Phillip Dampier: A cable trade publication is lecturing its readership on better broadband the industry spent years claiming nobody wanted or needed.
Remember the good old days when cable and phone companies told you there was no demand for faster Internet speeds when 6Mbps from the phone company was all you and your family really needed?
Those days are apparently over.
Multichannel News, the largest trade publication for cable industry executives, warns cable companies gigabit broadband speeds are right around the corner and the technological transformation that will unleash has been constrained for far too long.
Say what?
Proving our theory that those loudest about dismissing the need for faster Internet speeds are the least equipped to deliver them, the forthcoming arrival of DOCSIS 3.1 technology and decreasing costs to deploy fiber optics will allow cable providers to partially meet the gigabit speed challenge, at least on the downstream. Before DOCSIS 3.1, consumers didn’t “need those speeds.” Now companies like Comcast claim it isn’t important what consumers need today — it’s where the world is headed tomorrow.
Comcast 2013:
Comcast executive vice president David L. Cohen writes that the allure of Google Fiber’s gigabit service doesn’t match the needs or capabilities of online Americans.
“For some, the discussion about the broadband Internet seems to begin and end on the issue of ‘gigabit’ access,” Cohen says, in a nod to Google Fiber. “The issue with such speed is really more about demand than supply. Our business customers can already order 10-gig connections. Most websites can’t deliver content as fast as current networks move, and most U.S. homes have routers that can’t support the speed already available to the home.” Essentially, Cohen argues that even if Comcast were to deliver web service as fast as Google Fiber’s 1,000Mbps downloads and uploads, most customers wouldn’t be able to get those speeds because they’ve got the wrong equipment at home.
Comcast 2015:
“We’ve consistently offered the most speeds to the most homes, but with the current pace of tech innovation, sometimes you need to go to where the world is headed and not focus on where it is today.”
“The next great Internet innovation is only an idea away, and we want to help customers push the boundaries of what the Internet can do and do our part to inspire developers to think about what’s possible in a multi-gigabit future. So, next month we will introduce Gigabit Pro, a new residential Internet service that offers symmetrical, 2-Gigabits-per-second (Gbps) speeds over fiber – at least double what anyone else provides.”

Nelson (Image: Multichannel News)
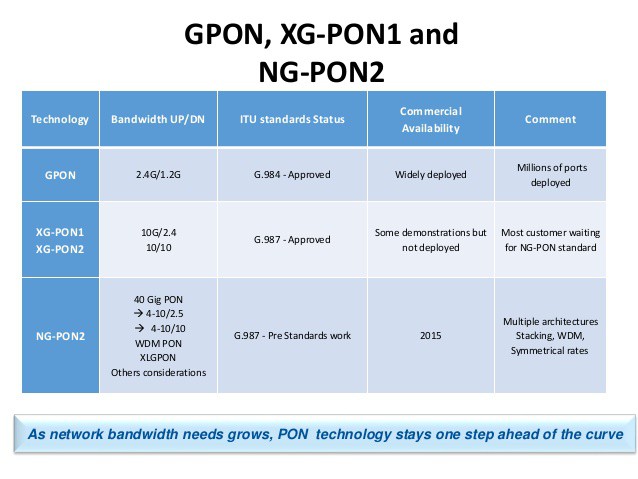
Rich Nelson’s guest column in Multichannel News makes it clear American broadband is behind the times. The senior vice president of marketing, broadband & connectivity at Broadcom Corporation says the average U.S. Internet connection of 11.5Mbps “is no longer enough” to support multiple family members streaming over-the-top video content, cloud storage, sharing high-resolution images, interactive online gaming and more.
Nelson credits Google Fiber with lighting a fire under providers to reconsider broadband speeds.
“Google’s Fiber program may have been the spark to light the fuse — Gigabit services have fostered healthy competition among Internet and telecommunications providers, who are now in a position to consider not ‘if’ but ‘when and how’ to deploy Gigabit broadband in order to meet consumer’s perceived ‘need for speed’ and maintain their competitive edge,” Nelson wrote.
But the greatest bottleneck to speed advances is spending money to pay for them. Verizon FiOS was one of the most extravagant network upgrades in years among large American telecom companies and the company was savaged by Wall Street for doing it. Although AT&T got less heat because its U-verse development costs were lower, most analysts still instinctively frown when a company proposes spending billions on network upgrades.
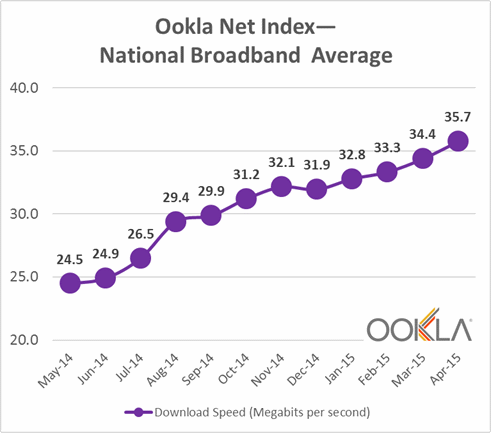
Customer demand for faster broadband is apparent as providers boost Internet speeds.
