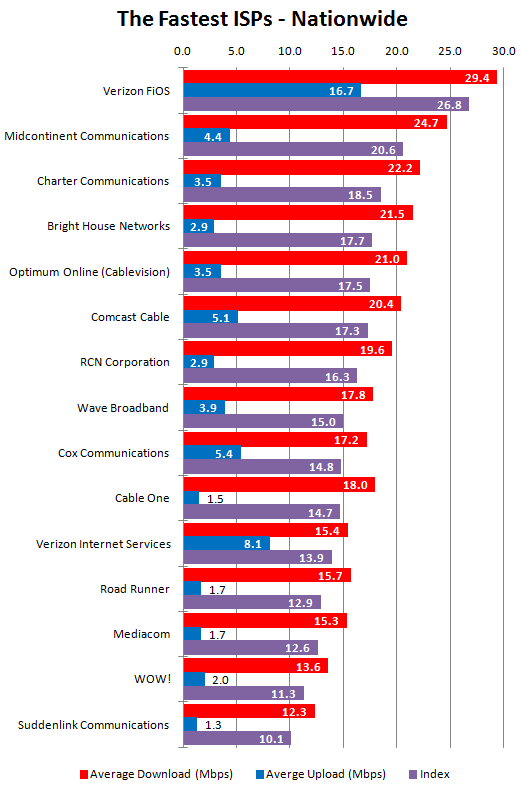
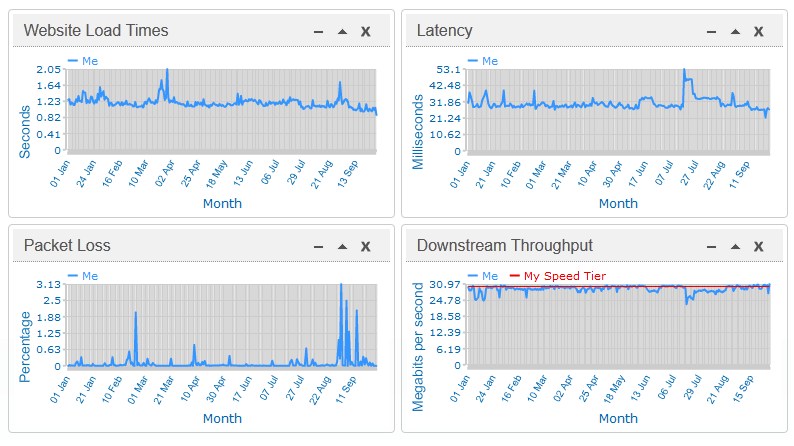
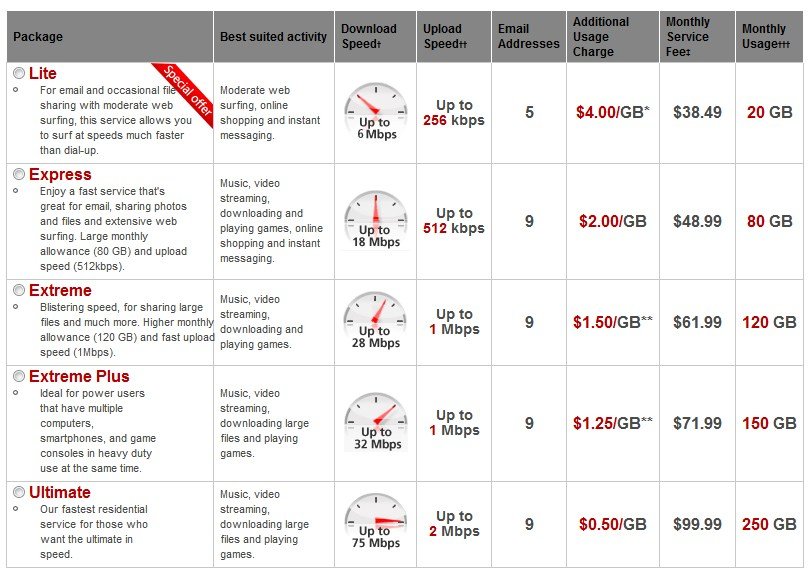
Even as DOCSIS 3 cable technology continues to roll-out across cable systems now offering faster Internet speeds, the next generation of cable broadband is on the way, reportedly capable of delivering up to 10/2Gbps service.
