 If the Federal Communications Commission weighed comments for and against the merger of Charter-Time Warner Cable-Bright House Networks based on volume, it would likely be a done deal.
If the Federal Communications Commission weighed comments for and against the merger of Charter-Time Warner Cable-Bright House Networks based on volume, it would likely be a done deal.
A major lobbying effort by the cable companies involved in the transaction has been underway to encourage politicians, business associations, non-profit groups, and programmers to write the FCC asking the deal be approved. Many are responding, including politicians receiving political donations and/or seeking expanded service for their communities, non-profits that depend on financial contributions from one or more of the companies involved, programmers that live or die based on winning carriage agreements with Charter, Bright House, and Time Warner Cable, and other groups with missions that seem miles away from a multi-billion dollar cable merger.
Stop the Cap! examined many of these curious letters of support. What, for instance, might motivate the New York Snowmobile Association to navigate the cumbersome comment filing systems of both the New York Public Service Commission and the Federal Communications Commission to express glowing support for a cable merger?

The International Soap Box Derby is all-in on the merger of Charter-TWC-Bright House.
What made the Maccabi World Union, the largest Jewish sports organization in the world, enthusiastic enough to dwell on a marriage of three cable companies?
How could the Montana Stockgrowers Association set aside their interest in helping state cattle ranchers to deliver safe and wholesome beef to American dinner tables to ponder modem fees in their letter to the Commission?
One Los Angeles non-profit organization contacted by Stop the Cap! shed some light on the subject, if we agreed to keep their name private.
“Like many non-profits, when Time Warner Cable makes a financial contribution to our organization, they attempt to find ways where both our organization and their company can benefit from goodwill generated by charitable contributions,” the director told Stop the Cap! “When the deal with Charter and Time Warner was announced, we received a gently worded request to participate in the public discussion about the merger.”
The group received information containing talking points about the deal’s benefits to consumers and businesses and was asked to consider using those points in a letter to state and federal regulators that would present a positive view of the deal.
“Non-profits need the contributions of large companies like Time Warner Cable and Charter, which both serve parts of Los Angeles County, to fund our programs,” the director said. “There isn’t any pressure on us to write the letters, but since they are in the public record, we know the cable companies know who wrote and who did not.”
 The director of this particular organization had qualms about getting involved in a regulatory matter that did not involve the organization he leads, but he was overruled by his board of directors.
The director of this particular organization had qualms about getting involved in a regulatory matter that did not involve the organization he leads, but he was overruled by his board of directors.
“Money is tight,” the director added. “I don’t want to comment on Charter Cable’s performance in Los Angeles except to say it is the main reason I use someone else.”
The director of the group would not comment when asked if it was uncomfortable signing a letter in support of a company who has failed to meet their personal expectations.
The fact non-profit groups spend time and resources writing letters on behalf of their donors bothers others as well.
Shawn Sheridan of Turlock, Calif. exhaustively researched over 250 pieces of correspondence the FCC has received in favor of the Charter acquisition, and he is not happy about what he found.
“The current public comments process has been infiltrated to purposely influence the independent review process,” Sheridan writes in a letter to the FCC. “I suggest to the Commission that conducting an independent analysis of the comments received from the public for [this merger] would reveal a nationwide campaign to improperly affect the Commission’s independent review of the applications, and reveal unique characteristics of who has and has not commented publicly.”
Sheridan categorized all the letters arriving from state/local representatives, Chamber of Commerce chapters, and non-profit groups:
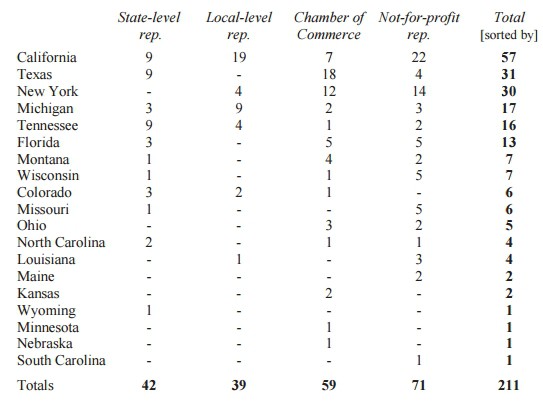
Letters from different chapters of the Chambers of Commerce, which typically count Time Warner Cable, Charter Communications, and/or Bright House Networks as dues-paying members, were oddly uniform in their praise of the transaction.
The Minnesota Chamber of Commerce, for example, didn’t seem too interested in getting into the specifics of the deal, satisfied instead to request “the FCC approve all matters related to this merger promptly.”
Dozens of other chapters of the business association used similar language praising the merger proposal. Notice the references to “$2.5 billion” promised to be spent on commercial fiber optics and “one million new residential lines” mentioned in a handful of the filings with the FCC:
The Minnesota Chamber of Commerce advocates giving Charter whatever it wants.
- “The Missoula Area Chamber of Commerce is the voice of business in Missoula County….We are excited by New Charter’s commitment to invest $2.5 billion into networks in commercial areas.”
- “As a member-driven organization, the Montana Chamber of Commerce represents the interests of business, ranging from small mom-and-pop operations to large companies….The new company would commit $2.5 billion to the commercial sector and would build out residential lines, improving both industry competition and local infrastructure.”
- “With nearly 700 members that employ more than 12,000 people, the Fremont Chamber of Commerce represents a vibrant, regional business community in eastern Nebraska….Specifically, we are told, the greater financial strength of the unified operations would lead to investment of at least $2.5 billion to upgrade commercial lines to fiber-optics….Therefore, based on their assurances to us, we believe New Charter would be a great partner….”
- “The Florida Chamber of Commerce is pleased to support Bright House Network’s merger with Charter Communications and Time Warner Cable into New Charter….New Charter would be committed to infrastructure investment. It would devote at least $2.5 billion towards commercial networks, contributing important upgrades and competition into this influential market.”
- [Clearwater Regional Chamber of Commerce:] “We understand that New Charter plans to invest $2.5 billion toward commercial networks, contributing important upgrades and competition
- into this influential market and to provide substantial investment throughout the entire State.”
- [Lakeland Area Chamber of Commerce:] “For example, New Charter has committed to $2.5 billion in commercial networks and would build out one million residential line extensions.”
- [San Diego Regional Chamber of Commerce:] “The proposal promises to bring in at least $2.5 billion in new commercial infrastructure investment, much of which will be invested in areas
where the Charter Communications currently does not operate.”
- “With more than 10,000 members, the Greater Cleveland Partnership (GCP) is a membership association of Northeast Ohio companies and organizations and one of the largest metropolitan
chambers of commerce in the nation….Specifically, it would commit at least $2.5 billion to build out commercial network lines and put up one million new residential lines….”
- “The Buffalo Niagara Partnership is the region’s private sector economic development organization and regional chamber of commerce….In the near future, our state will benefit from
a $2.5 billion expansion in the build-out of networks into commercial sectors.”
- “At the Finger Lakes Chamber of Commerce, we serve as the voice of our local business community….We have [been] made aware of a major change in the cable broadband industry. The potential merger of Charter Communications, Time Warner Cable, and Bright House Networks into New Charter….”
The language that implies these are not spontaneous, coincidental pieces of correspondence was couched using phrases like, “we are told,” “we understand,” and “we have [been] made aware.”
These talking points actually originate from Charter Communications’ Resource Center, which distributes pro-merger information to organizations in Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks’ service areas. The references to $2.5 billion for commercial upgrades and line extensions to one million new residential customers originate in documents like this, tailored in this case to New Yorkers.
Some organizations devote more time to customizing their correspondence than others. The Business Council of New York State and the Orange County Partnership couldn’t be bothered, and essentially cut and paste nearly identical language in their “individual” letters of support:

