
Smoke signals achieve a faster transmission rate than DSL can manage in the Scottish village of Kettleholm.
The village of Kettleholm, near Lockerbie in Scotland has effectively given up on DSL service from British Telecom and has upgraded the community’s telecommunications service to technologies including smoke signals, messages inserted into bottles and thrown into nearby streams, carrier pigeons, and for urgent communications — the village’s pony express.
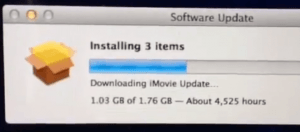
All of these communications methods have proven much more effective than the area’s copper wire-based DSL service, which villagers report is often less than useless. In fact, it can take at least 10 minutes to load Google’s home page in Kettleholm on a bad day, and Apple software updates require additional patience — more than 4,525 hours worth (that is more than 188 days) for the latest version of iMovie to arrive.
BT engineers sent to the area to investigate found nothing wrong with the service, which they initially said was operating within normal expectations for DSL “broadband.” But at least 150 local residents strongly disagree, and several made their point producing a video demonstrating how two yogurt cups attached by string provide more reliable communications than BT was managing in their part of Scotland.
The problem, according to local residents, is the decrepit state of the copper-wire based telephone exchange, installed just after World War 2. Broadband advocates say the solution is rubbishing the ancient copper wiring and replacing it with optical fiber that is spreading across the rest of Great Britain. But neither BT or Virgin Media consider Kettleholm worth the investment, placing the village squarely in the undistinguished category of last priority — the one-third of the United Kingdom deemed economically unsuitable for fiber broadband.
UK residents are paying for broadband improvements as part of their TV License Fee, and the government has amassed at least £800 million for upgrades. It irritates some residents that their portion of the license fee is paying for someone else’s broadband upgrades, and salt is rubbed in those wounds when viewers see BT — the largest recipient of government money — spending it on advertisements mailed to Kettleholm residents for services they can never get.
Even worse, the BBC recently learned the phone company isn’t exactly spending every resource on better broadband in the UK. BT recently found £738 million laying around to pay for the rights to Premier League football games for the next three years.
 Where there is smoke (signals) there is fire, especially after the BBC picked up the story. BT suddenly had a change of heart about the state of their network in Dumfries and Galloway:
Where there is smoke (signals) there is fire, especially after the BBC picked up the story. BT suddenly had a change of heart about the state of their network in Dumfries and Galloway:
“Kettleholm telephone exchange is a modern digital exchange, System X and offers broadband speeds of up to 8mb/s. We were not initially aware of a problem with broadband in Kettleholm as only a small number of the 120 end users reported problems with their service. The service appears to have gradually degraded over time without triggering any of our alarms. Engineers recently reset equipment in the exchange and tests show that broadband speeds have risen. We will continue to monitor the situation and would like to apologise to everyone for the frustration and inconvenience they have experienced.”
Kettleholm residents appreciate the new attention BT is paying to their network, but the village has been reminding everyone they can find that BT is their sole provider and when they stop paying attention to their DSL facilities, the entire community suffers.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Kettleholm Poor Broadband 6-2012.flv[/flv]
The village of Kettleholm shows off their new telecommunications systems: smoke signals, carrier pigeons, messages inserted into bottles, semaphores, the pony express, and yogurt cups attached by string. All perform better than BT’s DSL service. (2 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe







