
Road to nowhere?
Frontier Communications has lost more than 150,000 customers in the last six months as company executives blamed bad marketing and the on-shoring of call centers that formerly supported Verizon customers in Texas, California, and Florida.
Some 99,000 customers dropped Frontier service in the last three months, and another 77,000 departed during the three months before that. In addition to losing customers, Frontier saw a net loss of $80 million in its third quarter, up from a the $14 million the company lost during the same quarter a year ago.
A clearly distraught Dan McCarthy, Frontier’s CEO, knew he was in for a pummeling from Wall Street analysts on a conference call with investors on Tuesday.
“I wanted to assure you, that I’m focused on addressing and resolving the issues hindering our performance,” McCarthy said. “I’m fully aware that the third quarter results underscore the urgent need for our expanded business to perform at the higher level, where I know it can and should. And you have my personal commitment that we will do so.”
Frontier lost $52 million in revenue in the last three months in part because of its disastrous transition of former Verizon customers in California, Texas, and Florida and because a growing number of broadband users have realized Frontier’s endless promises of better service have rarely come to fruition and those customers chose other providers.
“This decline is unacceptable and reflects a level of performance, [and] I’m committed to change it,” McCarthy promised.
Unfortunately for customers and investors, that “change” is primarily rearranging the deck chairs with a haphazard, and likely soon-to-be-an-afterthought “reorganization,” and the usual treatment prescribed when executives fail to deliver Wall Street the results they expect: big layoffs of employees that had nothing to do with Frontier’s problems and have in fact been warning the company about some of their more boneheaded moves. The idea for quick layoffs may have come from Frontier’s newest chief financial officer R. Perley McBride, a pick McCarthy said will be “laser focused” on cost management. That’s code for cost-cutting, not exactly the best idea for a company that has shown a near-constant aversion to investing adequately in its network and on necessary broadband upgrades.
Analysts didn’t seem to be terribly interested in Mr. McCarthy’s grand reorganization plan either, detailed in this veritable word salad:
Let me also highlight that today, we announced a new customer-focused organizational structure, and the creation of commercial and consumer business units. This change is designed to improve our execution and operational effectiveness, increases spans of control in the organization and makes us more nimble, while at the same time eliminating duplicative costs associated with our former structure. In the first month of operating our new properties, it became apparent that this change was necessary.

McCarthy
Some investors pondered if these operational problems were all so readily identifiable and apparent, why didn’t Mr. McCarthy carry out changes after assuming leadership of the company more than a year ago.
McCarthy’s realization that big changes were needed is not what he was telling investors in May, when he was downplaying the impact of the Verizon customer cutover as affecting less than 1% of customers and wasn’t material. That level of happy talk puts McCarthy dangerously close to Wells Fargo territory, where a few million fake bank accounts weren’t material either.
McCarthy loves to use catchphrases to minimize the problems experienced at Frontier, as well as countering any negative developments with aspirational talk about the future.
For example, Frontier’s decision not to carefully scrutinize customer data provided by Verizon before cutting over customers to Frontier’s systems, leaving many without service for days to weeks was the result of “imperfect data extracts and network complexities” according to McCarthy. That cost Frontier plenty as the company issued bill credits to potentially tens of thousands of customers left without service because of ‘imperfections.’ Many just decided to leave and never looked back.
In May, McCarthy told investors “After a month of operating these properties, we are very pleased with the progress we have made, and we want to thank customers for their patience during the transition period. The entire Frontier team remains focused on cultivating growth by retaining and attracting new customers. We will continue to drive Frontier’s performance to maintain free cash flow that provides an attractive and sustainable dividend payout ratio.”
Not so much anymore. This week, McCarthy hit the red alert button and suddenly declared an urgent need for a major reorganization, oddly pegging Frontier’s problems partly on organizational inefficiencies:
“Historically, Frontier was organized around a regional structure, each one of the regions had its own resources that included marketing, finance, engineering, human resources. And in doing that, we – when we were a much smaller entity, it really did serve us well at that point in time. The more we looked at it today, the less differences there are in a lot of the markets and the way we’re going to market whether it’s around a Vantage product or it’s around FiOS or it’s around next-generation broadband products. So, when we looked at it, we did a really a trade-off on it, so we’ve essentially eliminated all of that redundancy in the organization.”

The unemployment line is in the future for 1,000 Frontier employees.
So what is the “redundancy” Frontier claims it has essentially eliminated? The forthcoming layoffs of 1,000 employees nationwide which Frontier management believes will make things much better for customers, at least according to McCarthy:
The impact is approximately 1,000 individuals that will be leaving the organization, and that translates directly into cost savings. And the nice part about it too is that the enhanced focus on commercial as well as consumer and Frontier has historically been a very consumer-focused organization. We’ve done well on the commercial side, but I really believe we can do much better with more focus, more attention and really putting the resources on those opportunities and making it, that’s what they do every day when they get up and they come to work, all they’re trying to do is grow the commercial revenue base.
So that’s really what we’ve done. It does change the focus on the field operations to really be engaged with the community as well as providing excellent service to customers and being that bridge, but really sales for both consumer and commercial are more centralized in a way that we can apply better resources and do it in a more efficient manner.
 So Frontier plans to become more engaged with the community and deliver better service locally by… getting rid of 1,000 local employees and centralizing its resources somewhere else, probably in another state. The cherry on top? Frontier also implemented a rate hike for customers to enjoy.
So Frontier plans to become more engaged with the community and deliver better service locally by… getting rid of 1,000 local employees and centralizing its resources somewhere else, probably in another state. The cherry on top? Frontier also implemented a rate hike for customers to enjoy.
McCarthy claimed Frontier has been a “very consumer-focused organization,” which seems hard to believe considering how many customers are saying goodbye to Frontier for good. He also implied customer sales are down because Frontier hasn’t effectively used their call center employees to sell service and Frontier alienated customers by moving those call centers from overseas back to the United States. Really?
The executive team at Frontier shrugs off further evidence of deepening customer dissatisfaction by ignoring customer losses in their “legacy” service areas — Frontier territories served by copper yesterday, today, and probably tomorrow. But ignoring problems is nothing new at Frontier:
- It’s not a problem that customers cannot order Frontier products and services on its website because of managerial ineptitude.
- It’s not a problem that customers are still stuck with 1-6Mbps copper-based DSL from Frontier while their cable competitor offers 200Mbps or more.
- It’s not a problem that several years after assuming control over almost all landlines in West Virginia, Frontier has only accomplished broadband speed upgrades for 23% of customers stuck in Frontier’s broadband molasses, and only after the company settled with the West Virginia Attorney’s General office in December 2015. For the record, that amounts to 6,320 customers. Don’t break a sweat there. Frontier’s performance in West Virginia has been so abysmal, the settlement between the state and the company represents the largest, independently negotiated consumer protection settlement in West Virginia history, which extends back to June 20, 1863.
- It’s not a problem that customers in Connecticut are still plagued by aftershocks from the tumultuous transfer from AT&T to Frontier in October 2014. On Oct. 19, 2016 countless DSL customers were reminded of that transition when they suffered another multi-hour outage and to add insult to injury, Frontier decided the time was also right to raise rates $4 a month for its Vantage TV service, which caused another round of customer cancellations.
McCarthy called the operational reorganization a “bridge” between field operations and providing excellent service to customers. We call it just another bridge to nowhere.
We’ve written for years that Frontier’s real problem isn’t cost management, organizational structure, or where it places employees and call centers. The real elephant in the room is that Frontier’s broadband service is terrible, especially where Frontier built the network all by itself or acquired it from another phone company decades earlier.
We are convinced Frontier’s management understands this, and so do many investors, but they just don’t care. One summed up the Frontier story this way:
So Frontier buys the whole wireline shooting match in one geographic area after another (labor force, wires, customers, DSL, even FIOS) paid for with billions in junk bond proceeds. Looking at an asset base that is disappearing before their eyes, the game is to squeeze as much out of it as possible before it crumbles completely. Minimum possible maintenance, minimum possible [investment], minimum possible headcount, and less every year.
From an investor’s standpoint, the key question is to figure out when the final collapse is going to take place.

Frontier’s “High Speed” fantasies extend back to 2010 when former CEO Maggie Wilderotter was telling customers Frontier was loaded with fiber.
When Rochester Telephone rebranded itself Frontier Communications in the 1990s, it did so looking forward to the future. The Frontier Communications experience of today is like immersing oneself in the History Channel. Nearly everything about Frontier these days is about the past and a promised future that never seems to arrive. Everything surrounds a legacy network still almost entirely dependent on last-century DSL for residential customers and various acquired networks from Verizon and AT&T mismanaged at conversion, forcing customers to clean up after Frontier’s repeated mistakes.
In legacy service areas where little has changed over the last decade, the four words that come to mind are “too little, too late” as customers make one last call to permanently drop service despite promises faster speeds are coming soon.
Too little investment in suitable broadband: Frontier dwells on its dividend payout to shareholders while customers languish with internet speeds that do not come close to the FCC’s definition of broadband. Instead of spending billions acquiring Verizon’s throwaway service areas, invest that money in your network and offer truly competitive 21st century broadband service.
Too late to matter: Frontier’s commitments to broadband upgrades happen too slowly and for too few customers. Much of Frontier’s state-of-the-art networks were built by other companies and simply acquired by Frontier, which now provides sleepy caretaker service. When people think Frontier Communications, they sure don’t think of words like “modern” and “innovative” and “excellence.” They think “yesterday,” “out of service,” and “slow.” There is a good reason why cable operators eat Frontier’s market share. People don’t love the cable company more than Frontier, but at least they are no longer stuck with broadband speeds that were common during the latter half of the Clinton Administration.
You’re a communications company, not the Geek Squad: While Frontier fritters away their customer base, those remaining are literally assaulted with promotions for dubious value services like tech support, virus protection, and cloud storage backup. There is a reason other phone and cable companies have not followed Frontier’s lead on emphasizing these services. They don’t matter to most customers and many of those who do have them are surprised when they find them on their phone bill because they don’t remember signing up. Sell reliable and fast phone, broadband, and video service, not gimmicks.
It is unfortunate another 1,000 Frontier employees are about to pay for the mistakes made at the top. Until that changes, customers would do well to consider their options and act accordingly. If reporting by The Hour is any indication, customers shouldn’t hold their breath. Frontier is still looking out for their most important asset: their shareholders.
If Frontier’s customer relations remain a work in progress, so does McCarthy’s job convincing investors to see the promise of his plan and that of his CEO predecessor Maggie Wilderotter to create a national broadband company from territories AT&T and Verizon have been willing to cast aside. Since closing at $6.54 on Oct. 31, 2014, on the eve of the switch [in Connecticut], two years later Frontier shares have hovered for the most part just above the $4 threshold.
With a new chief financial officer in place in former Frontier executive Perley McBride, McCarthy promised to get Frontier on track from an investor perspective, even as the company works to get its customer relations on an even keel.
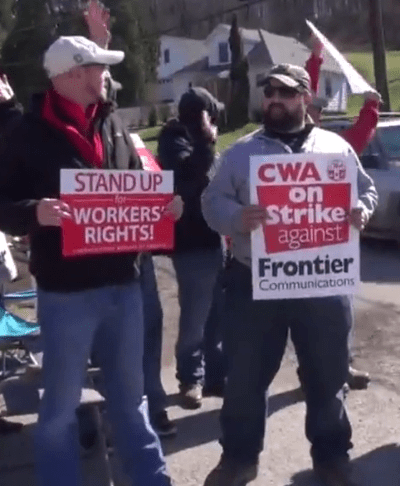 After 10 months of negotiations between Frontier Communications and the Communications Workers of America (CWA) over the phone company’s job cuts, 1,400 Frontier workers in West Virginia and Ashburn, Va., walked off the job Sunday.
After 10 months of negotiations between Frontier Communications and the Communications Workers of America (CWA) over the phone company’s job cuts, 1,400 Frontier workers in West Virginia and Ashburn, Va., walked off the job Sunday.

 Subscribe
Subscribe An undisclosed number of Frontier Communications customers in West Virginia were without phone service during the Christmas-New Year’s Day holidays because of copper thefts and slow repair crews that did not begin repairs for up to two weeks after the outages were reported.
An undisclosed number of Frontier Communications customers in West Virginia were without phone service during the Christmas-New Year’s Day holidays because of copper thefts and slow repair crews that did not begin repairs for up to two weeks after the outages were reported.
 If advertised claims of lightning fast DSL internet don’t match reality, it never hurts to bring evidence to the table if you want to prove your state’s biggest telecom company is lying through its teeth.
If advertised claims of lightning fast DSL internet don’t match reality, it never hurts to bring evidence to the table if you want to prove your state’s biggest telecom company is lying through its teeth.




 So Frontier plans to become more engaged with the community and deliver better service locally by… getting rid of 1,000 local employees and centralizing its resources somewhere else, probably in another state. The cherry on top? Frontier also implemented a rate hike for customers to enjoy.
So Frontier plans to become more engaged with the community and deliver better service locally by… getting rid of 1,000 local employees and centralizing its resources somewhere else, probably in another state. The cherry on top? Frontier also implemented a rate hike for customers to enjoy.
