Frontier Communications CEO Maggie Wilderotter has bought a first class ticket to Fiber Fantasy Island, where phone companies dream of delivering fiber-optic broadband service without actually deploying fiber. They just tell you they did.
In an interview published today in The Oregonian, Wilderotter tries to convince residents Frontier’s arrival is good news, making promises about broadband and service improvements based on a company track record an independent observer would conclude she simply made up.
If Wilderotter’s command of the facts about her own company are reflective of “a distinct, improved image in its new territories,” Oregon is in big trouble.
Let’s review:
CLAIM: “We deploy fiber to the home all across the country. We don’t call it FiOS. We call it high-speed Internet. For our customers, the technology doesn’t matter. What matters is access, speed and capacity.”
REALITY CHECK: Frontier, as far as we have been able to determine, has not deployed fiber to the home anywhere in the country, with the exception of the FiOS network it acquired from Verizon. Frontier Communications’ deployment of fiber optics to the home is comparable to the amount of fiber found in a box of Cookie Crisp cereal. In their largest market, Rochester, N.Y., Frontier relies on the same legacy copper wire phone network it utilizes everywhere else. It is highly misleading for Wilderotter to represent otherwise. Fiber to the home means exactly that — fiber optic cable brought right to the home. This is not a case of “you call it corn, we call it maize.”
Fiber optic cable is not also known as “high-speed Internet,” just as the cute kitten on the left is not called an iguana. For the significant number of customers who ask Frontier to disconnect their service year-after-year, technology matters very much, and this particular phone company lacks it. Frontier relies on the same DSL technology other phone companies and customers increasingly consider yesterday’s news.
In many Frontier service areas, there is no access to broadband because line quality will not support the service. In Brighton, N.Y., a suburb of Rochester less than a minute from the Rochester city line, Frontier could only manage to deliver 3.1Mbps DSL speeds, and until recently Frontier was crying it needed a 5GB usage allowance because of the threat higher amounts of consumption might have on its network capacity. Access, speed, and capacity does matter, which is why Time Warner Cable is picking up the bulk of its new broadband subscribers at Frontier’s expense.
CLAIM: “For high-speed, it means having speed and capacity in addition to reach. We’ll do add-on services. We have a terrific Yahoo-Frontier portal that will be a gateway on our high-speed Internet service. We are in the throes of putting together Wi-Fi hotspots that will be distributed throughout this market for customers. If you’re a high-speed Internet customer of ours it’s free. We’re looking to put one at Hillsboro Stadium. Typically, we put them in hotels, convention centers, truck stops, trailer parks, outside parks, campuses for colleges, shopping centers, business campuses.”
REALITY CHECK: Those “add-on services,” such as Frontier’s Peace of Mind, come with a price tag and are often required components of a bundled service discount offer. As first impressions go, a company still relying on Yahoo! for a front end is not exactly on the cutting edge, nor are “portals.” It’s like trying to impress new customers with free web space through GeoCities. Actually, that is something Frontier could offer because GeoCities is now owned by Yahoo!
Frontier’s Peace of Mind Services
- Hard Drive Backup: $4.99 per month
- Hard Drive Backup + Unlimited Technical Support: $9.99 per month
- Hard Drive Backup + Unlimited Technical Support + Inside Wire Maintenance: $12.99 per month
- $50 early cancellation penalty if you get these services with a term commitment
Rochester’s experience with Frontier Wi-Fi has not been very impressive. Most residents don’t even know the service exists. The city and several suburbs offer limited Frontier pay-walled Wi-Fi service and a handful of free access hotspots in cooperation with Monroe County. Unfortunately, many of the fee-based and free hotspots have fallen into disrepair and no longer function. Signal strength is not impressive either, and many were not usable indoors. We tested several of the free hotspots and discovered one only delivered a signal into a suburban parking lot, another only into an empty soccer field, and the third was not functioning at all. Frontier’s record in Wi-Fi delivered more promises than actual service.