The advent of DOCSIS 3.1 — the next generation of cable broadband technology — suggests a win-win-win for Wall Street, cable operators, and consumers. No streets will have to be torn up, no new fiber cables will have to be laid. Most providers will be able to exponentially boost Internet speeds by reallocating bandwidth formerly reserved for analog cable television channels to broadband. The more available bandwidth reserved for broadband, the faster the speeds a company can offer.
Many industry observers predict the cable line will eventually be 100% devoted to broadband, over which telephone, television and Internet access can be delivered just as Verizon does today with FiOS and AT&T manages with its U-verse service.
The benefits of gigabit speeds are not limited to faster Internet browsing however.
Nelson notes communities and municipalities are now using gigabit broadband speeds as a competitive tool selling homes and attracting new businesses to an area. According to a study from the Fiber to the Home (FTTH) Council, communities with widely available gigabit access have experienced a positive impact on economic activity — to the tune of more than $1.4 billion in GDP growth. Those bypassed or stuck in a broadband backwater are now at risk of losing digital economy jobs as businesses and entrepreneurs look elsewhere.
The gigabit broadband gap will increasingly impact the local economies of communities left behind with inadequate Internet speeds as app developers, content producers, and other innovative startups leverage gigabit broadband to market new products and services.
The Pew Research Center envisioned what the next generation of gigabit killer apps might look like. Those communities stuck on the slow lane will likely not have access to an entire generation of applications that simply will never work over DSL.
But before celebrating the fact your local cable company promises to deliver the speed the new apps will need, there is a skunk that threatens to ruin your ultra high speed future: usage-based pricing and caps.
At the same time DOCSIS 3.1 will save the cable industry billions on infrastructure upgrade costs, the price for moving data across the next generation of super high-capacity broadband networks will be lower than ever before. But cable operators are not planning to pass their savings on to you. In fact, broadband prices are rising, along with efforts to apply arbitrary usage limits or charge usage-based pricing. Both are counter-intuitive and unjustified. It would be like charging for a bag of sand in the Sahara Desert or handing a ration book to shoreline residents with coupons allowing them one glass of water each from Lake Ontario.
 Cox plans to limit its gigabit customers to 2TB of usage a month. AT&T U-verse with GigaPower has a (currently unenforced) limit of 1TB a month, while Suddenlink thinks 550GB is more than enough for its gigabit customers. Comcast is market testing 300GB usage caps in several cities but strangely has no usage cap on its usage-gobbling gigabit plan. Why cap the customers least-equipped to run up usage into the ionosphere while giving gigabit customers a free pass? It doesn’t make much sense.
Cox plans to limit its gigabit customers to 2TB of usage a month. AT&T U-verse with GigaPower has a (currently unenforced) limit of 1TB a month, while Suddenlink thinks 550GB is more than enough for its gigabit customers. Comcast is market testing 300GB usage caps in several cities but strangely has no usage cap on its usage-gobbling gigabit plan. Why cap the customers least-equipped to run up usage into the ionosphere while giving gigabit customers a free pass? It doesn’t make much sense.
But then usage caps have never made sense or been justified on wired broadband networks and are questionable on some wireless ones as well.
Stop the Cap! began fighting against usage caps and usage pricing in the summer of 2008 when Frontier Communications proposed to limit its DSL customers to an ‘ample’ 5GB of usage per month. That’s right — 5GB. We predicted then that usage caps would become a growing problem in the United States. With a comfortable duopoly, providers could easily ration Internet access with the flimsiest of excuses to boost profits. Here is what we told the Associated Press seven years ago:
“This isn’t really an issue that’s just going to be about Frontier,” said Phillip Dampier, a Rochester-based technology writer who is campaigning to get Frontier to back off its plans. “Virtually every broadband provider has been suddenly discovering that there’s this so-called ‘bandwidth crisis’ going on in the United States.”
That year, Frontier claimed most of its 559,300 broadband subscribers consumed less than 1.5 gigabytes per month, so 5GB was generous. Frontier CEO Maggie Wilderotter trotted out the same excuses companies like Cox and Suddenlink are still using today to justify these pricing schemes: “The growth of traffic means the company has to invest millions in its network and infrastructure, threatening its profitability.”
Just one year later, Frontier spent $5.3 billion to acquire Verizon landline customers in around two dozen states, so apparently Internet usage growth did not hurt them financially after all. Frankly, usage growth never does. As we told the AP in 2008, the costs of network equipment and connecting to the wider Internet are falling. It still is.
