
Some Clearwire customers remain unhappy when speeds are throttled to “manage” the network.
Clear (formerly known as Clearwire) has announced a general rate increase of about 10 percent for customers using its legacy 4G WiMAX broadband service.
As a result, most customers will pay about $5 more per month for fixed wireless or “on the go” broadband service.
“We instituted this to remain competitive and manage our costs,” a Sprint representative told Broadcasting & Cable. “Like our competitors, we must respond to customer trends, and provide a good user experience, and as a result we will make adjustments to fees and services from time to time. Our offer is still comparable to other offerings in the marketplace.”
Some customers would argue with Sprint’s definition of a “good user experience,” as complaints continue about heavy-handed throttling of Clear’s service that makes high bandwidth applications painful or impossible to use in the evening.
Stop the Cap! reader Akos contacted us this week to complain Clear still advertises and contracts for “unlimited data and top speeds,” while not exactly being upfront about targeting certain traffic for a prime time speed throttle that effectively keeps customers from streaming video.
“They openly admit their service is being throttled by software at each tower site that activates when it detects streaming video services like Netflix, reducing speed from 1.3Mbps to as little as 20kbps, rendering it unusable,” said Akos.
The speed throttle is usually active from 8pm-1:30am daily, when traffic is anticipated to be highest. Clear speaks about its network management speed throttle in the fine print: its Acceptable Use Policy.
Akos complains Clear’s speed throttle makes it easy to blame the streaming service, not Clear itself, because customers running speed tests will not see throttled speeds.
“It fools people to think the problem is on their end or with the streaming service, so customers don’t complain to Clear,” says Akos.
As a result, people using streaming video services get about 30 seconds of uninterrupted video before the throttle kicks in bringing extensive buffering delays.
Clearwire’s Speed Throttle Subject of Lawsuits
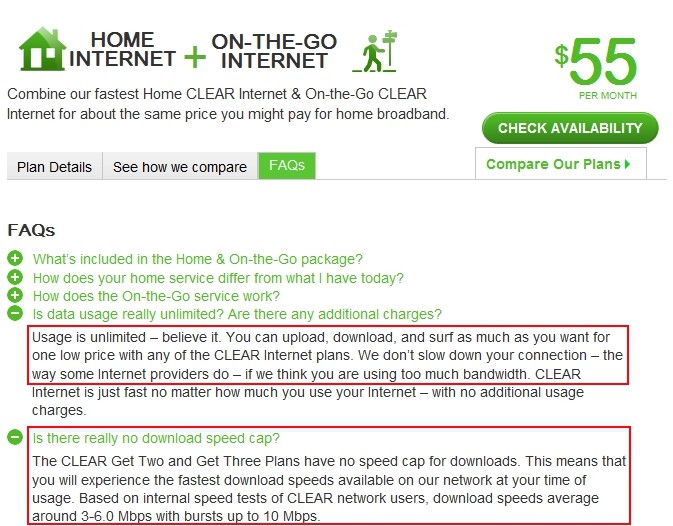
Clear’s own 2010 marketing promises unlimited usage with no speed reductions, like those “other” providers.
Clearwire’s speed throttle has been a part of life with the wireless service since 2010. Clearwire had significant legal exposure over its choice of network management because the company routinely advertised “unlimited service” with no speed throttles or overlimit fees. At least three lawsuits were filed against the company for its undisclosed throttling practices, eventually condensed into a single class action case that was finally settled last month.
Under the terms of the settlement, Clear admits no wrongdoing, but will clearly disclose it uses “network management” practices — a term that generally means usage caps and/or speed throttles — and will give customers information about the speeds they can expect when the throttle is active. As of today, Clear has not done that. Clear also volunteered to suspend term contracts and waive early termination fees for customers complaining about speed issues.
At least seven law firms handling the case will split a total award fee of $1,887,792.91 and expenses of $62,207.09. Individual representative plaintiffs each receive up to $2,000. Everyone else identified as part of the class action case that returned a claim form prior to Jan. 3, will receive an average of less than $30:
- a 50% refund of any early termination fee charged after a customer canceled service because of speed throttling;
- a rebate of $14 for customers signing up for Clearwire before Sept. 1, 2010 and experiencing speed throttling or a rebate of at least $7 for Clearwire customers signing up on or after Sept. 1, 2010;
- plus varying amounts for each month of service prior to Feb. 27, 2012 during which Clearwire’s records show it throttled a customer’s Internet speed. Customers throttled at 0.25Mbps will receive $5.00 for each month throttled, 0.60 Mbps: $3.00, and 1.0 Mbps: $2.00.
Court documents reveal of the 2,733,406 customers identified in Clearwire’s records as being speed throttled, only 83,840 submitted timely claims as part of the class action case. This represents a claims rate of about 3.1%. Of those, 76,199 were for speed throttling, 2,331 were requests for reimbursement of early termination fees.
The Future of Clear’s WiMAX and Sprint’s 4G

