 Windstream this week introduced its fiber to the neighborhood service Kinetic – its attempt to bring a competitive triple-play package of broadband, home phone, and television service to about 50,000 homes initially in Lincoln, Neb.
Windstream this week introduced its fiber to the neighborhood service Kinetic – its attempt to bring a competitive triple-play package of broadband, home phone, and television service to about 50,000 homes initially in Lincoln, Neb.
“We’re extremely excited to launch Kinetic in Lincoln,” said David Redmond, president of small business and consumer at Windstream. “Over the last year, we have heard loudly and clearly that this community is excited and eager for an alternative TV service. Windstream is confident that residents that sign up for Kinetic will find a highly interactive experience and a smarter way to watch TV than cable or satellite.”
The project in Lincoln will test consumer reaction and help the company plan if or how it plans to expand the service across many of its other service areas across the country.
Powered by the Ericsson Mediaroom platform, Kinetic is Windstream’s effort to squeeze about as much use of its existing copper wire infrastructure as possible. Like AT&T U-verse, Kinetic requires a fiber connection part of the way to customers, but continues to rely on existing copper telephone wiring already in the subscriber’s neighborhood. In effect, it’s an enhanced DSL platform that will split available bandwidth between television, Internet access and home phone service.
One unique aspect of Kinetic is its use of a next generation, compact whole home DVR that can record four shows at the same time, supplemented with wireless set-top boxes ($7/mo each), that allow subscribers to take the service to any television in the home without wiring. A subscriber can even move a television out into the yard and not lose service.
Remarkably, Windstream — an independent telephone company — completely de-emphasizes its own phone service in its up front promotions. Unless customers dig deeper into the Kinetic website, they will find prominently featured double play packages of television and Internet service starting at $59.98 a month. Telephone service is offered (and priced) almost as an afterthought, bundled into various packages for $5 extra a month. Phone customers get unlimited nationwide local and long distance calling.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Windstream Kinetic TV 4-2015.flv[/flv]
Windstream produced this introductory video to its new Kinetic TV service, offered initially to 50,000 homes in Lincoln, Neb. (1:20)
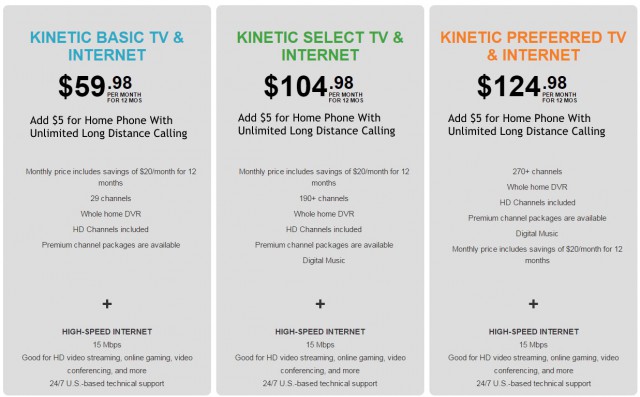
We added the pricing details for Home Phone service.
The biggest limitation Windstream faces marketing the service is its legacy network of copper wires. Customers can only qualify for the service if the connection between their home and Windstream’s central office is good enough to sustain the speeds required to handle all three services at the same time. The company is focusing Kinetic squarely on customers looking for a cable television alternative to Lincoln’s only other provider — Time Warner Cable. That may be because Kinetic remains disadvantaged in the broadband department.
The highest Internet speed a Kinetic customer can buy is 15Mbps, which is the speed Time Warner Cable offers in its “Standard” package. Time Warner currently sells up to 50/5Mbps in Lincoln — more than three times faster than Windstream’s Kinetic. Many Windstream DSL customers have complained they don’t come close to the speeds they are paying for, particularly during peak usage periods. A Facebook group with over 500 customers exists to discuss exactly that issue. Whether it will be different for Kinetic customers is not yet known, but the company’s lawyers are prepared for that possibility.

Windstream’s Whole House DVR is only about the length of its remote control.
“Windstream cannot guarantee speeds or uninterrupted, error-free service,” the company says in its terms and conditions. “Internet speed claims represent maximum network service capability speeds. Actual customer speeds may vary based on factors including simultaneous use of multiple devices, use of other Windstream services, customer device capabilities, Internet and Network congestion, website traffic, content provider service capacity, customer location, network conditions, and bandwidth devoted to carriage or protocol and network information.”
At least there are no usage caps.
Kinetic subscribers are also warned that just like DSL broadband, line quality will impact the kind of television service received.
“Kinetic TV includes digital channels (including local channels), one receiver and up to four standard direct video streams to the customer residence,” Windstream notes. “Of the four standard direct video streams per residence, customer’s location will determine both high definition (“HD”) availability and the maximum number of HD video streams (between one and four) a customer can view and record in HD at any one time, regardless of the number of receivers in the residence. The remaining streams will be standard definition.”
Kinetic’s channel lineup is comparable to that of Time Warner Cable, with some minor exceptions. Time Warner imports some regional over the air channels from adjacent cities, Windstream does not. Certain channels like Turner Classic Movies are available on Kinetic, but only for customers subscribing to the most expensive tier. Time Warner offers that channel on its less expensive Standard tier.

