 A Washington state man who just moved into his new home is now being forced to consider selling it to somebody else because Comcast repeatedly misled him about its ability to provide service.
A Washington state man who just moved into his new home is now being forced to consider selling it to somebody else because Comcast repeatedly misled him about its ability to provide service.
Seth told his extensive story to The Consumerist, which detailed his repeated attempts to get Comcast broadband service after multiple missed or unfinished service appointments. More importantly, Seth is representative of many Americans who have been told broadband is a fiercely competitive industry, yet they cannot sign up for service at a reasonable price from any provider.
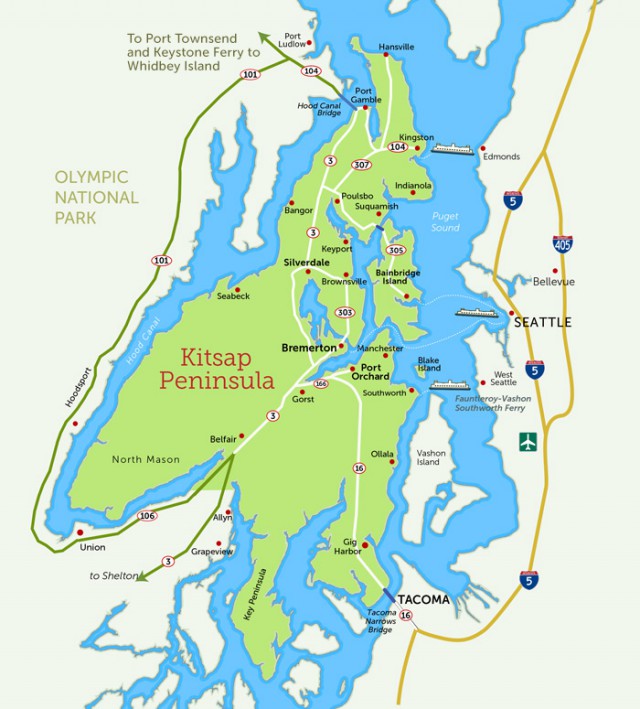
For Seth, having reliable broadband service is not just a convenience — it is essential if he wants to stay employed. Before even considering making an offer on his new home in Kitsap County, Seth did his homework verifying Comcast provided service in the neighborhood. Comcast repeatedly assured him it did, and one sales rep confirmed a former resident at the same address had Comcast service. Seth was satisfied, bought the home and called to get Comcast service installed. But when a Comcast crew arrived Jan. 31, they quickly discovered there was no cable line strung to Seth’s property. That isn’t typically a deal-breaker and the techs completed a “drop bury request” that would normally result in the arrival of a Comcast cable burial crew to bring service from a nearby utility pole. Not this time.
Comcast determined the same home that its own sales rep promised used to have Comcast service was now suddenly too far away from Comcast’s infrastructure. If it decided to offer Seth service, the company quoted an installation fee approaching $60,000.
Seth consulted the FCC’s Broadband Map which depicted Kitsap County a veritable paradise of competition, with at least 10 providers fighting for his business. But Seth quickly realized the FCC’s map was misleading and inaccurate.
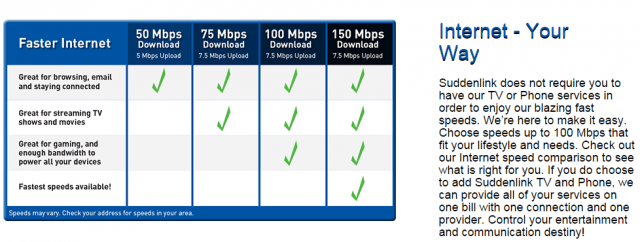
 Four of his options were wireless carriers that don’t provide a strong signal to his home or charge obscenely high prices for usage capped Internet access. ViaSat was on the list promising up to 25Mbps, but ViaSat satellite customers can testify the actual speeds received are much slower, and do not reliably support the VPN access Seth required.
Four of his options were wireless carriers that don’t provide a strong signal to his home or charge obscenely high prices for usage capped Internet access. ViaSat was on the list promising up to 25Mbps, but ViaSat satellite customers can testify the actual speeds received are much slower, and do not reliably support the VPN access Seth required.
Neither Comcast or CenturyLink offer broadband service to Seth, despite the fact both told the FCC they did for the purpose of its map. StarTouch uses microwave signals to reach its customers, but not in Seth’s part of Kitsap County. It seems someone put up a large building in between StarTouch’s transmission facilities and Seth’s home, blocking the service for a significant part of the county.
XO Communications does provide reliable T1 service to businesses at speeds from 1.544Mbps – 6Mbps. The biggest downside is its cost — $600 a month. Finally, Seth’s only other alternative is a gigabit fiber network run by the Kitsap Public Utility District. But cable companies like Comcast effectively lobbied to guarantee those types of networks would never be a competitor by pushing for laws that forbid retail service to individual homes or businesses. In Washington, the law only allows the utility district to sell wholesale access to its network to companies like… Comcast.
In the end, Comcast decided it wasn’t interested in serving Seth even if he found the $60,000 to cover the installation fee. CenturyLink shrugged its shoulders over why it isn’t offering DSL in Seth’s neighborhood. Seth is preparing to put his home back on the market. It’s a perfect choice for Luddites everywhere.
The moral of the story?
- Comcast is not always forthcoming and honest when signing up customers and led Seth through two months of missed appointments and misinformation;
- The accuracy of the FCC’s broadband availability map is questionable.


 Subscribe
Subscribe


 Greenlight Networks, a fiber overbuilder serving select neighborhoods in the greater Rochester, N.Y. area, today announced it was cutting the price of its gigabit broadband offering by 60 percent.
Greenlight Networks, a fiber overbuilder serving select neighborhoods in the greater Rochester, N.Y. area, today announced it was cutting the price of its gigabit broadband offering by 60 percent.