 T-Mobile USA and Sprint have agreed to a $26.5 billion all-stock merger, creating the second largest wireless company in the country with 70 million customers, rivaled only by larger Verizon Wireless with 111 million customers and potentially-third-place AT&T with 78 million.
T-Mobile USA and Sprint have agreed to a $26.5 billion all-stock merger, creating the second largest wireless company in the country with 70 million customers, rivaled only by larger Verizon Wireless with 111 million customers and potentially-third-place AT&T with 78 million.
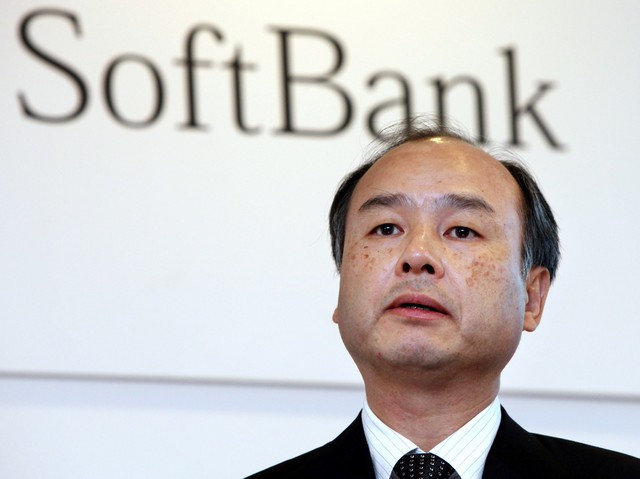
The merged company will keep the T-Mobile name and its maverick CEO, John Legere. The board will include SoftBank CEO Masayoshi Son, who took control of Sprint several years ago but failed to change its status as the fourth largest carrier in the country.
“This combination will create a fierce competitor with the network scale to deliver more for consumers and businesses in the form of lower prices, more innovation, and a second-to-none network experience – and do it all so much faster than either company could on its own,” Legere said in the statement.
T-Mobile’s owner, Deutsche Telekom, will control 42% of the company, with SoftBank retaining a 27% ownership stake.
This is the third time Masayoshi has attempted a merger of Sprint and T-Mobile, first failing over regulators’ antitrust/anti-competition objections during the Obama Administration, and a second time over arguments about which company would ultimately control the merged operation.
Wall Street is likely to applaud the deal because of the major cost savings the merger would bring. Tens of thousands of job losses are likely at both companies, delivering significant savings. Sprint has already slashed its workforce from 40,000 in 2011 to fewer than 28,000 today in a series of cost cutting moves. T-Mobile is bloated by comparison, with 50,000 employees as of 2017, leaving much room for layoffs. Overlapping coverage areas could also be consolidated to reduce equipment and cell tower expenses.
Investors are also concerned about the future rollout costs of 5G wireless technology. Reducing the number of competitors offering the service would allow for higher prices and faster return on investment. But company officials are promoting the merger with claims it will accelerate the deployment of 5G networks and attract new investment. Both companies have complained about profit-draining competition, so removing one competitor to leave just three national choices for wireless service will allow carriers to boost prices and ease price wars. Executives have also worried that as the wireless marketplace gets saturated with smartphones for everyone, growing the business in the future has become a major challenge.

Legere
Consumer groups are reading between the lines of the business case for the merger and argue the reduced competition that will result will lead to higher prices, less aggressive competition and upgrades, and big layoffs. Most observers expect activists will seek to block the merger on anti-competition grounds.
“Unlike good wine or a good movie, this long-rumored deal only gets worse with age and repeat viewings. No one but T-Mobile and Sprint executives and Wall Street brokers wants to see this merger go through. Greed and a desire to reach deeper into people’s wallets by taking away their choices are the only things motivating this deal,” said Free Press policy director Matt Wood. “What we know about the wireless market is that customers actually win when mergers are blocked. That market has been relatively competitive in recent years, but only because the FCC and DoJ signaled they would block AT&T’s attempted takeover of T-Mobile in 2011, along with T-Mobile and Sprint’s several previous attempts to combine.”
Wood notes that because of fierce competition from Sprint -and- T-Mobile, their larger rivals AT&T and Verizon have been forced to reintroduce popular unlimited data plans, cut prices, and get rid of onerous multi-year service contracts.
“The notion that this deal would produce better wireless services is a flat-out fiction. We’ve seen the results from the tax cuts and other destructive deregulation in the Trump era,” Wood added. “The combined entity here would just use this deal to line its own pockets, pay down the massive debt these companies carry, and reward shareholders with more stock buybacks. It would fund further acquisitions of content companies, too, as wireless carriers like Verizon and AT&T rush to join the race for targeted advertising revenues built on privacy abuses like those already built into Facebook’s and Google’s ad models.”
So far, the Trump Administration’s record on mergers is mixed. The Justice Department has shown surprising resistance to blockbuster corporate telecom mergers, and is currently suing AT&T and Time Warner, Inc. to unwind their merger proposal. But Trump’s FCC has bent over backwards in favor of mergers involving the administration’s political allies, notably Sinclair Broadcast Group’s local station acquisitions which have received favorable treatment from FCC Chairman Ajit Pai.
“The legal standard for approving giant horizontal mergers like this is not whether Wall Street or President Trump and his cronies likes it. Communications mergers must enhance competition and serve the public interest,” said Wood. “This deal would do just the opposite: It would destroy competition, eliminate jobs and harm the public in numerous irreversible ways. So unless Ajit Pai wants wants to add yet another blemish to his already disastrous tenure at the helm of the FCC, the chairman should speak out and show us he’s willing to do more than rubber stamp any harmful deal that crosses his desk.”