“If they continue to make the necessary investments … there’s no reason they can’t keep up” with increasing customer traffic, we said at the time.
We are happy to report we won our battle with Frontier Communications and today the company even markets the fact their broadband service comes without usage caps. In many of Frontier’s rural service areas, they are the only Internet Service Provider available. Imagine the impact a 5GB usage cap would have had on customers trying to run a home-based business, have kids using the Internet to complete homework assignments, or rely on the Internet for video entertainment.
So why do some providers still try to ration Internet usage? To make more money of course. When the public believes the phony tales of network costs and traffic growth, the duped masses open their wallets and pay even more for what is already overpriced broadband service. Just check this chart produced by the BBC, based on data from the Organization for Economic Co‑operation and Development. Value for money is an alien concept to U.S. providers:
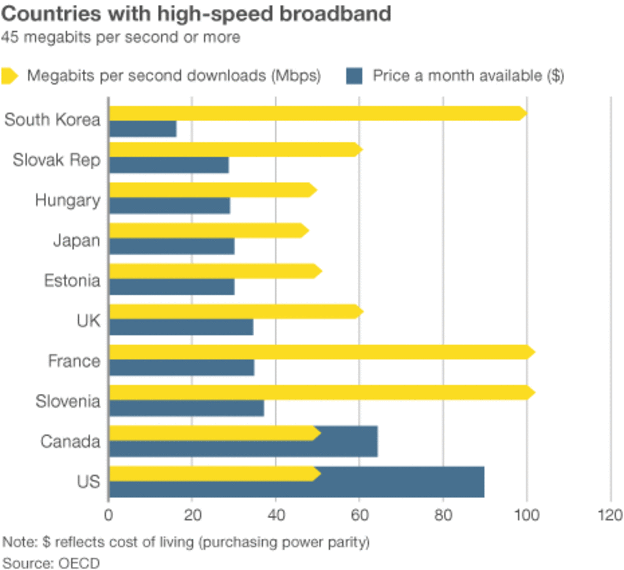
The usual method of combating pricing excess is robust competition. With a chasm-sized gap between fat profits and the real cost of the service, competitors usually lower the price to attract more customers. But the fewer competitors, the bigger the chance the marketplace will gravitate towards comfort-level pricing and avoid rocking the boat with a ruinous price war. It is one of the first principles of capitalism — charging what the market will bear. We’ve seen how well that works in the past 100+ years. Back in 2010, we found an uncomfortable similarity between broadband prices of today with the railroad pricing schemes of the 1800s. A handful of executives and shareholders reap the rewards of monopolistic pricing and pillage not only consumers but threaten local economies as well.
 The abuses were so bad, Congress finally stepped in and authorized regulators to break up the railroad monopolies and regulate abusive pricing. We may be headed in the same direction with broadband. We do not advocate regulation for the sake of regulation. Competition is a much more efficient way to check abusive business practices. But where an effective monopoly or duopoly exists, competition alone will not help. Without consumer-conscious oversight, the forthcoming gigabit broadband revolution will be stalled by speed bumps and toll booths for the benefit of a few giant telecommunications corporations. That will allow other countries to once again leap ahead of the United States and Canada, just as they have done with Internet speeds, delivering superior service at a lower price.
The abuses were so bad, Congress finally stepped in and authorized regulators to break up the railroad monopolies and regulate abusive pricing. We may be headed in the same direction with broadband. We do not advocate regulation for the sake of regulation. Competition is a much more efficient way to check abusive business practices. But where an effective monopoly or duopoly exists, competition alone will not help. Without consumer-conscious oversight, the forthcoming gigabit broadband revolution will be stalled by speed bumps and toll booths for the benefit of a few giant telecommunications corporations. That will allow other countries to once again leap ahead of the United States and Canada, just as they have done with Internet speeds, delivering superior service at a lower price.
China now ranks first in the world in terms of the total number of fiber to the home broadband subscribers. So far, it isn’t even close to the fastest broadband country because much of China still gets access to the Internet over DSL. The Chinese government considers that unacceptable. It sees the economic opportunities of widespread fiber broadband and has targeted the scrapping of every DSL Internet connection in favor of fiber optics by the end of 2017. As a result, with more than 200 million likely fiber customers, China will become the global leader in fiber infrastructure, fiber technology, and fiber development. What country will lose the most from that transition? The United States. Today, Corning produces 40% of the world’s optical fiber.
Global optical fiber capacity amounted to 13,000 tons in 2014, mainly concentrated in the United States, Japan and China (totaling as much as 85.2% of the world’s total), of which China already ranked first with a share of 39.8%. Besides a big producer of optical fiber, China is also a large consumer, demanding 6,639 tons in 2014, 60.9% of global demand. The figure is expected to increase to 7,144 tons in 2015. Before 2010, over 70% of China’s optical fiber was imported, primarily from the United States. This year, 72.6% of China’s optical fiber will be produced by Chinese companies, which are also exporting a growing amount of fiber around the world.
