 This isn’t going to be your parent’s HBO much longer.
This isn’t going to be your parent’s HBO much longer.
In a recent town hall attended by 150 employees, AT&T laid out its new vision for the premium network it recently acquired. one almost similar at times to the business plan of a drug pusher.
“We need hours a day,” said John Stankey, a recent transplant from AT&T’s executive suites now tapped to run WarnerMedia — AT&T’s new name for what used to be Time Warner (Entertainment) and owner of HBO. Stankey was complaining that HBO was out of touch with the times, attracting too few viewers to its multiplex of premium channels only a handful of times a week, if that. In a world shared by Netflix, that was not nearly good enough.
HBO, which began life as Home Box Office in November, 1972 is by far America’s oldest cable television channel. Originally a venue for high profile, unedited, commercial-free movies, along with sports and specials, HBO grew into a well-respected producer of high budget (often millions of dollars per episode), cutting-edge original movies and series, showcased to loyal audiences on Sunday nights for years. Series like The Wire, The Sopranos, Sex in the City, Oz and Game of Thrones are well-known across the country, but fewer than half of Americans subscribe to HBO to watch them. HBO has also been the critics’ choice for original content, showering awards on the network in unprecedented numbers for almost 20 years.
Now that AT&T is in charge, that is all about to change, as executives prepare to shift HBO away from “quality over quantity” towards “quality and quantity.” Stankey also made it clear the changes are first and foremost about making money — a lot of it earned by keeping subscribers on HBO property so their viewing habits can be studied and sold.
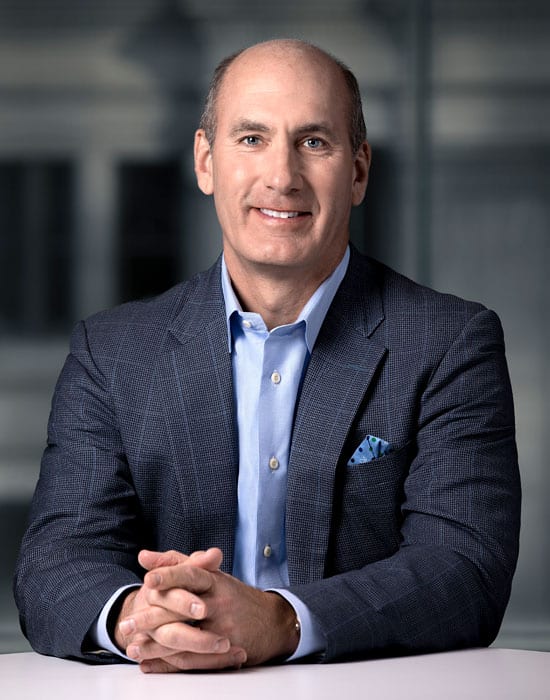

Stankey
“It’s going to be a tough year,” Stankey warned. “It’s going to be a lot of work to alter and change direction a little bit.”
“It’s not hours a week, and it’s not hours a month,” Stankey said of how long he expects HBO subscribers to spend time watching the service. “It’s hours a day. You are competing with devices that sit in people’s hands that capture their attention every 15 minutes. I want more hours of engagement. Why are more hours of engagement important? Because you get more data and information about a customer that then allows you to do things like monetize through alternate models of advertising as well as subscriptions, which I think is very important to play in tomorrow’s world.”
That will be a major shift for a network overseen top to bottom since 1992 by Richard Plepler, HBO’s chief executive. Plepler expanded on HBO original movies by launching expensive scripted series in the late 1990s that stood out by escaping broadcast television network censorship. But Plepler was very selective about the number of shows on HBO’s schedule, with some series taking years to develop. Under Stankey’s leadership, HBO will now be expected to dramatically expand original content, much like Netflix has done to keep viewers coming back for more.
“As I step back and think about what’s unique about the brand and where it needs to go, there’s got to be a little more depth to it, there’s got to be more frequent engagement,” Stankey said, adding HBO’s brand has to broaden its appeal to new audiences.
That will require a big boost to HBO’s budget. The pay movie channel is already extremely profitable, making almost $6 billion in profits over the last three years. It invested $2 billion in programming development, much less than the $8 billion Netflix is investing in less costly, but more prolific programming. HBO’s business plan depends heavily on American cable subscribers paying $10-15 a month for the network. It also earns money selling its original shows to television outlets in other countries. Its high monthly cost has always limited subscriber numbers, especially these days with cord-cutting and bill shaving. Premium movie channels are often the first networks to be dropped in return for a lower bill.
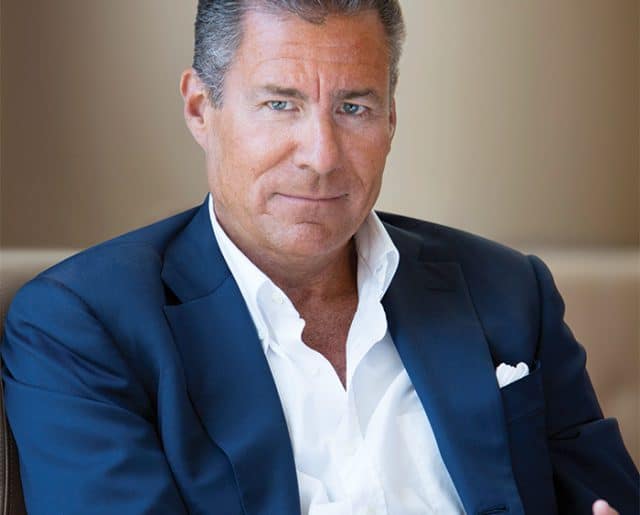