Those Wi-Fi services, by the way, are not free for all Frontier broadband customers. Evidently Ms. Wilderotter is not acquainted with her own company’s products and services, nor Frontier’s own website:
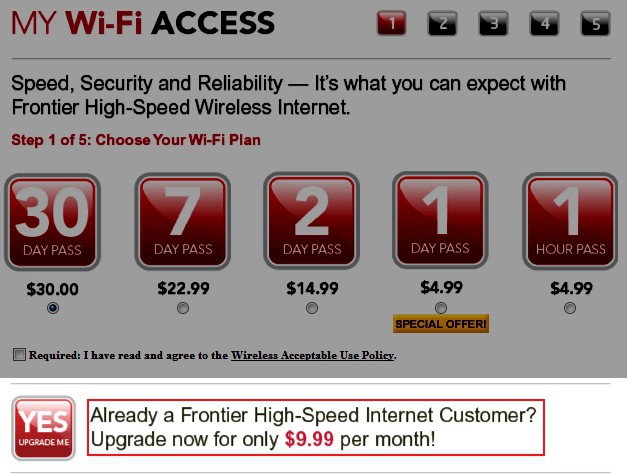
So much for Wilderotter's claim Frontier's Wi-Fi network was free for all Frontier broadband customers.
CLAIM: “We deliver the highest value for the price you pay. We also have excellent customer service. We also don’t raise our rates every 12 months, no matter what.”
REALITY CHECK: In Rochester, the out-the-door price Frontier charges its broadband customers is actually higher than that charged by Time Warner Cable, which delivers far faster connections. In West Virginia, the state’s Consumer Advocate put together a chart depicting Frontier’s broadband prices. Determine for yourself if it delivers the “highest value for the price you pay.”
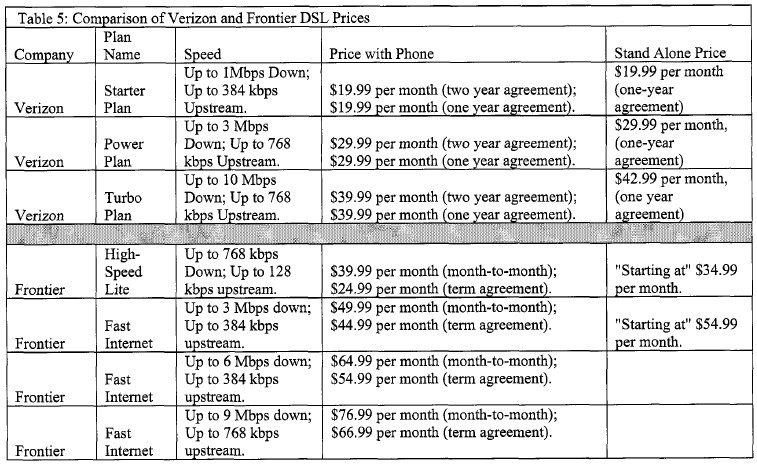
Comparing Prices: Frontier's pricing doesn't look as exciting as Wilderotter would have you believe, as the West Virginia Consumer Advocate discovered
CLAIM: “If I look across the board at our basic service pricing, I don’t think we’ve raised prices anywhere in the last four or five years.”
REALITY CHECK: We looked and found Frontier demanding the right to increase basic service rates in New York by $2 a month each year for up to two years. In fact, last November, the New York State Public Service Commission, at the request of Frontier, sent the company a letter authorizing a rate hike of $2 a month for customers in the state. Even more enlightening was Frontier’s filing in August 2005 with the PSC demanding near-complete deregulation and rate relief allowing Frontier to raise rates up to $1 per month annually indefinitely for basic service. Frontier also wanted consumer protection rules “relaxed” and ban the PSC from investigating consumer complaints. One of the reasons they cited is that basic phone service is not the same critical service it used to be because people can communicate through blogs instead.
