 Spectrum Mobile customers who sign up for cell service can expect an inquiry about their creditworthiness, and some customers with near-perfect FICO scores are embarrassed to discover Spectrum considers them too risky, thanks to an Experian credit scoring model developed specifically for utilities, phone and cable companies.
Spectrum Mobile customers who sign up for cell service can expect an inquiry about their creditworthiness, and some customers with near-perfect FICO scores are embarrassed to discover Spectrum considers them too risky, thanks to an Experian credit scoring model developed specifically for utilities, phone and cable companies.
When you inquired about our device(s) and mobile service(s), we evaluated your credit score of 797 and determined we can only offer you a limited number of our available devices for purchase.
This decision was made solely by Spectrum Mobile though such decision was based on the information supplied by Experian, a consumer reporting agency. The terms we are offering may be less favorable than the terms offered to customers who have a better credit score. Experian will not be able to provide you with any information relating to Spectrum Mobile’s decision or any other Spectrum policies, devices, and/or services.
In practical terms, the letter means this Reddit contributor will be limited to just one line of service on his account.

Spectrum Mobile is relying on a special credit risk management product to score its customers. The TEC Connect 2.0™ “risk model” stands for “T”elecommunications, “E”nergy, and “C”able, and was created exclusively for utility and telecommunications companies. It was designed to predict the likelihood you will pay utility and cable bills on time and in full. During times of economic distress, telecom and energy bills often get paid later than mortgages, auto loans, and credit cards. Still, with a score range of 400-900, the recipient’s 797 ranking represents a low credit risk, probably undeserving of a one line limit.
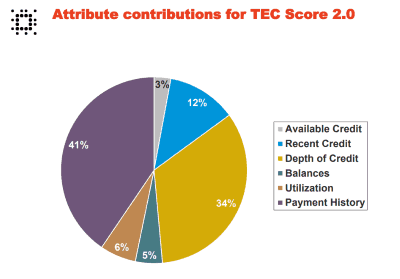
What counts the most towards your TEC Score?
Experian cited four adversities on this individual’s TEC Connect 2.0 report:
00011 – The date you opened your oldest joint revolver is too recent
00070 – Lack of sufficient relevant real estate/HELOC account information
00003 – Credit amount on your open first mortgage account is too low
00058 – Your most recently opened account is too new
That would seem to imply the customer is a relatively young borrower, or someone who closes older credit lines, which can count against your credit score. The report also seems to include conflicting information about any owned property and if it is mortgaged, which might mean the applicant is actually a renter. Recently opened credit accounts will diminish a TEC Score, and having a recent history of opening multiple new accounts could signal you are potentially over applying for credit or are overextended. Even if your FICO score reflects a good credit history, if you are a late-payer of energy or telecommunications bills, your TEC Score will reflect that and expose you to rejection of your application, line limits, and advance deposits.
Critics of Experian’s TEC Connect score note many utility companies do not report or report incomplete payment histories, many accounts are often missing from credit reports, and even those with perfect payment histories and a high FICO score can still run afoul of TEC Connect’s scoring model.
If you receive notice of an adverse credit decision, always take advantage of the opportunity to receive and review your report, free of charge. You are entitled to correct errors and have those corrections sent on to companies like Spectrum Mobile for a credit re-evaluation.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Charter Spectrum’s broadband-only customers run up more than double the amount of broadband usage average customers subscribing to both cable TV and broadband use, and that consumption is growing fast.
Charter Spectrum’s broadband-only customers run up more than double the amount of broadband usage average customers subscribing to both cable TV and broadband use, and that consumption is growing fast.
 Verizon Communications has indefinitely suspended plans to charge customers an extra $10 a month for access to Verizon’s extremely spotty and uneven 5G service, which launched earlier this month in Chicago and Minneapolis.
Verizon Communications has indefinitely suspended plans to charge customers an extra $10 a month for access to Verizon’s extremely spotty and uneven 5G service, which launched earlier this month in Chicago and Minneapolis. Verizon’s not-quite-ready-for-prime-time mobile 5G network hurriedly held a public launch event April 3rd using a small network of 5G millimeter wave small cells installed in downtown Chicago and Minneapolis, despite employee admissions there were significant issues with the network’s reliability, coverage, and stability.
Verizon’s not-quite-ready-for-prime-time mobile 5G network hurriedly held a public launch event April 3rd using a small network of 5G millimeter wave small cells installed in downtown Chicago and Minneapolis, despite employee admissions there were significant issues with the network’s reliability, coverage, and stability.
 Justice Department staffers have told T-Mobile and Sprint that their $26 billion merger is unlikely to win approval as presently structured, according to
Justice Department staffers have told T-Mobile and Sprint that their $26 billion merger is unlikely to win approval as presently structured, according to 