 Comcast told the New York Public Service Commission that the overwhelming majority of the substantive comments submitted to the regulator “express a strong desire and enthusiasm for the improved and expanded voice, data, video, and broadband services” that the merger of Comcast and Time Warner Cable will bring to the state.
Comcast told the New York Public Service Commission that the overwhelming majority of the substantive comments submitted to the regulator “express a strong desire and enthusiasm for the improved and expanded voice, data, video, and broadband services” that the merger of Comcast and Time Warner Cable will bring to the state.
 “Given these many concrete benefits, and the lack of any harm to competition or consumers, it should come as no surprise that the overwhelming majority of the substantive comments (approximately 110 out of a total of about 140 substantive comments) filed in this proceeding support Commission approval of the transaction,” Comcast wrote in its latest submission.[1]
“Given these many concrete benefits, and the lack of any harm to competition or consumers, it should come as no surprise that the overwhelming majority of the substantive comments (approximately 110 out of a total of about 140 substantive comments) filed in this proceeding support Commission approval of the transaction,” Comcast wrote in its latest submission.[1]
Comcast’s “new math” applies a subjective (and undisclosed) standard about what constitutes “substantive,” but in the end the cable company has urged the Commission to disregard the sentiments of more than 2,700 New York State residents who have filed comments in strong opposition to the merger because their remarks simply fell beneath Comcast’s standards.
“The minority of organizations and individuals who filed substantive comments opposing the transaction largely ignore the significant public interest benefits of the transaction,” writes Comcast. “Instead, these detractors raise issues that are not relevant to the transaction and are factually inaccurate and speculative – such as unfounded concerns about Comcast’s broadband management practices, misplaced criticisms of Internet Essentials, and general fears that ‘big is bad.’ None of these commenters identify any reasonable basis to reject or condition the Joint Petition.”
Comcast did not apply the same rigorous standards of ‘substantiveness’ to comments sent by its supporters, who often used what New York Assemblyman Joe Morelle admitted was a Comcast-supplied template ghost-written by the company itself.[2]
“Supporters of the transaction span a wide range of groups and individuals, including governmental officials (e.g., mayors, town supervisors, county commissioners, city councils, state legislators, and school superintendents); businesses and non-profits; state and local organizations focused on economic development; community service, youth and family, and diversity organizations; arts and education groups; and others,” writes Comcast.
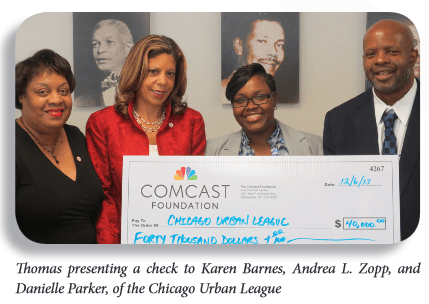 But the company never disclosed the many financial ties between Comcast and its political and civic supporters. In fact, a large percentage of the “template” letters of support originated from politicians like Assemblyman Morelle, who recently received a $1,000 check from Comcast[3] and Rochester city councilman Adam McFadden, whose group claims to receive $50,000 annually from Comcast.[4] [5]
But the company never disclosed the many financial ties between Comcast and its political and civic supporters. In fact, a large percentage of the “template” letters of support originated from politicians like Assemblyman Morelle, who recently received a $1,000 check from Comcast[3] and Rochester city councilman Adam McFadden, whose group claims to receive $50,000 annually from Comcast.[4] [5]
In fact, it is hard not to find financial connections between Comcast’s supporters and the cable company itself. A random sampling uncovers multiple instances of Comcast contributions that were followed by letters of support for its merger:
The Urban League has received at least $12 million in in-kind contributions from Comcast since 2007, in addition to direct financial contributions to local chapters around Comcast’s service area.[6] In just one example Stephen Thomas, Comcast’s area vice president, who also serves on the Chicago chapter’s board of directors, presented the organization with a check for $40,000.[7] Just a few months later, Andrea L. Zopp, president of the Chicago Urban League, wrote to urge the FCC to approve Comcast’s merger deal.[8]
“Comcast is a strong supporter of the Urban League movement throughout the country. … I sincerely ask that you approve this transaction so that the Urban Leaguers and everyone else can benefit,” Zopp wrote.
