The French press continues to report, with some bewilderment, that U.S. consumers are being fleeced by the country’s biggest telecom companies while politicians do nothing to regulate a duopoly market or force more competition to stop the pick-pocketing. The Francophone press is responding to reports that cable baron Patrick Drahi is vacuuming up profits from his American subsidiary Altice USA — which owns Cablevision and Suddenlink — and is likely to get much bigger in 2017, all thanks to the U.S. regulatory landscape.
The French press continues to report, with some bewilderment, that U.S. consumers are being fleeced by the country’s biggest telecom companies while politicians do nothing to regulate a duopoly market or force more competition to stop the pick-pocketing. The Francophone press is responding to reports that cable baron Patrick Drahi is vacuuming up profits from his American subsidiary Altice USA — which owns Cablevision and Suddenlink — and is likely to get much bigger in 2017, all thanks to the U.S. regulatory landscape.
“Americans live under a corrupt politician-sanctioned broadband monopoly in many places, and this assures telecoms operators in the United States can earn astounding profit margins impossible in European markets,” notes Giga France.
Le Figaro reported this month Altice’s directors had an easy job figuring out where much of the global conglomerate’s future profits would come from: the United States.
“Given the structure of the telecom market, [Altice’s] margin for growth in France is low, whereas in the United States it is considerable,” the newspaper reported. The reason is a persistent lack of competition, made possible by politicians that accepted the recommendations of lobbyists and corporate special interest think tanks on how to structure the broadband market.
Drahi
In the United States, providers have won near-absolute control of their networks and need not share access with competitors. Large telecom companies argued that requiring shared access to their infrastructure would threaten investment and stall broadband network deployment. Ironically, some even argued it would lead to reduced competition. But the reverse turned out to be true and the United States has fallen far behind in competition and network quality, while more traditionally regulated markets in Europe now enjoy low prices, faster internet speeds, and a larger number of competitors vying for consumers’ business.
Wall Street indirectly conspires to keep the status quo by discouraging the entry of new fixed line providers, claiming it will destroy shareholder value and consume billions of investor dollars constructing competing networks that will be unlikely to attract enough subscribers fast enough to give shareholders a timely return on their investment.
With a provider-friendly Trump Administration in power, and more importantly the installation of Ajit Pai, a notorious telecoms-friendly regulator as chairman of the FCC, Altice’s directors consider 2017 to be one of the most inviting years for expansion in the United States.
Le Figaro reports there is plenty of opportunity for Altice’s empire to become more dominant in North America. In France, its SFR unit now holds a 25% share in the fixed line market, but that number is unlikely to grow much considering ongoing price wars that come from fierce competition in France. In the U.S., Altice only holds barely 3% of the market, and Drahi has made no secret he would like to become at least the second-largest provider in the United States.
Les Echos suggested Altice is quietly preparing a full-scale ambush on the U.S. market starting with a much-anticipated IPO expected this year. Wall Street doesn’t welcome Altice entering the U.S. cable business as a market disruptor. Instead, investment banks are willing to loan huge sums to Altice for the purpose of acquiring telecom companies, maintaining the existing duopoly of one cable and one phone company for the majority of Americans.
“In the past, every time he introduced a publicly traded asset, Drahi proceeded with acquisitions: Numericable, in 2013, SFR the following year; and by 2015 Cablevision and Suddenlink in the U.S.A.,” reports Les Echos.
In France, up to four providers compete head to head for fixed line telecom customers. In other parts of Europe, telecom networks are often forced open to competitors. Neither is the case in the States, and consumers are paying very high telecom bills as a result.
Les Echos notes the U.S. cable business is so lucrative, “never before has a French company made such an important investment in the country of Uncle Sam.”
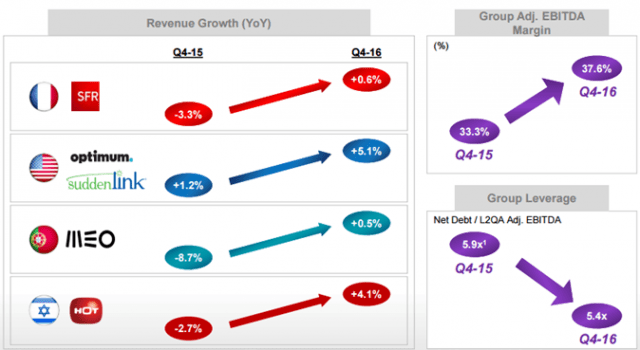
Suddenlink and Cablevision: Consistent source for fat revenue growth for Altice.
Drahi told investors more than a year ago he wanted to eventually generate 50% of Altice’s business overseas, primarily in the profitable U.S.
Altice has so far only bought up smaller cable operators, but observers expect Drahi will aim for much larger targets, including the possibility of buying out a wireless provider or even targeting Comcast, AT&T, or Charter. Les Echos quotes Vincent Maulay, an analyst at Oddo who notes that Drahi may be able to collect future assets inexpensively if Verizon decides to move on an acquisition of Charter. Regulators will likely force the combined company to shed cable assets in New York State where Verizon and Charter currently compete. That would allow Drahi’s Cablevision to pick up divested service areas, perhaps even in Manhattan.
 Reuters is reporting the Republican-dominated Federal Communications Commission has reversed a pro-consumer mandate requiring Charter to overbuild at least one million homes to offer competitive internet service. The requirement was imposed on Charter Communications as part of the FCC’s approval of its merger deal with Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks in 2016.
Reuters is reporting the Republican-dominated Federal Communications Commission has reversed a pro-consumer mandate requiring Charter to overbuild at least one million homes to offer competitive internet service. The requirement was imposed on Charter Communications as part of the FCC’s approval of its merger deal with Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks in 2016.

 Subscribe
Subscribe