 CenturyLink is ready to capitulate in its competitive war with the cable industry, conceding its residential broadband business is a money loser that will no longer get broad-based upgrades and investment under the management of incoming CEO Jeff Storey, who will refocus CenturyLink on its larger business/enterprise customers.
CenturyLink is ready to capitulate in its competitive war with the cable industry, conceding its residential broadband business is a money loser that will no longer get broad-based upgrades and investment under the management of incoming CEO Jeff Storey, who will refocus CenturyLink on its larger business/enterprise customers.
The independent phone company has sent strong signals it is going to focus only on residential customers that are cheapest and easiest to reach, promising to fund broadband urban and suburban upgrades only where costs are low and the chances of a significant return is high. In rural areas, CenturyLink will depend heavily on capital made available by the FCC’s Connect America Fund when choosing areas worthy of upgrades.
“We’ll focus more on return on investment, which includes rural capital from the CAF II program,” said Sunit Patel, CFO of CenturyLink.
Patel, along with CenturyLink’s incoming CEO, originally worked for Level 3 Communications, a business and enterprise internet company acquired by CenturyLink in 2016. Now top Level 3 executives, at the behest of Wall Street and shareholders, are gradually taking over the top management positions of CenturyLink, pushing out current CEO Glen Post III with an early retirement this spring. With Post leaving, there is clear evidence CenturyLink is embarking on a transformation away from low return residential phone and broadband service and towards the kind of high profit business and enterprise connectivity Level 3 has provided for years.
Wall Street increasingly sees CenturyLink’s residential business as costing the company a lot of money for network upgrades that simply don’t deliver shareholder expectations of return on that investment, especially as the cable industry continues to aggressively deploy faster speed service to its customers.
In the fourth quarter of 2017, CenturyLink lost another 105,000 broadband subscribers, bringing internet subscriber numbers down to around 5.7 million nationwide. That represents a 4.8% reduction year over year, despite repeated promises of upgrades to stem those customer losses.
Last November, Post blamed those losses on customers served by CenturyLink’s legacy copper/DSL service areas where speeds and performance are lowest.

Soon to be CenturyLink Ex-CEO and President Glen F. Post
“We saw a much higher than expected loss of customers at the 20 Mbps and below speeds in a lot of the markets where we have that,” Post said during a late fall earnings call, according to a Seeking Alpha earnings transcript. “We had a much higher loss there. I think a couple of reasons, first of all, you see cable rolling out more with more aggressive offers, higher speeds and just the demand for bandwidth in those markets.”
Last fall, Post emphasized his broad-based residential and commercial broadband upgrade transformation plan to stop those losses. Post committed CenturyLink would provide 90% of homes with at least 40 Mbps, 70% of homes and businesses with 100 Mbps and over 20% with 1 Gbps or higher no later than 2020.
That was before activist shareholders and Wall Street joined forces to successfully push CenturyLink’s board to replace Post with business-oriented Level 3 CEO Jeff Storey. CenturyLink stock had been down by about one-third of its value over the last nine months, which only aggravated investors to push harder for dramatic management changes at the phone company. Activists argued CenturyLink shouldn’t be devoting much attention to its legacy businesses. In their eyes, only “strategic/success” businesses are worthy of investment, and those include commercial and enterprise broadband, metro ethernet, and cloud/backup services. The revenue eating “legacy” businesses, namely residential landline and DSL service, represent a drain on profits and threaten the company’s shareholder dividend. About two-thirds of CenturyLink customers are commercial enterprises.