Sprint purchased the assets of Clearwire Corporation in July, rebranded the network “Clear,” and as of the end of August, stopped selling WiMAX devices to customers. Although Clear will still activate existing equipment, potential new customers are being marketed broadband plans on the Sprint network instead.
Former Clear dealers have received word Sprint plans to eventually decommission its acquired WiMAX network as early as 2014, most likely by gradually converting portions of the 2.5GHz spectrum Clear’s WiMAX service now uses in favor of Sprint’s 4G LTE service in urban and high congestion areas. Clearwire itself was in the process of adopting a variant of 4G LTE technology that would gradually replace the outdated WiMAX standard when Sprint acquired the company.
Although Sprint runs its own 3G network, it partnered with Clearwire to provide 4G WiMAX for Sprint customers. In 2011, Sprint announced it would stop selling devices with built-in support for WiMAX and announced it would launch its own 4G LTE network. Sprint will adopt the same version of LTE other North American carriers are using: FD-LTE, or Frequency Division LTE, which requires one transmit channel and one receive channel. But it will also support and continue Clearwire’s upgrade to TD-LTE, or Time Division LTE, a slightly different standard that supports receiving and transmitting signals on a single frequency at slightly different time intervals, providing enhanced spectrum efficiency. At least 5,500 towers should be active with TD-LTE service by the end of this year. End users will care only to the extent their devices support one or both standards.
Sprint’s 4G LTE rollout will depend primarily on higher frequency spectrum that is disadvantageous indoors and over extended distances. Sprint’s competitors AT&T and Verizon Wireless primarily depend on lower 700MHz frequencies that penetrate buildings better and can serve a larger coverage area. But a combination of Sprint and Clearwire’s spectrum assets give Sprint the most wireless spectrum of any U.S. carrier, which means potentially faster speeds and more capacity.
- 1900MHz: Sprint’s primary 4G FD-LTE service is now available in 151 cities on more than 20,000 cell towers;
- 2500MHz: Now used by Clear’s legacy WiMAX network, will see a transition towards Sprint’s TD-LTE service which will be targeted to urban and high congestion areas from “small cell” sites;
- 800MHz: The former home of now-shuttered Nextel, Sprint will eventually launch FD-LTE service on this band which will offer better indoor and marginal area reception.
Customers can expect devices that support both FD-LTE and TD-LTE in 2014.




 Subscribe
Subscribe



 A new research report issued by Time Warner Cable concludes cell phone companies like AT&T and Verizon Wireless cannot meet the future data demands of customers over their 4G LTE wireless networks without punitive usage caps and high fees to deter usage, even with new spectrum becoming available for the wireless industry’s use.
A new research report issued by Time Warner Cable concludes cell phone companies like AT&T and Verizon Wireless cannot meet the future data demands of customers over their 4G LTE wireless networks without punitive usage caps and high fees to deter usage, even with new spectrum becoming available for the wireless industry’s use. “Given a choice, more than 80 percent of tablet, laptop, and eReader owners would either prefer Wi-Fi to mobile access, or have no preference,” Cisco concluded. “And, just over half of smartphone owners would prefer to use Wi-Fi, or are ambivalent about the two access networks.”
“Given a choice, more than 80 percent of tablet, laptop, and eReader owners would either prefer Wi-Fi to mobile access, or have no preference,” Cisco concluded. “And, just over half of smartphone owners would prefer to use Wi-Fi, or are ambivalent about the two access networks.”
 Comcast
Comcast 