In fact, consumers should be asking why Frontier’s rates haven’t decreased. From that same filing: “Frontier believes that with the decreasing costs and increasing bandwidths of new technologies and the acceleration of intermodal market entry, the market will cause rates for non-basic services in all parts of the State to decline.”
CLAIM: Local regulators tell me they did see a spike in billing complaints after Verizon took over. Any thoughts on why? — “Whenever there’s a change — you change the name on the bill, you change the format — customers tend to look at it more closely. We always expect a spike in billing calls whenever we’ve done acquisitions. It has already (settled out).”
REALITY CHECK: As Stop the Cap! has reported, Frontier’s takeover in West Virginia has hardly “settled out.” Service interruptions, forgotten service calls, and other problems have plagued the state to the point the PSC needed new hearings to review the situation. Many of Frontier’s billing complaints come from customers choosing to cancel Frontier service, only to find unjustified early termination fees added to their final bills, even when customers never agreed to a term contract. That problem was so serious in New York, the state Attorney General fined the company and ordered customer refunds. Changing a customer’s bill by adding $100 or more to the total amount due will always get a customer to look at the bill more closely.
CLAIM: “One of the big opportunities that we’re working on is the ability to display Internet content and video on the television set.”
REALITY CHECK: That “big opportunity” has been available to broadband users for several years now.
 CLAIM: We also have a new site that’s called myfitv.com. We carry over 100,000 titles of free television content on this site. It’s a little bit like Hulu on steroids. It’s provided free of charge to all our customers.
CLAIM: We also have a new site that’s called myfitv.com. We carry over 100,000 titles of free television content on this site. It’s a little bit like Hulu on steroids. It’s provided free of charge to all our customers.
REALITY CHECK: MyFitv is not “a little bit like Hulu on steroids.” In fact, it is Hulu. Frontier simply used Hulu’s “embed” feature to take content, slap the Frontier logo on it, and add Google ads in an attempt to rake in a few extra dollars. You can do exactly the same thing yourself. Meanwhile, the service is added to customer bills showing an amount of $0.00, a very inexpensive way to try and impress customers with content Frontier never developed, deployed, or created — just like their phantom fiber to the home network.
CLAIM: “We think over time the Internet will also provide different packaging, different prices, different ways to buy content than the traditional viewing platform. We also think that mobility is important. We want to make sure that whatever you do you’ll be able to take it with you. The Sling technology is interesting, too. It’s something we’re talking about DISH Network with.”
REALITY CHECK: Every time Maggie has talked about “different packaging and prices,” it has been in the context of an Internet Overcharging scheme — limited usage allowances, extremely high rate increases for those deemed to have consumed too much, etc. And yes, Sling technology is interesting. A company conceived of the idea, built it, developed a marketing plan, and sold it. That’s a concept Frontier needs to understand. You cannot transform a legacy network with words alone. Here’s an idea. How about conceiving of a real fiber-to-the-home network, build one, develop a marketing plan, and then sell it. For those in markets like Rochester, it’s the only way Frontier Communications will avoid becoming the horse and buggy carriage maker of the 21st century.
CLAIM: You’re around Seattle, around Portland, but not in them yet. Is there any possibility that Frontier would build into another company’s market? — “There’s always a possibility. It’s not a priority for us. And the reason why it’s not a priority is we’ve got a lot to do, just in the service areas that we own today. When I’m humming on all cylinders there, and I’ve been able to do everything I possibly can in those areas, then I might look to extend service areas out.”
REALITY CHECK: Translation — “when pigs fly.” Frontier would be laughed out of the Seattle and Portland markets.
Ms. Wilderotter needs to be a lot more open and forthcoming with the press. Frontier’s business plan makes it clear the company’s future is serving uncompetitive rural markets that will be forced to tolerate the products and pricing Frontier delivers. Where competition exists, let’s face facts. Frontier is not gaining market share — it is losing it, eroded away year after year by uncompetitive, substandard products at high prices.
That’s a reality you are bound to miss if you spend too much time with Mr. Rourke and Tattoo.


 Subscribe
Subscribe