Limited bandwidth may limit your broadband speeds and the number of HD channels you can watch at any one time.
Time Warner Cable spokesman Mike Hogan took indirect shots at both the City of Lincoln and Windstream in response to the introduction of Kinetic.
“Lincoln residents can count on the fact that Time Warner Cable will offer the best choices for TV, Internet, home phone and home security to the entire city — in sharp contrast to competitors who only serve select areas, or won’t even say where they will or won’t serve,” Hogan said in an email to the Journal-Star.
That’s a reference to Windstream’s refusal to specify exactly where in Lincoln Kinetic is available.
Stop the Cap! surveyed more than 100 Lincoln-area addresses this morning and found Kinetic available primarily in wealthy and newer neighborhoods south and southeast of the city center, including zip codes such as 68516. A review of real estate transactions across the city of Lincoln showed home prices in this area are well above other parts of the city. That suggests Windstream is targeting the service to higher-income neighborhoods during its initial rollout, which plans to reach up to 45 percent of city households.
Although Windstream officials expect to bring Kinetic to about 80% of Lincoln, the city has given the company 15 years to complete the project. Further expansion may also depend on how customers respond to Kinetic.
With plenty of time, Windstream may choose to turn its attention elsewhere, eventually introducing the service in other cities across its 18-state service area of Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Iowa, Kentucky, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New Mexico, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, South Carolina and Texas, before it gets around to wiring urban poor neighborhoods in Lincoln.
Cable industry defenders believe Time Warner Cable and Windstream are being treated differently by city officials. Hogan notes the cable company is required to serve the entire metropolitan area, unlike Windstream that critics contend may be interested only in cherry-picking the low-hanging fruit.
Windstream’s announcement leaves just two significant independent telephone companies without IPTV offerings: FairPoint and Frontier Communications.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KLKN Lincoln New television service in Lincoln 4-16-15.mp4[/flv]
KLKN in Lincoln covered the Windstream event introducing Kinetic TV to Lincoln and talked with company officials about what the new service offers Lincoln and how much it costs in comparison to Time Warner Cable, the area’s incumbent cable company. (2:29)
 Philadelphia Mayor Michael Nutter has gone all out for Comcast, headquartered in the city he oversees. Not only has Nutter organized 51 mayors to sign a joint letter supporting Comcast’s $45 billion bid to take control of Time Warner Cable, he is also helping protect the cable company from embarrassing revelations about its performance in the city.
Philadelphia Mayor Michael Nutter has gone all out for Comcast, headquartered in the city he oversees. Not only has Nutter organized 51 mayors to sign a joint letter supporting Comcast’s $45 billion bid to take control of Time Warner Cable, he is also helping protect the cable company from embarrassing revelations about its performance in the city. The mayor’s office has remained elusive explaining why a survey conducted using taxpayer dollars has been kept away from taxpayers.
The mayor’s office has remained elusive explaining why a survey conducted using taxpayer dollars has been kept away from taxpayers.

 Subscribe
Subscribe Staff attorneys that have reviewed details of the Time Warner Cable/Comcast merger proposal are prepared to make a recommendation as early as next week that the Department of Justice should block the deal because it is anti-competitive and anti-consumer.
Staff attorneys that have reviewed details of the Time Warner Cable/Comcast merger proposal are prepared to make a recommendation as early as next week that the Department of Justice should block the deal because it is anti-competitive and anti-consumer. Under consideration by the Justice Department:
Under consideration by the Justice Department: Windstream this week
Windstream this week 




 Comcast officials have repeatedly stressed its 2Gbps tier will be exempt from usage caps, which makes it the only unlimited residential broadband offering available to Comcast customers in Atlanta. Other residential customers are now subjected to a 300GB usage cap with $10/50GB overlimit fee.
Comcast officials have repeatedly stressed its 2Gbps tier will be exempt from usage caps, which makes it the only unlimited residential broadband offering available to Comcast customers in Atlanta. Other residential customers are now subjected to a 300GB usage cap with $10/50GB overlimit fee.