Even as DOCSIS 3 cable technology continues to roll-out across cable systems now offering faster Internet speeds, the next generation of cable broadband is on the way, reportedly capable of delivering up to 10/2Gbps service.
CableLabs’ DOCSIS 3.1 project will be the subject of a special panel at an upcoming cable engineer conference later this month.
“DOCSIS 3.1 specification development is a significant milestone on the industry’s road map to next-generation services,” said CableLabs chief technology officer Ralph Brown. “Our SCTE Cable-Tec Expo panel will identify the motivations, requirements and key technology building blocks under development with the collaboration of the vendor community. DOCSIS 3.1 solutions will provide both residential and commercial cable customers with faster data rates — both upstream and downstream — that support increasingly compelling broadband services.”
The new standard will incorporate changes in how cable spectrum is utilized for broadband, vastly expanding potential bandwidth. Although the standard can support gigabit broadband speeds, nobody expects cable companies to offer those speeds in the near term.
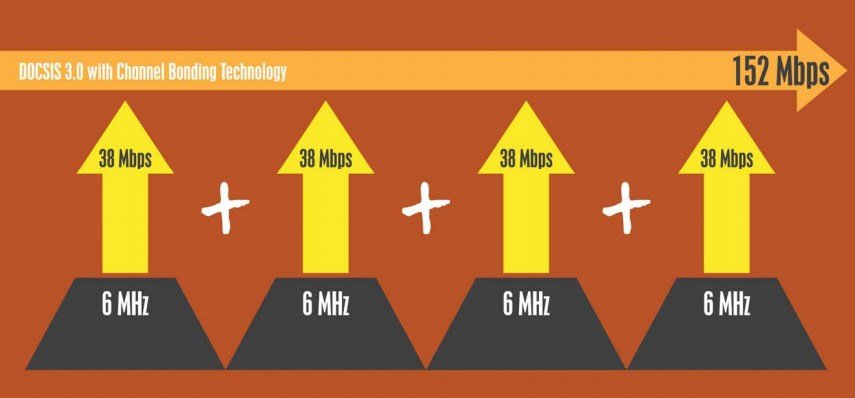
Instead, providers are more interested in addressing their upstream speed limitations. From the earliest days of cable broadband, the assumption was that customers would care far more about downstream speeds and consider uploading an afterthought. The result was a network that prioritized download speed. But as users continue to upload more multimedia content and embrace cloud storage, slow upload speeds are starting to aggravate customers.
DOCSIS 3.1 is rumored to de-emphasize the current QAM modulation cable operators use for broadband in favor of more robust technologies such as orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM), already used by the wireless industry. Unlike interference/noise-prone QAM, OFDM uses much smaller subcarriers that work better in noisy signal conditions. Although coaxial cable is capable of delivering a large amount of spectrum to cable operators, all of it cannot be practically used because of external interference from electrical equipment, broadcast radio and television signals, and other sources. Error-correcting technologies can let operators use more of their available spectrum without reducing the quality of service to customers.
The study group working on DOCSIS 3.1 is also reviewing the incorporation of “low density parity-check” (LDPC) error correction that would efficiently improve noise rejection over today’s Reed-Solomon approach. Combining OFDM and LDPC could improve spectral efficiency up to 25 percent.
The cable industry is pressuring the study group to preserve backwards compatibility with the older DOCSIS 3.0 standard just now coming into widespread use. Some industry insiders predict cable operators will keep today’s QAM modulation for downstream speeds while boosting upstream speeds using OFDM.
Cable operators across the country are gradually moving away from analog service in favor of digital with the ultimate goal of an entirely IP-based network for television, phone, and broadband. The pressure is on for DOCSIS 3.1 to help accelerate that transformation, but most industry experts don’t believe the new standard will be finalized until at least the middle of 2013, with at least 6-12 months before equipment shows up supporting the finalized standard.


 Subscribe
Subscribe