
The next standard for cable broadband is now due by 2020.
CableLabs is working on the next generation of broadband over existing Hybrid Fiber-Coax (HFC) networks, finally achieving identical upload and download speed and supporting more spectrum on existing cable lines, which could mean another leap in broadband speed.
DOCSIS 4.0 is still evolving, but according to Light Reading, the next upgrade will fully support Full Duplex DOCSIS, allowing customers to get the same upload speed as their download speed, and will fully implement Low Latency DOCSIS which could reduce traffic delays to under 1 ms. The new standard will also introduce Extended Spectrum DOCSIS, which will open up broadband traffic on frequencies up to 1.8 GHz — 600 Mhz more bandwidth than available today. That additional spectrum will allow for speed increases in excess of 1 Gbps, support IP video traffic, and backhaul for wireless applications like small cells.
According to Light Reading, people familiar with the development of the cable broadband specification believe much of the work will be complete by the end of 2019, with the spectrum expansion specification expected before mid-2020. This would allow the introduction of DOCSIS 4.0 modems for purchase beginning in 2021.
Cable operators are largely taking a break on large investments this year, with few planning major infrastructure changes beyond some projects underway at Comcast and Altice-Cablevision’s ongoing replacement of its HFC network with fiber to the home service. In 2020, operators will make crucial decisions about their next upgrade commitments. Comcast and Altice will have the easiest time delivering symmetrical broadband because Comcast will support the “Node+0” design that eliminates amplifiers between the nearest node and the customer’s home. This will facilitate the introduction of symmetrical speeds. Altice is dropping the DOCSIS standard as it moves to fiber service, which already supports symmetrical speeds.
Other cable operators are not currently committed to removing amplifiers from their networks, supporting alternate designs like “Node+1,” “Node+2,” etc., which are similar to today’s cable system designs. Instead, they are hoping to leverage Extended Spectrum DOCSIS to boost their speeds. Most will likely offer significant speed bumps for uploading, but those speeds won’t match download speed. For example, Charter Spectrum or Cox might upgrade customers to 500/100 Mbps service, on the theory that 100 Mbps upload speed will still be a welcome change for customers, and not noticeably slower for most current applications, such as uploading videos or file storage in the cloud.
 Industry trade association NCTA reports that Comcast, Charter, Cox, Mediacom, Midco, Rogers (Canada), Shaw Communications (Canada), Vodafone (Europe), Taiwan Broadband Communications, Telecom Argentina, Liberty Global (Europe/Latin America) are all implementing the industry’s 10G initiative, with lab trials already underway, and field trials beginning in 2020. DOCSIS 4.0 will ultimately be a part of that project.
Industry trade association NCTA reports that Comcast, Charter, Cox, Mediacom, Midco, Rogers (Canada), Shaw Communications (Canada), Vodafone (Europe), Taiwan Broadband Communications, Telecom Argentina, Liberty Global (Europe/Latin America) are all implementing the industry’s 10G initiative, with lab trials already underway, and field trials beginning in 2020. DOCSIS 4.0 will ultimately be a part of that project.
CableLabs is already making plans for DOCSIS 4.1 (our name, not theirs), that will further extend DOCSIS spectrum up to 3 GHz — a massive upgrade in usable spectrum. Whether that will be technically plausible on aging cable systems last rebuilt in the 1990s isn’t known, and probably won’t be for two or more years. But if it proves technically feasible, DOCSIS 4.1 could be one of the last DOCSIS standards before cable systems consider abandoning HFC in favor of all-fiber networks.
CableLabs has proved itself to be adept at squeezing every bit of performance out of a network that was originally built with simple coaxial copper cable and designed to distribute analog TV signals. DOCSIS 4.1 would support speeds potentially as high as 25 Gbps downstream and 10 Gbps upstream. Customers would require new cable modems and cable systems would have to tighten standards to take aging infrastructure out of service more frequently. Upload traffic would likely be assigned spectrum below 1 GHz, with 1-3 GHz reserved for downloads. By then, television, phone, and internet services would likely all be a part of a single broadband pipe.
Cable systems have enjoyed enormous cost savings over the last 20 years deploying DOCSIS upgrades instead of scrapping their existing HFC networks in favor of all-fiber. Charter Spectrum admitted the cost to upgrade from DOCSIS 3.0 to DOCSIS 3.1 was just $9 per subscriber.
 AT&T today announced it was donating $500,000 to the non-profit group behind Locast, the online streaming service offering free access to local TV stations in more than a dozen U.S. cities.
AT&T today announced it was donating $500,000 to the non-profit group behind Locast, the online streaming service offering free access to local TV stations in more than a dozen U.S. cities.

 Subscribe
Subscribe CenturyLink’s stock is being pummeled after the company announced a cut in divided payouts to shareholders earlier this year, preferring to keep the money in-house to reduce debt and increase spending on necessary broadband upgrades.
CenturyLink’s stock is being pummeled after the company announced a cut in divided payouts to shareholders earlier this year, preferring to keep the money in-house to reduce debt and increase spending on necessary broadband upgrades. Investors were not impressed with those plans, and CenturyLink’s share price cratered.
Investors were not impressed with those plans, and CenturyLink’s share price cratered.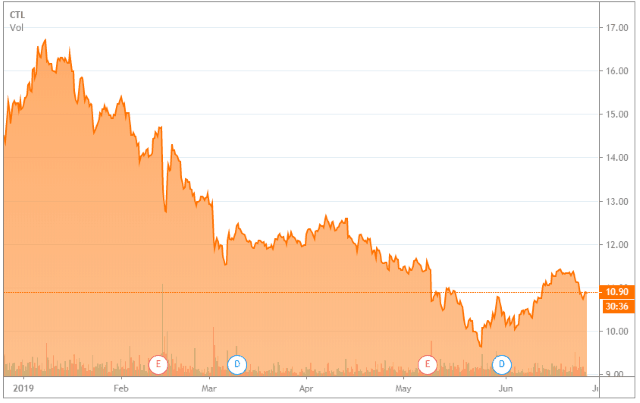
 Bell (Canada)
Bell (Canada) 
 Industry trade association NCTA reports that Comcast, Charter, Cox, Mediacom, Midco, Rogers (Canada), Shaw Communications (Canada), Vodafone (Europe), Taiwan Broadband Communications, Telecom Argentina, Liberty Global (Europe/Latin America) are all implementing the industry’s 10G initiative, with lab trials already underway, and field trials beginning in 2020. DOCSIS 4.0 will ultimately be a part of that project.
Industry trade association NCTA reports that Comcast, Charter, Cox, Mediacom, Midco, Rogers (Canada), Shaw Communications (Canada), Vodafone (Europe), Taiwan Broadband Communications, Telecom Argentina, Liberty Global (Europe/Latin America) are all implementing the industry’s 10G initiative, with lab trials already underway, and field trials beginning in 2020. DOCSIS 4.0 will ultimately be a part of that project. As some Netflix shareholders grumble about
As some Netflix shareholders grumble about 
