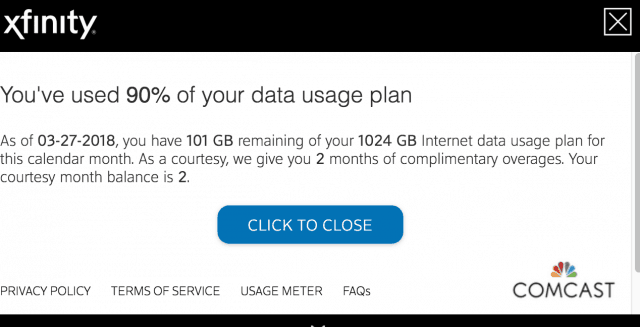
 Comcast has put its proverbial finger to the wind to define an “appropriate” data cap it declares “generous,” regardless of how subjectively random that cap happens to be. Although 1,000 GB — a terabyte — usage allowance represents a lot of internet traffic, more and more customers are finding they are flirting with exceeding that cap, and Comcast has never been proactive about regularly adjusting it to reflect the reality of rapidly growing internet traffic. That means customers must protect themselves by checking their usage and take steps if they are nearing the 1 TB limit.
Comcast has put its proverbial finger to the wind to define an “appropriate” data cap it declares “generous,” regardless of how subjectively random that cap happens to be. Although 1,000 GB — a terabyte — usage allowance represents a lot of internet traffic, more and more customers are finding they are flirting with exceeding that cap, and Comcast has never been proactive about regularly adjusting it to reflect the reality of rapidly growing internet traffic. That means customers must protect themselves by checking their usage and take steps if they are nearing the 1 TB limit.
If you do exceed your allowance, Comcast will provide two “grace periods” that will protect you from overlimit fees, currently $10 for each extra 50 GB allotment of data you use. Another alternative Comcast will happily sell you is an insurance policy to prevent any risk of overlimit fees. For an extra $50 a month, they will take the cap off your internet plan allowing unlimited usage. But $50 a month is close to paying for your internet service twice and is indefensible considering how little Comcast pays for its customers’ internet traffic. It is just one more way Comcast can pick up extra revenue without doing much of anything.
Customers that do regularly break through the 1 TB data cap often have a guilt complex, believing they have no right to complain about data caps and should pay more because they must cost Comcast a lot more money to service. In fact, Time Warner Cable executives broadly considered internet traffic expenses as little more than a “rounding error” to their bottom line, according to internal emails obtained by the New York Attorney General’s office. Managing customers’ data usage is far less costly than network plant upkeep, the regularly increasing costs of video content, and expenses related to expanding service to new locations.
One VentureBeat reader investigated what chewed through Comcast’s data allowance the most, and it wasn’t easy:
Xfinity pretends to make this easier for you, but that’s a load of horsesh*t. Its X-Fi app claims to give you usage stats for your connected devices — only nothing appears up-to-date. The phone I was using to look at the X-Fi app doesn’t even appear on the connected-devices list. You also have to look at each device individually. I saw no way to sort a list of devices by data usage, which would obviously help a lot.
Some of the biggest data users are connected households, where multiple family members use a range of devices, often at the same time. Customers with multiple internet-connected computers, video game consoles, and streaming devices are most at risk of exceeding their cap.
 Video Games Consoles/PCs
Video Games Consoles/PCs
The biggest data consumption does not come from gameplay itself. It comes from frequent software updates, some exceeding 50 GB. If you play a number of games, updates can come frequently. In the case of the VentureBeat author, 17% of daily usage came from the home’s primary desktop PC. Another 12% was traced to the family’s Xbox One. An in-home media server that also runs Steam and auto-updates frequently was also suspect.
Streaming Devices
If you are not into video games and do not depend on cloud storage or large file transfers to move data back and forth, streaming set-top boxes and devices are almost certainly going to be the primary source of your biggest monthly data usage. Video resolution can make a difference in how much data is consumed. If you are regularly approaching or exceeding your monthly cap, consider locking down maximum video resolution for streaming on large televisions to 720p, and 480p for smartphones. Some streaming services offer customized resolution options in their settings menu.
Autoplay, also known as the ‘binge’ option can also consume a lot of video when a service automatically starts playback of the next episode in a series. Some people switch off their televisions without stopping video playback, which can mean you watched one episode but actually streamed six or more. Check the streaming software for an option to not autoplay videos.
Remember that cable TV replacements like DirecTV Now and YouTube TV will continue streaming live broadcasts until you stop them. Do not just switch off the television. Many live/linear TV apps will prompt you every few hours if you have not changed channels to make sure there is someone still watching. If you do not respond, streaming will stop automatically.
Cloud Storage Backups
When customers report staggering data usage during a month, cloud storage backup software is often the culprit. If you are new to cloud storage backup services like Dropbox or Carbonite, your PC may be uploading a significant part of your hard drive to create a full backup of your computer. This alone can consume terabytes of data. Fortunately, most backup services throttle uploads and do not automatically assume you need to backup your entire hard drive. Many offer options to limit upload speed, the total amount of data that can be uploaded each month, and options to selectively backup certain files and folders.
Your Wi-Fi Network is Insecure
In areas where data caps are pervasive, those who want to use a lot more data and do not want to pay for it may quietly hop on your home Wi-Fi network and effectively bill that usage to you. This is most common in large multi-dwelling units where lots of neighbors are within range of your home Wi-Fi. The best way to reduce the risk of a Wi-Fi intrusion is to create a password that is exceptionally difficult to guess, using a mixture of special characters (!, ^, %, etc.) and mixed case random letters and numbers. Although this can be inconvenient for guests, it will probably keep intruders out and prevent them from running up your bill.
It is unfortunate customers have to jump through these kinds of hoops and compromise their online experience. But where cable and phone companies lack competition, they can charge a small fortune for internet access and still feel it is appropriate to cap usage and ask for even more money when customers “use too much.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe Starry, Inc., a fixed wireless internet provider, this week
Starry, Inc., a fixed wireless internet provider, this week  Cable One has the highest average revenue per customer of any publicly traded cable company in the United States, with
Cable One has the highest average revenue per customer of any publicly traded cable company in the United States, with 
 Charter Spectrum’s broadband-only customers run up more than double the amount of broadband usage average customers subscribing to both cable TV and broadband use, and that consumption is growing fast.
Charter Spectrum’s broadband-only customers run up more than double the amount of broadband usage average customers subscribing to both cable TV and broadband use, and that consumption is growing fast.