Various chapters of the Boys and Girls Club also submitted glowing letters in favor of the merger. Comcast has partnered with local Boys & Girls Clubs since 2000, providing more than $68 million in cash and in-kind contributions. But no chapter was willing to openly admit Comcast asked them to share their views with New York regulators and only a few disclosed the financial ties the organization has with Comcast. The Boys and Girls Club has been a very loyal supporter of whatever Comcast has on its corporate agenda. Chapters submitted letters urging regulators to approve the Comcast-NBC merger in 2010 as well.[9]
Another strong supporter Comcast quotes from in its filing is the National Black Chamber of Commerce. But they don’t mention Comcast is a corporate sponsor of the group.[10]
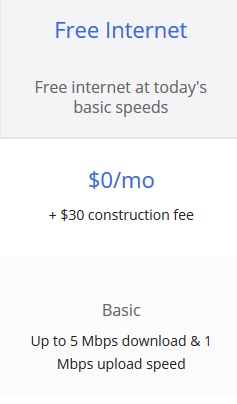
Comcast (falsely) claims their $9.95 Internet Essentials is the country’s only discount Internet program for the disadvantaged. But Google Fiber gives it away for free to anyone who wants it.
Comcast also called criticism of its Internet Essentials discount Internet program “inaccurate and unavailing,” despite the fact the company’s own senior vice president David Cohen admitted the program was stalled to use as a political chip to win approval of its merger with NBCUniversal.[11]
Comcast also falsely claims it is the only Internet discount program for the poor of its kind.
“[Critics] simply advocate a different broadband adoption program – one that no company has ever implemented, that has never been attempted or even analyzed, and that may not be equally sustainable or popular or easy to publicize,” Comcast wrote. “Comcast is the only company to offer a program of this kind, and it has continually and voluntarily expanded the scope, breadth, and eligibility for and benefits of the program.”
In fact, it may have escaped Comcast’s attention that Google has provided residents in their fiber service areas with free Internet service with absolutely no income qualification or needs test, after paying a “construction fee” ranging from $30 in Provo, Utah [12] to $300 in Kansas City.[13] Residents in the latter community can break the somewhat steep construction fee into 12 payments of $25 each and have a guarantee of free service for up to seven years. Over the course of both programs, Google offers a more compelling and less expensive offer without onerous qualification requirements.
Yr Google Fiber Cost Comcast Internet Essentials Cost (@$9.95/mo)
1 $300 $119.40
2 $0 $119.40
3 $0 $119.40
4 $0 $119.40
5 $0 $119.40
6 $0 $119.40
7 $0 $119.40
Over the course of seven years, a Google Fiber customer selecting discounted Internet would pay $300. A Comcast customer would pay $835.80 – a difference of $535.80.
While Google Fiber’s service area is very limited, it does offer an evidence-based challenge to Comcast’s inaccurate claim that its Internet Essentials program is unprecedented and represents the best solution for New York. A well-designed program designed to help New Yorkers will sell itself far better than the complicated, restrictive, and revenue-protection-oriented Internet Essentials, and its lack of penetration in long-standing Comcast service areas speaks for itself.
The California Emerging Technologies Fund also found serious problems with Internet Essentials from top to bottom.[14]
“Comcast makes the sign-up process long and cumbersome,” CETF claimed.[15] “The application process often takes 2-3 months, far too long for customers who are skeptical about the product in the first place, and have other pressing demands on their budgets. The waiting period between the initial call to Comcast and the CIE [Comcast Internet Essentials] application arriving in the mail can stretch 8-12 weeks, if it comes at all. After submitting the application, another 2-4 weeks elapse before the equipment arrives. Many low-income residents do not have Social Security Numbers (SSNs) and are required to travel long distances to verify their identities because Comcast has closed many of its regional offices. Recently, some potential subscribers with SSNs were rejected over the phone and told they had to visit a Comcast office. Comcast has a pilot effort in Florida that should be expanded to allow customers to fax or e-mail photocopied IDs as proof of identification.”
CETF also found widespread violations of Comcast’s own program rules when the cable company conducted credit checks on customers, which can reduce a customer’s already challenged FICO score with a credit inquiry on their file.