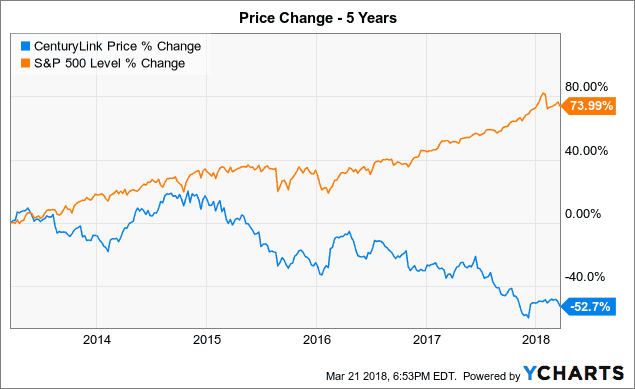
(Blue) CenturyLink (Orange) Level 3
On March 6, 2018 the company announced Post’s retirement effective the day of its annual shareholder meeting in May. Post had originally planned to leave at the end of 2018, but some shareholders were unwilling to wait that long.
Strategic changes in CenturyLink’s future were previewed at the Morgan Stanley Technology, Media & Telecom conference earlier this month, where Patel outlined the company’s new vision.
“On the consumer side, the focus will be on enabling higher broadband speeds,” Patel said, but added a caution. “We won’t be spending capital on 5-20 Mbps connections, but rather on 100 Mbps and higher speeds. In urban areas we want to make sure we’re spending the capital where the returns make sense so focusing on multi-dwelling units make more sense in urban areas.”
Since the company is now going to target upgrades only in areas that “make more sense,” Post’s goal of better broadband for all by 2020 seem doomed
Another key piece of evidence is the retirement of CenturyLink executive Duane Ring, who announced he is leaving after 34 years despite a recent promotion. Ring, who led CenturyLink’s 12-state midwest region, was also behind much of CenturyLink’s residential broadband enhancement effort, including the 2005 launch of Prism TV — CenturyLink’s cable-TV alternative, as well as deploying gigabit speed services in several midwestern states. In 2016, he oversaw the deployment of 500 Mbps service for multi-dwelling units in 44 Platteville, Wisc. buildings that included nearly 800 apartments.
Broadband industry analyst Dave Burstein already sees the writing on the wall.
“Their fiber and G.fast plans, modest already, have been cut,” he noted. “They simply aren’t competitive with cable, which by 2020 will have a gigabit to 90% [of customers]. I look at the network and say if they don’t cut the dividend, trouble is near. Depreciation was $3 billion more than capex the last three years. Dividends were higher than income.”
As cable broadband speeds increase and customers defect from CenturyLink, few may choose to come back, making investments in broadband upgrades even more questionable.
“The rumor is they will virtually abandon much of the wireline network,” Burstein noted. “They will temporarily draw cash out to upgrade where they have better prospects,” referring to areas Patel identified as worthy targets for upgrades.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 “I shouldn’t have been surprised to learn industry completely re-wrote proposed broadband legislation to their favor as a ‘substitute bill’ in legislative committee today,” Orr wrote on her Facebook page on Feb. 19. “The substitute bill is substantially different than the original bill. And it wasn’t posted online or anywhere for anyone except insiders to have access to. CenturyLink and Spectrum are bullies. It’s wrong, and they are hurting Cheyenne and other Wyoming communities from gaining affordable access.”
“I shouldn’t have been surprised to learn industry completely re-wrote proposed broadband legislation to their favor as a ‘substitute bill’ in legislative committee today,” Orr wrote on her Facebook page on Feb. 19. “The substitute bill is substantially different than the original bill. And it wasn’t posted online or anywhere for anyone except insiders to have access to. CenturyLink and Spectrum are bullies. It’s wrong, and they are hurting Cheyenne and other Wyoming communities from gaining affordable access.” CenturyLink Stream, the phone company’s planned nationwide alternative to cable television, will shut down its streamed package of nearly 50 channels on March 31.
CenturyLink Stream, the phone company’s planned nationwide alternative to cable television, will shut down its streamed package of nearly 50 channels on March 31.

 Despite claims from some industry-backed researchers and former members of Congress that Net Neutrality
Despite claims from some industry-backed researchers and former members of Congress that Net Neutrality 
