 Windstream is relying on the Federal Communications Commission’s Connect America Fund to double the areas where it will offer 100 Mbps broadband service, expected to reach 30% of the company’s 18-state local service area by the end of the first quarter of 2019.
Windstream is relying on the Federal Communications Commission’s Connect America Fund to double the areas where it will offer 100 Mbps broadband service, expected to reach 30% of the company’s 18-state local service area by the end of the first quarter of 2019.
“Windstream understands that premium internet speeds are critical to families and businesses in rural America, and we are systematically enhancing our network to meet that urgent demand,” said Jeff Small, president of consumer and small and medium-sized business services. “Network upgrades are expensive, especially in rural areas where there are relatively few customers, so Windstream is using a combination of its own capital and crucial support from the FCC’s Connect America Fund to make faster speeds more widely available. Without support from the Connect America Fund, many of these projects simply would not be economically feasible.”
Thomas told attendees at the Citi 2019 TMT West Conference Windstream’s legacy copper wire telephone network is not up to the job of handling the kinds of internet speeds more modern technologies can manage.
In urban and larger service areas, Windstream is most likely to deploy fiber to the home service in new housing developments and select gentrified neighborhoods where a business case exists to invest in fiber upgrades. The company also typically replaces its copper wireline infrastructure with fiber where road construction projects or damage forces the company to replace or relocate its lines. Suburban and more densely populated rural areas are likely to receive an upgraded version of Windstream’s DSL service that can manage up to 50 or 100 Mbps. In Windstream’s significant rural service area, the phone company is increasingly turning to fixed wireless technology, especially in flat midwestern states like Nebraska and Iowa where it plans to offer a combination of 3.5 GHz “CBRS” and 5G millimeter wave fixed wireless broadband capable of delivering up to 1,000 Mbps.
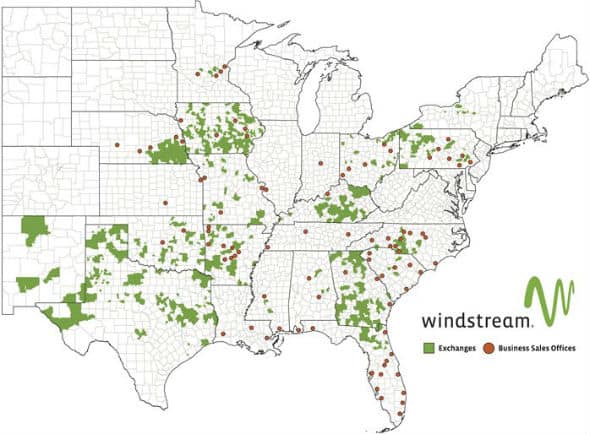
Windstream’s service area
“[We are deploying wireless internet] probably at a larger scale than a lot of the larger wireless companies,” Thomas said, especially in flatter areas where wireless signals go a long way.
Because most current broadband expansion fund programs require companies to commit to at least 25/3 Mbps service, simply expanding basic ADSL technology has proven inadequate to meet the government’s speed requirements. But wiring fiber to the home service to get faster speeds in rural areas does not meet the Return On Investment requirements Windstream’s shareholders demand. Windstream claims fixed wireless can solve both problems.
“You can get 100 Mbps out there very cost-effectively,” Thomas claimed. “You are really blowing away copper infrastructure and making it irrelevant because you’re embracing this 100 Mbps technology.”
As of early 2019, Windstream claims that 60% of its customers can get at least 25 Mbps service, 40% can receive at least 50 Mbps service. By the end of March, 30% will be able to receive 100 Mbps service.
A satisfied Windstream customer talks about his upgrade to 50/8 Mbps, which replaces his old 6 Mbps DSL service. (6:03)


 Subscribe
Subscribe A
A  The 101-page filing maintains the FCC overreached by imposing any deal conditions on the 2016 multi-billion dollar merger deal, especially those that might require the merged company to spend money to improve service to customers. CEI argued such conditions were “arbitrary and capricious” and had no place as part of approving a business merger transaction.
The 101-page filing maintains the FCC overreached by imposing any deal conditions on the 2016 multi-billion dollar merger deal, especially those that might require the merged company to spend money to improve service to customers. CEI argued such conditions were “arbitrary and capricious” and had no place as part of approving a business merger transaction.
 Wall Street had been increasingly pessimistic about Netflix’s revenue and profit projections because of ongoing increases in spending to finance an avalanche of original Netflix productions. The company’s stock price dropped by 21 percent, from a peak of $423.21 last June to $332.94 just before the market opened this morning. Netflix’s chief content officer told the media last spring about 85% of the company’s estimated $8 billion in content spending for 2018 was for original TV shows, movies, and other productions. By summer, Netflix had $12 billion in debt before borrowing another $2 billion in October. But that debt never changed Netflix’s plans to premiere 1,000 new movies and TV series in 2018, with an even larger number of productions scheduled for 2019.
Wall Street had been increasingly pessimistic about Netflix’s revenue and profit projections because of ongoing increases in spending to finance an avalanche of original Netflix productions. The company’s stock price dropped by 21 percent, from a peak of $423.21 last June to $332.94 just before the market opened this morning. Netflix’s chief content officer told the media last spring about 85% of the company’s estimated $8 billion in content spending for 2018 was for original TV shows, movies, and other productions. By summer, Netflix had $12 billion in debt before borrowing another $2 billion in October. But that debt never changed Netflix’s plans to premiere 1,000 new movies and TV series in 2018, with an even larger number of productions scheduled for 2019. Comcast-owned NBCUniversal today announced a 2020 launch of a new, advertiser-supported streaming service, relying on content libraries and distribution platforms from America’s NBCUniversal and Europe’s Sky.
Comcast-owned NBCUniversal today announced a 2020 launch of a new, advertiser-supported streaming service, relying on content libraries and distribution platforms from America’s NBCUniversal and Europe’s Sky.
 For the sixth time, the New York State Public Service Commission has
For the sixth time, the New York State Public Service Commission has 