“Comcast conducts credit checks for some customers, contrary to CIE rules,” the CETF filing said. “Dozens of clients are receiving letters from Comcast saying that they have failed a credit check. Comcast specifically states and advertises no credit check is needed for CIE. This has repercussions beyond obtaining broadband service. The act of performing a credit check can negatively impact the consumer’s credit worthiness. Initially, some CIE service representatives told customers they could pay $150 deposit to avoid a credit check, also contrary to program rules.”
Customers have also been redirected to Comcast sales call centers, where they receive aggressive sales pitches for higher-cost products and services.
Comcast’s celebration of its commitment to minority television programming does not mention the expansion of minority programming was a condition of the FCC’s approval of the Comcast-NBCUniversal merger.

Among Comcast’s “compelling” minority programming that customers are asked to pay for: Baby First Americas, a network for bilingual infants aged 0 to 3.
Subscribers got less than compelling programming and more rate increases to pay for it.
National Public Radio noted Comcast’s new minority channels are not exactly drawing significant audiences[16]:
Out of the gate, well, first was Baby First America — for bilingual infants aged 0 to 3.

ASPiRE, a channel focused on African-Americans, is mostly reruns and talk shows. Writer Anita Wilson Pringle called the network’s programming “crap.”
Next came Aspire, a family-oriented network from ex-basketball star and entertainment impresario Magic Johnson. Its lineup includes reruns of The Cosby Show plus even older fare: Julia, Soul Train and The Flip Wilson Show.
Writer Anita Wilson Pringle, for one, is no fan of that lineup of TV retreads.
“He promised innovative, new fresh ideas, new fresh programming, and it’s not,” she says.
Pringle is upset that Aspire’s managers were merely reshuffled from the old Gospel Music Channel. And she says the people Aspire is supposed to serve — African Americans — don’t exactly need more reruns or talk shows.
“It’s crap, if you really want to know the truth,” she says. “But my thing is, they did this to break that monopoly that Comcast was having on all these stations, and all that has happened is that Comcast has a stronger monopoly.”
Comcast’s commitment to improve energy efficiency is comparable to Time Warner Cable’s own commitments, providing no net gain for New York consumers.[17]
Comcast’s promised commitments to deliver better customer service have been made annually for several years with no significant improvement, as measured by independent customer satisfaction studies. Comcast relies on a quotation from a Wall Street analyst, Craig Moffett, who provides only anecdotal evidence of customer service improvements and has supported the merger’s potential benefits for shareholders.

Comcast’s idea of effective competition is using your Verizon Wireless connection for home broadband use. A 16GB monthly plan will cost consumers as much as $170 a month before taxes and fees.
Comcast’s assertion that the Commission should ignore or downplay bad customer service experiences of customers outside New York is made despite their own admission they serve only a tiny number of New York customers today. Is Comcast suggesting it would be inappropriate to consider their customer service record in comparable-sized cities across the country, some likely served by the same national and offshore customer care centers New Yorkers will reach when they have future problems with Comcast?
Comcast’s claims of plentiful broadband competition also do not exist in the real world for many New Yorkers. The Commission has faced such a large number of complaints about Verizon landline service, which also supports DSL, it launched a Verizon Service Quality Improvement Plan. When a Verizon landline becomes inoperable for several months, as customers in Inwood experienced earlier this year[18], their DSL broadband is also inoperable. For customers served by cable, but not reached by DSL service from telephone companies like Verizon, Windstream, and Frontier Communications, their only realistic home broadband connection comes from the local cable company. Wireless broadband, advocated as a competitive alternative by Comcast, does not penetrate well indoors in large sections of rural upstate New York and is constrained by very expensive service plans and severe limits on data usage, compelling customers to pay excessive fees to obtain service.
A family consuming 16GB of data per month (less than today’s average use per person) would face Internet bills of $170 a month with Verizon Wireless ($40/mo Monthly Line Access – Internet Device + 16GB Data Plan ($130/mo Monthly Account Access)[19] Wired broadband accounts from Time Warner Cable in comparison cost as little as $14.99 a month for unlimited usage.
Where DSL service is available, it is typically offered at speeds lower than a cable operator can offer. As an example, at our residence in the Town of Brighton, N.Y., Frontier Communications can only offer a maximum speed of 3.1Mbps from their DSL service because of our distance from the central office.
