Dish Network Offers $25.5 Billion for Sprint, Topping Softbank’s Bid; Will Keep Unlimited Data Plans

Satellite television provider Dish Network today offered $25.5 billion for Sprint Nextel Corp., in an unsolicited bid that surprised the wireless industry.
The bid, announced by CEO Charles Ergen, is $5.5 billion higher than that offered by Japan’s Softbank, which already had a pending deal to take a 70 percent stake in the third largest wireless carrier.
The bidding may not yet be over if Softbank decides to counter with a higher offer or if other bidders emerge in the coming weeks.
Ergen has signaled his interest in entering wireless markets to compensate for slowing earnings in the satellite television business.
“He is trying to transform his own business,” Vijay Jayant, an analyst at International Strategy & Investment Group in New York told Bloomberg News. “He’s trying to reinvent himself, moving from satellite to wireless.”
 Ergen’s vision would include a bundled package of satellite television, broadband wireless Internet and cellular telephone service. Providing suitable wireless broadband Internet in rural areas may be the biggest challenge because of Sprint’s more limited network coverage, but a marketing deal combining satellite television from Dish and Sprint cell phone service would be easier to carry out.
Ergen’s vision would include a bundled package of satellite television, broadband wireless Internet and cellular telephone service. Providing suitable wireless broadband Internet in rural areas may be the biggest challenge because of Sprint’s more limited network coverage, but a marketing deal combining satellite television from Dish and Sprint cell phone service would be easier to carry out.
Ergen’s offer includes $8.2 billion in stock and $17.3 billion in cash. Ergen’s company has stockpiled at least $10 billion from selling bonds over the last year. He intends to borrow the rest.
Ergen earlier had attempted to disrupt a deal that would have consolidated Clearwire into Sprint. Ergen offered $3.30 a share for Clearwire, 33 cents higher than the $2.97 per share offer from Sprint. Ergen also reportedly approached both MetroPCS and Deutsche Telekom’s T-Mobile USA looking for a deal to no avail.
Some analysts question whether Ergen has enough experience to manage a major wireless company with only his past involvement selling satellite TV subscriptions. But he arrives with more than just cash and stock options. Ergen has acquired mobile spectrum from bankrupt TerreStar Networks and DBSD North America. Ergen says he has no interest in building his own wireless network, but a combined Sprint/Dish could manage the spectrum through Sprint’s existing operations.
Ergen told Bloomberg News combining the spectrum Dish owns with the spectrum owned by Sprint and Clearwire would assure Americans of a robust wireless data platform that will not have capacity constraints or require individual device fees. That is in keeping with Sprint’s existing marketing as a provider of truly unlimited wireless data plans.
Several Wall Street analysts told CNBC and Bloomberg News the deal with Softbank may be more ideal for shareholders and consumers, because it would strengthen Sprint’s leverage with equipment manufacturers to offer cheaper and more robust devices.
Consumer advocates have mixed feelings. Dish has no prior association to the wireless industry so the deal does not represent direct, competitive consolidation. It also would boost Sprint as a more formidable competitor to AT&T and Verizon Wireless. But it could also further orphan T-Mobile USA.
“Right now, we have two giants and two also-rans, and now you’re getting potentially three giants dividing up the American market place, with T-Mobile lagging far behind,” Susan Crawford told the New York Times.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Bloomberg What Does Dish See in Sprint Thats Worth 25B 4-15-13.flv[/flv]
Bloomberg News explores what Dish sees in Sprint that is worth a bid of $25.5 billion to acquire the country’s third largest mobile company. (2 minutes)
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Bloomberg Dish Bids 25-5 Billion for Sprint to Challenge Softbank 4-15-13.flv[/flv]
Bloomberg says Dish has been stockpiling $10 billion in cash for new acquisitions to transform its business away from a satellite TV-only company. (2 minutes)
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Bloomberg All Things Are on the Table for Sprint 4-15-13.flv[/flv]
Christopher Marangi, of Gabelli Asset Fund talks with Bloomberg’s Erik Schatzker about Dish Network’s unsolicited $25.5 billion offer for Sprint and what options are available to Sprint with the offers it has on the table. (2 minutes)
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Bloomberg Dish Bid for Sprint Lacks Capital Chaplin Says 4-15-13.flv[/flv]
Jonathan Chaplin, an analyst with New Street Research LLP, thinks Softbank’s original offer is superior to the one from Dish. (6 minutes)
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Bloomberg Bidding for Sprint Is Not Over Fritzshe 4-15-13.flv[/flv]
Jennifer Fritzsche, Managing Director of Equity Research at Wells Fargo Securities, discusses the likelihood of other players making bids. (2 minutes)
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Bloomberg What Did Dish CEO Ergen Say About Sprint Bid 4-15-13.flv[/flv]
A Bloomberg News reporter interviewed Charlie Ergen about why he wants to enter the wireless business. Ergen’s vision includes no nickel and diming customers with monthly device fees and usage charges. (4 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe Canada’s effort to expand mobile competition has likely failed with news that three of the most significant new independent entrants have put themselves up for sale, with one likely to be acquired by Telus, western Canada’s largest phone company.
Canada’s effort to expand mobile competition has likely failed with news that three of the most significant new independent entrants have put themselves up for sale, with one likely to be acquired by Telus, western Canada’s largest phone company. The three companies have competed with the dominant players for about three years with little success. Combined, the three have not managed to achieve even a combined 10 percent market share. Most sell unlimited talk and text plans to customers that would normally buy prepaid service.
The three companies have competed with the dominant players for about three years with little success. Combined, the three have not managed to achieve even a combined 10 percent market share. Most sell unlimited talk and text plans to customers that would normally buy prepaid service.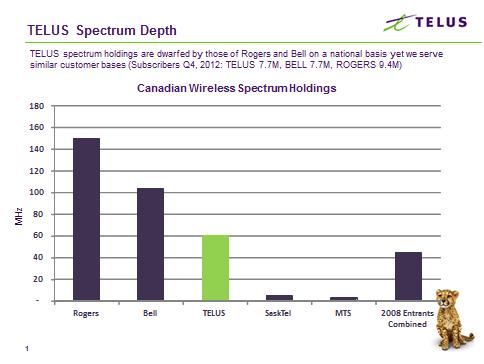






 A Financial Times blog post has started a buying frenzy for Vodafone Group Plc on news AT&T and Verizon Communications are about to bid for the British mobile phone giant, despite denials from Verizon it is involved in any deal to acquire the British mobile phone company.
A Financial Times blog post has started a buying frenzy for Vodafone Group Plc on news AT&T and Verizon Communications are about to bid for the British mobile phone giant, despite denials from Verizon it is involved in any deal to acquire the British mobile phone company. The sources told the Times they expect the deal will initially merge Vodafone and Verizon into a single entity, but only briefly. Verizon would promptly sell Vodafone’s extensive international assets to AT&T at a premium. Verizon would end up the sole owner of Verizon Wireless, and AT&T would acquire Vodafone’s enormous wireless operations in Europe, Asia, Africa and the Middle East.
The sources told the Times they expect the deal will initially merge Vodafone and Verizon into a single entity, but only briefly. Verizon would promptly sell Vodafone’s extensive international assets to AT&T at a premium. Verizon would end up the sole owner of Verizon Wireless, and AT&T would acquire Vodafone’s enormous wireless operations in Europe, Asia, Africa and the Middle East.