John Lively, principal analyst at LightCounting Market Research, predicts China could conquer the fiber market in just a few short years and become a global broadband leader, “exporting their broadband networking expertise and technology, just like it does with its energy and transportation programs.”
Meanwhile in the United States, customers will be arguing with Comcast about the accuracy of their usage meter in light of a 300GB usage cap and Frontier’s DSL customers will still be fighting to get speeds better than the 3-6Mbps they get today.



 Subscribe
Subscribe To complete an acquisition of landline assets in California, Florida, and Texas from Verizon Communications, Frontier Communications is hoping to raise
To complete an acquisition of landline assets in California, Florida, and Texas from Verizon Communications, Frontier Communications is hoping to raise  Californian consumers are among those most concerned about a Frontier takeover of landline and FiOS service. Verizon ventured far beyond its original service area extending from Maine to Virginia after it acquired independent telephone networks operated by General Telephone (GTE) and Continental Telephone (Contel) in 2000. In 2015, the company wants to return to its core landline service area in the northeast.
Californian consumers are among those most concerned about a Frontier takeover of landline and FiOS service. Verizon ventured far beyond its original service area extending from Maine to Virginia after it acquired independent telephone networks operated by General Telephone (GTE) and Continental Telephone (Contel) in 2000. In 2015, the company wants to return to its core landline service area in the northeast. David Lazarus, a consumer reporter for the Los Angeles Times,
David Lazarus, a consumer reporter for the Los Angeles Times,  As AT&T and Verizon ponder ditching high-cost landline customers, so long as there are companies like Frontier willing to buy, the deal works for both. Verizon gets a tax-free transaction that benefits both executives and shareholders. An already debt-laden Frontier satisfies shareholders by growing the business, which usually makes the balance sheet look good each quarter.
As AT&T and Verizon ponder ditching high-cost landline customers, so long as there are companies like Frontier willing to buy, the deal works for both. Verizon gets a tax-free transaction that benefits both executives and shareholders. An already debt-laden Frontier satisfies shareholders by growing the business, which usually makes the balance sheet look good each quarter. Those losses have to be reflected somewhere, and customers complain they are paying the highest price.
Those losses have to be reflected somewhere, and customers complain they are paying the highest price. 


 Cox plans to limit its gigabit customers to 2TB of usage a month. AT&T U-verse with GigaPower has a (currently unenforced) limit of 1TB a month, while Suddenlink thinks 550GB is more than enough for its gigabit customers. Comcast is market testing 300GB usage caps in several cities but strangely has no usage cap on its usage-gobbling gigabit plan. Why cap the customers least-equipped to run up usage into the ionosphere while giving gigabit customers a free pass? It doesn’t make much sense.
Cox plans to limit its gigabit customers to 2TB of usage a month. AT&T U-verse with GigaPower has a (currently unenforced) limit of 1TB a month, while Suddenlink thinks 550GB is more than enough for its gigabit customers. Comcast is market testing 300GB usage caps in several cities but strangely has no usage cap on its usage-gobbling gigabit plan. Why cap the customers least-equipped to run up usage into the ionosphere while giving gigabit customers a free pass? It doesn’t make much sense.
 The abuses were so bad, Congress finally stepped in and authorized regulators to break up the railroad monopolies and regulate abusive pricing. We may be headed in the same direction with broadband. We do not advocate regulation for the sake of regulation. Competition is a much more efficient way to check abusive business practices. But where an effective monopoly or duopoly exists, competition alone will not help. Without consumer-conscious oversight, the forthcoming gigabit broadband revolution will be stalled by speed bumps and toll booths for the benefit of a few giant telecommunications corporations. That will allow other countries to once again leap ahead of the United States and Canada, just as they have done with Internet speeds, delivering superior service at a lower price.
The abuses were so bad, Congress finally stepped in and authorized regulators to break up the railroad monopolies and regulate abusive pricing. We may be headed in the same direction with broadband. We do not advocate regulation for the sake of regulation. Competition is a much more efficient way to check abusive business practices. But where an effective monopoly or duopoly exists, competition alone will not help. Without consumer-conscious oversight, the forthcoming gigabit broadband revolution will be stalled by speed bumps and toll booths for the benefit of a few giant telecommunications corporations. That will allow other countries to once again leap ahead of the United States and Canada, just as they have done with Internet speeds, delivering superior service at a lower price.
 Verizon is ready to push speeds beyond 1Gbps on its fiber to the home network FiOS, after
Verizon is ready to push speeds beyond 1Gbps on its fiber to the home network FiOS, after