 Comcast’s discounted Internet service for the poor forces customers to jump through hoops to get the service and considers protecting revenue from existing customers more important than expanding the service to reach those who need it most.
Comcast’s discounted Internet service for the poor forces customers to jump through hoops to get the service and considers protecting revenue from existing customers more important than expanding the service to reach those who need it most.
Those are the views of John Randall, program manager at the Roosevelt Institute/Telecommunications Equity Project.
For $9.95 a month, those that can meet some complicated eligibility requirements and prove they are not existing Comcast customers are qualified for 3Mbps broadband service with a 768kbps upload rate. It represents a $30 savings off Comcast’s regular price — a considerable amount of revenue that Comcast is effectively forfeiting for the benefit of poor families who live in Comcast’s footprint.
Except Comcast isn’t actually “out” that much at all, argues Randall.
Of the 2.6 million households eligible for Internet Essentials from Comcast, only 150,000 have taken Comcast up on their offer. That represents only 5.8 percent of those eligible. In Comcast’s hometown — Philadelphia — there are just 3,250 families hooked up, which represents only 3.3 percent of those eligible.
Randall calls the program ineffective and says the onerous requirements to qualify (and re-qualify) are such a hassle, few families bother. What is worse, those families already sacrificing something else in their lives to get broadband service for the benefit of their school-age children are punished for their noble efforts — they are completely ineligible for Internet Essentials regardless of income or need because they are existing customers. Randall argues Comcast carefully constructed the program more as a public (and government) relations exercise than a charitable endeavor. Comcast zealously protects its existing revenues from being cannibalized by customers switching to the discount plan.
Some might argue that Comcast is managing the program with costs in mind, but Randall dismisses that as nonsense.
 “Within its footprint (which spans 50 million households in 39 states– 45 percent of the US population), the cost for Comcast to connect additional households is vanishingly low,” says Randall. “With no additional network build needed, Internet Essentials represents almost pure profit for Comcast.”
“Within its footprint (which spans 50 million households in 39 states– 45 percent of the US population), the cost for Comcast to connect additional households is vanishingly low,” says Randall. “With no additional network build needed, Internet Essentials represents almost pure profit for Comcast.”
Randall claims Comcast’s gross profit margin on its broadband service is around 95 percent where the network has already been built. At that rate, Comcast’s cheap Internet still delivers almost $18 million in additional income, and there is a promise of much more as soon as a customer defaults on a bill, misses a qualification deadline, or their children graduate. When any of these occur, Comcast will reset customers to regular rates.
“While most observers might assume that the program is an act of corporate generosity, it was originally conceived in the fall of 2009 as a way to turn a profit by offering slower connections to certain low-income households,” said Randall.
“These plans were temporarily tabled at the direction of Comcast lobbyist David Cohen, who knew that this type of program would be attractive to the FCC and thus useful as a bargaining chip. When the time came for negotiations over Comcast’s $13.75 billion takeover of NBC Universal, Comcast was able to offer something it was planning on doing anyway. In the end, the FCC was able to claim credit for forcing Comcast to implement a program to combat the digital divide, while in reality no arm-twisting was needed,” he added.
One of the biggest challenges of America’s digital divide is making affordable Internet access available. Cable companies in particular are prepared to wring even more money from their Internet customers in the form of higher prices, new and increasing equipment rental fees, and consumption billing schemes that charge more for less service.
But that isn’t the story elected officials receive from Congress.
The potential public relations benefits far outweigh any costs to offer the service. Randall notes Comcast had delivered the Internet Essentials message to over 100 members of Congress and more than 2,000 state and local officials. To broaden its outreach effort, Comcast also engaged leading intergovernmental associations at the state and local level such as the National Governors Association, National Conference of State Legislatures, U.S. Conference of Mayors, and various other organizations of elected officials. On top of that, Comcast says that the impressions generated by media coverage of Internet Essentials launch events earned it “millions of dollars” worth of media.
What message don’t these public officials hear?
America is subjected to local broadband monopolies and duopolies that guarantee the lack of competition for high-speed Internet access.
“It earns Comcast good press while distracting regulators and public officials into thinking that changes in policy aren’t needed and that digital divide problems will somehow work themselves out on their own as a result of corporate generosity. In the long run, Comcast Internet Essentials will do no more than contribute to the delay of much-needed regulation,” concludes Randall.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Verizon Wireless customers and public safety personnel are upset that the cell phone company was caught unprepared after a rural roaming agreement with AT&T expired at the end of June, leaving police officers without communications and others with no way to reach 911.
Verizon Wireless customers and public safety personnel are upset that the cell phone company was caught unprepared after a rural roaming agreement with AT&T expired at the end of June, leaving police officers without communications and others with no way to reach 911.
 After negative media coverage reported Verizon’s inability to provide quality cell service in rural Montana, the company agreed to temporarily deploy portable cell towers to improve coverage.
After negative media coverage reported Verizon’s inability to provide quality cell service in rural Montana, the company agreed to temporarily deploy portable cell towers to improve coverage.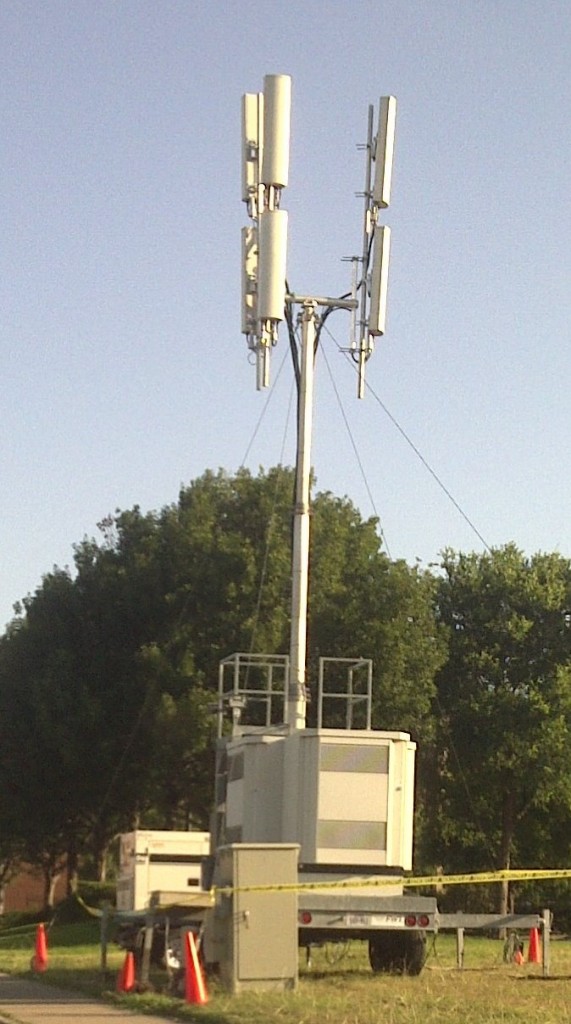



 Despite every effort by Verizon, Fire Island residents that lost landline service are increasingly opposed to Voice Link, if the public comments filed with the Commission are any indication.
Despite every effort by Verizon, Fire Island residents that lost landline service are increasingly opposed to Voice Link, if the public comments filed with the Commission are any indication.