Comcast will have a near-total monopoly on all broadband service in excess of 15Mbps in current Time Warner Cable territories not serviced by Verizon FiOS. Verizon’s maximum speed DSL offer is for speeds “up to 15Mbps.”[20] Verizon FiOS expansion outside of already-committed territories has ended, and the majority of upstate New York is not served by Verizon’s FiOS fiber upgrades.
Comcast claims there is a world of difference between highly regulated energy-generation utilities and the “competitive” marketplace for telecommunications.
“Proposals that the Commission approach this transaction with the same mindset, and apply the same types of burdensome conditions, are entirely unjustified,” argues Comcast.
“Electric and gas utilities remain the quintessential public service utilities,” says the cable company. “Their markets are characterized by a lack of competition, captive customer bases, and direct rate-setting and operational oversight by the Commission.”
In fact, many cable customers in New York do face a lack of competition for fast broadband speeds, are stuck with the single cable operator serving their community, and lack the consumer protections offered by the Commission that apply to other utilities.
The Commission can test Comcast’s claims of competitiveness for itself. Stop the Cap! offers a challenge to find more than one provider that can deliver consistent, widely obtainable broadband speeds of 15/3Mbps or greater in downtown Buffalo, Rochester, Albany or Syracuse.
The Commission will discover there is only one provider now capable of delivering that service across the entire urban centers of upstate New York: the local cable company.
In far western New York, Verizon FiOS is available only in small parts of South Buffalo and North Buffalo and select suburbs.
In Rochester, Frontier Communications does not offer consistent access to speeds greater than 10Mbps.
Albany and Syracuse are also bypassed by Verizon FiOS, left with Verizon DSL, which only offers speeds “up to 15/1Mbps.” Most customers get less.
Comcast would have the Commission believe any review of its broadband service is off-limits and outside of their jurisdiction anyway.
“The Commission has no authority to review broadband transactions and lacks statutory authority to regulate broadband services – and beyond this, cable broadband services are interstate information services that are not properly subject to state jurisdiction,” claimed Comcast.
It further argued the Commission must ignore “matters beyond the Commission’s jurisdiction,” quoting from a 2006 proceeding.
 Comcast evidently forgets the law has changed in New York. In 2006, the Commission had to disprove a petition was in the public interest to reject it. In 2014, the applicant is solely responsible for carrying the burden of proof that their proposal is in the public interest.
Comcast evidently forgets the law has changed in New York. In 2006, the Commission had to disprove a petition was in the public interest to reject it. In 2014, the applicant is solely responsible for carrying the burden of proof that their proposal is in the public interest.
Nothing in Section 222 of the Public Service Law places restrictions on what the Commission can consider when weighing public interest benefits.
Comcast’s claims of its wish to expand service into rural, unserved areas also must be questioned. Comcast automatically sets a high bar for expansion suggesting it will occur only “where economically feasible,” which is the same standard in place with the incumbent cable operator.
“Where economically feasible” is the reason cable companies in New York have rarely expanded their service territories, except in high growth areas where population density warrants expansion. All cable operators have an internal formula governing Return On Investment requirements that must be met before expansion begins. The Commission must review that information and compare the standards used by both applicants, because it will ultimately govern any future natural expansion of cable service in rural New York.
Conclusion
Comcast’s rosy picture of New York’s future with a merged Time Warner Cable-Comcast is belied by the real world experiences of New York consumers who have learned from long, hard experience that when a cable company starts promising a better deal, the result has too often been higher rates and fees, unwanted channels, poorer customer service, and new restrictions.

Don’t close your eyes to the facts.
Cable operators have enjoyed unfettered power to escape oversight with inflated claims of fierce competitiveness that they suggest will keep prices and abusive behavior in check, but in reality rates are rising and Comcast’s customer approval ratings live in the basement.
Comcast’s most recent filing continues to dismiss these very real concerns for New Yorkers who will not have a choice of a cable operator other than Time Warner Cable or Comcast. Calling the comments of more than 2,700 New Yorkers largely opposed to this merger “unsubstantive” is precisely the attitude of a cable company that has earned its bad reputation with customers.
Sending “templates” to politicians and non-profits that have received funding from Comcast and asking them to send letters to regulators urging approval of the company’s latest item on the agenda is the kind of “substantive” evidence Comcast wants the Commission to rely on in this proceeding.