The merger is expected to get significant regulatory scrutiny.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Charter Communications’ takeover of Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks has not proved popular, according to a new survey from Temkin Group.
Charter Communications’ takeover of Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks has not proved popular, according to a new survey from Temkin Group. This marks the eighth year Temkin has published its Temkin Experience Ratings, generated from compiling the results of a survey of 10,000 U.S. consumers about their recent interactions with 318 significant U.S. companies. Temkin measures three dimensions of a customer’s experience:
This marks the eighth year Temkin has published its Temkin Experience Ratings, generated from compiling the results of a survey of 10,000 U.S. consumers about their recent interactions with 318 significant U.S. companies. Temkin measures three dimensions of a customer’s experience: Charter Communications is taking the city of El Centro, Calif., to federal court for interfering in a dispute between Spectrum and a local TV station owner that has resulted in two stations being blacked out on the local cable system for nearly three months.
Charter Communications is taking the city of El Centro, Calif., to federal court for interfering in a dispute between Spectrum and a local TV station owner that has resulted in two stations being blacked out on the local cable system for nearly three months. “Northwest’s pulling its authorization for Charter to carry its broadcast signals is not a ‘service interruption’ within the meaning of the City Code provisions in question,” Charter argued in its lawsuit. “Even if it were, while El Centro demands that Charter ‘cure’ its alleged violations, the only means for Charter to do so is to finalize a retransmission agreement with Northwest. The City’s citations are thus intended to pressure Charter to accept Northwest’s unreasonable terms by imposing fines and intentionally damaging Charter’s reputation and harming its goodwill and relationships with its existing and prospective customers.”
“Northwest’s pulling its authorization for Charter to carry its broadcast signals is not a ‘service interruption’ within the meaning of the City Code provisions in question,” Charter argued in its lawsuit. “Even if it were, while El Centro demands that Charter ‘cure’ its alleged violations, the only means for Charter to do so is to finalize a retransmission agreement with Northwest. The City’s citations are thus intended to pressure Charter to accept Northwest’s unreasonable terms by imposing fines and intentionally damaging Charter’s reputation and harming its goodwill and relationships with its existing and prospective customers.” “Rather than negotiating in good faith like all other parties would do and what the law requires, Charter has taken a ‘take it or leave it’ approach,” added Brady. “In an effort this week to get this back on track, Northwest submitted a new proposal to Spectrum. Spectrum’s representative communicated that they really wanted to get this resolved, but would not counter Northwest’s proposal and would not respond at all in writing. Odd behavior for a company that claims to be negotiating in good faith. It appears that Charter would rather bully a small municipality than to engage in a good faith negotiation.”
“Rather than negotiating in good faith like all other parties would do and what the law requires, Charter has taken a ‘take it or leave it’ approach,” added Brady. “In an effort this week to get this back on track, Northwest submitted a new proposal to Spectrum. Spectrum’s representative communicated that they really wanted to get this resolved, but would not counter Northwest’s proposal and would not respond at all in writing. Odd behavior for a company that claims to be negotiating in good faith. It appears that Charter would rather bully a small municipality than to engage in a good faith negotiation.” “Despite the fact the fee is itemized and justified as a pass-through, Charter did not eliminate or reduce that fee, even though it was no longer incurring costs associated with carriage of … at least two network affiliates,” Crescent City officials told the FCC.
“Despite the fact the fee is itemized and justified as a pass-through, Charter did not eliminate or reduce that fee, even though it was no longer incurring costs associated with carriage of … at least two network affiliates,” Crescent City officials told the FCC. Nathan Gray woke up one morning this month and received an alarming notification from Comcast, his internet provider, claiming he had exceeded his Comcast
Nathan Gray woke up one morning this month and received an alarming notification from Comcast, his internet provider, claiming he had exceeded his Comcast  “Today when I logged in, I had apparently used 196 GB yesterday,” Amaasing wrote. “196 GB in 24 hours? Seriously?”
“Today when I logged in, I had apparently used 196 GB yesterday,” Amaasing wrote. “196 GB in 24 hours? Seriously?”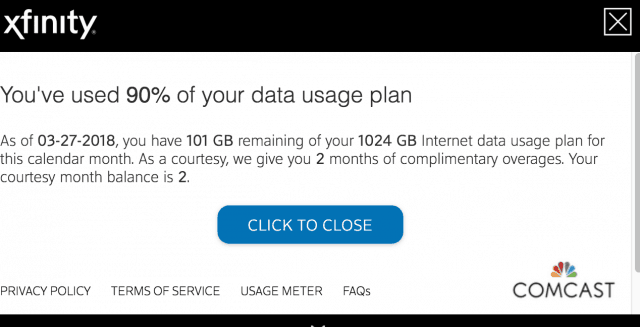 After “courtesy months” expire, you are on the hook for whatever excess usage Comcast determines you have consumed. Some Comcast customers assume the courtesy month counter resets each calendar year, but in fact it only resets after 12 consecutive months of staying within your allowance limit.
After “courtesy months” expire, you are on the hook for whatever excess usage Comcast determines you have consumed. Some Comcast customers assume the courtesy month counter resets each calendar year, but in fact it only resets after 12 consecutive months of staying within your allowance limit.
