like TNT, HBO, and the Warner Bros. studio.- Netflix: Acquiring one of the best assets cord cutters have might prove difficult with regulators in Washington, but buying the ultimate TV Everywhere experience could deliver a digital platform that puts Comcast’s own online content portal to shame. The deal would also come with the talent that made Netflix an international success. If Comcast were to acquire Netflix, it would combine a superior streaming platform with an enormous content library.
- Acquire online video content sites and producers: Linear live television continues to be challenged by an array of on-demand content and video clips from various websites like Vice — videos that could be further monetized by matching Comcast’s advertising sales team with online media.
- Next generation online video set-top box manufacturers: The traditional cable box is dead to a lot of subscribers who prefer the simplicity (and price) of Roku and other similar alternatives. Current cable boxes are huge, expensive, and simply lack the creative imagination of the competition. If Comcast can’t beat Roku, it could buy it.
- Buy Sprint or T-Mobile: Greenfield believes Comcast lacks a wireless component in its product lineup as consumers increasingly move towards portable devices. Comcast would be financially foolish to build a network from the ground up, so acquiring an existing one makes more sense. AT&T and Verizon Wireless are likely out of reach, but Sprint and T-Mobile are not. Both carriers’ parent companies seem ready to sell, if the price is right. Of the two, Sprint might be willing to sell first. Sprint’s owner — Japan’s Softbank — has discovered the United States is a huge country that can swallow up endless amounts of investment and still leave it saddled with a second-rate network.
Greenfield is only speculating and there are no indications Comcast is seriously considering a next move should the Time Warner Cable deal be killed in Washington. But it does signal Wall Street does expect Comcast to do something.


 Subscribe
Subscribe

 Comcast rates are going up again this fall in the Pacific Northwest, now exceeding $70 a month.
Comcast rates are going up again this fall in the Pacific Northwest, now exceeding $70 a month.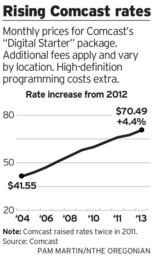
 Pay television providers forced Al Jazeera to remove or block its online video content from American viewers in return for launching its new news channel on cable systems this week.
Pay television providers forced Al Jazeera to remove or block its online video content from American viewers in return for launching its new news channel on cable systems this week.