But worst of all, Comcast suggests that any review of the company’s broadband service, its pricing and performance, and the potential for usage allowances and usage fees above and beyond the current high cost of Internet service is off-limits to New York regulators. The Commission already recognizes the growing importance of broadband in New York State and that it is, in reality, nearly a necessity.
Time Warner Cable recognizes that and is moving ahead on an upgrade program that delivers broadband benefits above those offered by Comcast and at a lower price, with no usage allowances or overlimit fees likely in the foreseeable future. It remains clear to us that Time Warner Cable is the better choice for New York. We have a well-documented history of not being great fans of Time Warner Cable, but we know worse when we see it, and we see it in Comcast.
[1] http://documents.dps.ny.gov/public/Common/ViewDoc.aspx?DocRefId={60D7F65E-3AAB-4507-B58D-7F14E31E130A}
[2] http://www.rochesterfirst.com/news/lawmakers-write-letters-supporting-comcast-deal/190434972
[3] http://www.rochesterfirst.com/news/lawmakers-write-letters-supporting-comcast-deal/190434972
[4] http://stopthecap.com/2014/08/11/rochester-city-councilman-adam-mcfaddens-love-for-comcast-and-the-50k/
[5] http://www.nlc.org/corporate-partnership-program/corporate-partners-program
[6] https://corporate.comcast.com/news-information/news-feed/national-urban-league-resource
[7] https://www.thechicagourbanleague.org/cms/lib07/IL07000264/Centricity/Domain/14/impact-jan-2014.pdf
[8] https://www.thewrap.com/consumer-groups-urge-fcc-to-reject-comcast/time-warner-cable-deal/
[9] https://ecfsapi.fcc.gov/file/7020462210.pdf
[10] https://www.nationalbcc.org/news/progress-reports/2107-recap-of-22nd-annual-conference
[11] http://stopthecap.com/2013/07/10/comcasts-internet-essentials-facade-padding-the-bottom-line-without-cannibalizing-your-base/
[12] https://fiber.google.com/legal/schedule/
[13] https://fiber.google.com/legal/schedule/
[14] https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2014/07/comcasts-internet-for-the-poor-too-hard-to-sign-up-for-advocates-say/
[15] http://www.cetfund.org/files/140711_CETF_Partners_Comcast-TWC_FCC_PR_and_Filing.pdf
[16] http://www.npr.org/2013/11/12/244558834/comcast-deal-puts-new-minority-run-channels-in-play
[17] http://www.timewarnercable.com/en/about-us/corporate-responsibility/environment.html
[18] http://manhattan.ny1.com/content/shows/ny1_for_you/203064/ny1foryou–inwood-verizon-customers-want-phone-service-outages-to-stop
[19] http://www.verizonwireless.com/wcms/consumer/shop/shop-data-plans/more-everything.html
[20] https://www.verizon.com/?lid=//global//residential
 But Frontier’s “flash cut” conversions in West Virginia and Connecticut led to months of serious service and billing problems leading to two state-level investigations into Frontier’s performance. Problems are still ongoing in parts of Connecticut several months after Frontier transferred Connecticut territories from AT&T. Customers in West Virginia continue to criticize Frontier Communications for its underwhelming broadband performance.
But Frontier’s “flash cut” conversions in West Virginia and Connecticut led to months of serious service and billing problems leading to two state-level investigations into Frontier’s performance. Problems are still ongoing in parts of Connecticut several months after Frontier transferred Connecticut territories from AT&T. Customers in West Virginia continue to criticize Frontier Communications for its underwhelming broadband performance.

 Subscribe
Subscribe

 Verizon spokesman Rick Young countered that Verizon has offered workers a straight 4% wage increase but admitted many existing contract provisions are decades old and no longer reflect current business reality. Young added Verizon union network technicians are paid $160,000 a year on average in total compensation, including salary, pension and health care. But Verizon management is insistent on cutting back the company’s health care costs, noting Verizon successfully reduced the cost of covering nonunionized workers to about $16,700 per family while union workers still receive coverage worth $20,000-24,000 a year per family.
Verizon spokesman Rick Young countered that Verizon has offered workers a straight 4% wage increase but admitted many existing contract provisions are decades old and no longer reflect current business reality. Young added Verizon union network technicians are paid $160,000 a year on average in total compensation, including salary, pension and health care. But Verizon management is insistent on cutting back the company’s health care costs, noting Verizon successfully reduced the cost of covering nonunionized workers to about $16,700 per family while union workers still receive coverage worth $20,000-24,000 a year per family.