Plepler
To monetize its subscriber base, HBO either has to cut the cost of the network, transform it into must-have television, or a combination of both. Stankey is unhappy HBO has wavered around 40 million subscribers (out of 142 million American potential households) for years. He told audiences the network has to find ways to move the network beyond its perpetual 35-40% penetration “to have this become a much more common product.”
There was a clear sense of tension between Plepler, who is part of the New York City entertainment scene, and Stankey, a business-focused Texan with decades of experience in the Bell System — later AT&T. Plepler’s deference to Stankey’s new vision seemed uncomfortable at times, as Stankey made it clear who was now in charge:
Stankey: “We’ve got to make money at the end of the day, right?”
Plepler: “We do that.”
Stankey: “Yes, you do, just not enough.”
Plepler’s clearly defined tenure and vision at HBO had not wavered much since taking over in the early 1990s. But that vision was nervously discarded almost immediately as Stankey looked on.
“I’ve said, ‘More is not better, only better is better,’ because that was the hand we had,” Plepler explained. “I’ve switched that, now that you’re here, to: ‘More isn’t better, only better is better — but we need a lot more to be even better.’”
As a result, HBO, which used to be the darling of critics and well-to-do viewers in big cities on the east and west coast is getting a radical makeover. Onlookers can expect a much more aggressive marketing effort and free samples of the service to attract and hold new customers. It will have to keep its pricing closer to the competition, particularly as many consumers already subscribe to 1-2 different streaming services. Then it will have to give people a reason to subscribe to just one more service.
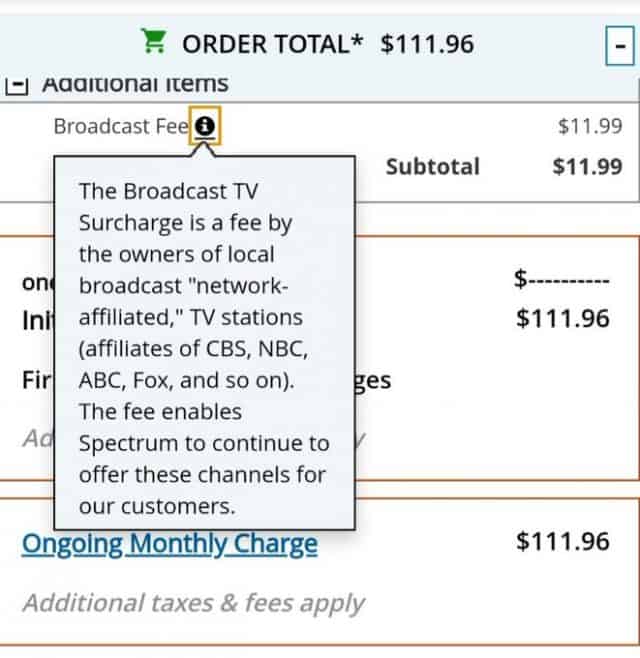 For the last several years, cable subscribers have lamented that the advertised price of service falls short of the real “out-the-door” cost shown on one’s monthly bill.
For the last several years, cable subscribers have lamented that the advertised price of service falls short of the real “out-the-door” cost shown on one’s monthly bill.

 Subscribe
Subscribe This isn’t going to be your parent’s HBO much longer.
This isn’t going to be your parent’s HBO much longer.

 Viacom and Charter Communications today announced a multi-year renewal of a carriage agreement that will bring back Viacom’s cable networks to almost all Spectrum cable television customers.
Viacom and Charter Communications today announced a multi-year renewal of a carriage agreement that will bring back Viacom’s cable networks to almost all Spectrum cable television customers. Charter indicated its agreement allows Spectrum to keep other Viacom-owned networks not mentioned above on its Silver or Gold tiers. The agreement also grants Charter customers access to Viacom networks’ on-demand programming through set-top boxes or mobile apps.
Charter indicated its agreement allows Spectrum to keep other Viacom-owned networks not mentioned above on its Silver or Gold tiers. The agreement also grants Charter customers access to Viacom networks’ on-demand programming through set-top boxes or mobile apps.