 “The deal allows Verizon to raise basic landline phone rates 36 percent over the next five years and it allows them to raise business line rates over 20 percent over the next five years,” said Seth Hahn, a CWA staff representative. Beyond that, the sky is the limit.
“The deal allows Verizon to raise basic landline phone rates 36 percent over the next five years and it allows them to raise business line rates over 20 percent over the next five years,” said Seth Hahn, a CWA staff representative. Beyond that, the sky is the limit.
 In Laurel Springs, customers have largely fled Verizon for Comcast, which is usually the only provider of broadband in the area. A package including broadband and phone service costs less than paying Verizon for a landline and Comcast for Internet access, so Verizon landline disconnects in the town are way up.
In Laurel Springs, customers have largely fled Verizon for Comcast, which is usually the only provider of broadband in the area. A package including broadband and phone service costs less than paying Verizon for a landline and Comcast for Internet access, so Verizon landline disconnects in the town are way up.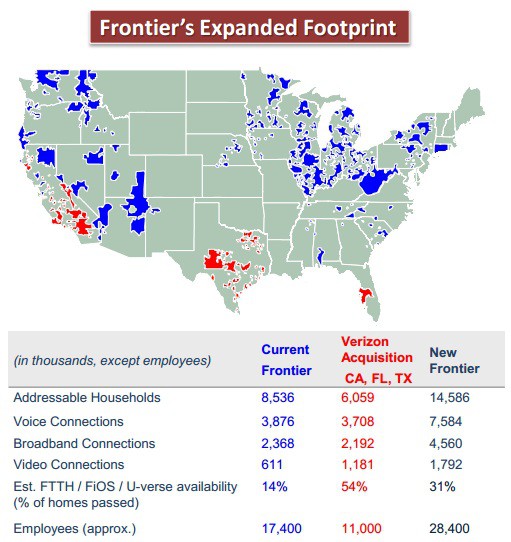
 Comcast told the New York Public Service Commission that the overwhelming majority of the substantive comments submitted to the regulator “express a strong desire and enthusiasm for the improved and expanded voice, data, video, and broadband services” that the merger of Comcast and Time Warner Cable will bring to the state.
Comcast told the New York Public Service Commission that the overwhelming majority of the substantive comments submitted to the regulator “express a strong desire and enthusiasm for the improved and expanded voice, data, video, and broadband services” that the merger of Comcast and Time Warner Cable will bring to the state. “Given these many concrete benefits, and the lack of any harm to competition or consumers, it should come as no surprise that the overwhelming majority of the substantive comments (approximately 110 out of a total of about 140 substantive comments) filed in this proceeding support Commission approval of the transaction,” Comcast wrote in its latest submission.[1]
“Given these many concrete benefits, and the lack of any harm to competition or consumers, it should come as no surprise that the overwhelming majority of the substantive comments (approximately 110 out of a total of about 140 substantive comments) filed in this proceeding support Commission approval of the transaction,” Comcast wrote in its latest submission.[1] But the company never disclosed the many financial ties between Comcast and its political and civic supporters. In fact, a large percentage of the “template” letters of support originated from politicians like Assemblyman Morelle, who recently received a $1,000 check from Comcast[3] and Rochester city councilman Adam McFadden, whose group claims to receive $50,000 annually from Comcast.[4] [5]
But the company never disclosed the many financial ties between Comcast and its political and civic supporters. In fact, a large percentage of the “template” letters of support originated from politicians like Assemblyman Morelle, who recently received a $1,000 check from Comcast[3] and Rochester city councilman Adam McFadden, whose group claims to receive $50,000 annually from Comcast.[4] [5]



 Comcast evidently forgets the law has changed in New York. In 2006, the Commission had to disprove a petition was in the public interest to reject it. In 2014, the applicant is solely responsible for carrying the burden of proof that their proposal is in the public interest.
Comcast evidently forgets the law has changed in New York. In 2006, the Commission had to disprove a petition was in the public interest to reject it. In 2014, the applicant is solely responsible for carrying the burden of proof that their proposal is in the public interest.