“We recognize that the information and communications sector is an increasingly critical component of a healthy economy….The Business Council understands that access to a reliable 21st Century communications infrastructure—with competitive options for service—is essential for New Yorkers in their homes, schools and workplaces.“

“The Partnership recognizes that the information and communication sector is an increasingly critical component of a healthy economy….We also understand that access to reliable 21st Century communications infrastructure, with competitive options for service, is a necessity for Orange County residents in their homes, schools and workplaces.“

…and the chances of a multibillion dollar cable merger winning regulatory approval.
Dominic J. Jacangelo was so nice, he liked Charter Communications’ merger twice — once on the letterhead of the New York Snowmobile Association, where he serves as executive director, and in a nearly identical letter signed by Jacangelo as Supervisor of the Town of Poestenkill, N.Y. He cited the same talking points the various Chambers of Commerce did.

Representing the interests of 2.5 million people worldwide or its member Time Warner Cable?
Sheridan disputes how merger supporters often attempt to give their views more weight by implying their positions are shared by their constituents. The Orange County Business Council claimed in its letter it represented nearly 300 Southern California businesses employing over 250,000 in the region and more than two million globally. Sheridan doubts more than 2.25 million people, many working outside the country, support the cable merger as much as OCBC suggests.
A larger question is what motivates the letter writers to weigh in on a cable merger in the first place?
For the ranchers in Montana, the desire for more rural broadband is well known. Cable operators usually don’t provide service to large, expansive ranches where a herd of cattle often vastly outnumbers the local population.
For Mr. Jacangelo, his LinkedIn page cites his talents for developing “professional relationships with business sponsors and [supporters], which might be helpful as the town of Poestenkill, like many other rural communities in upstate New York, seek expanded broadband service.
In 2009, the Maccabi World Union partnered with Jewish Life Television to provide in-depth coverage of the Maccabiah Games, a global sporting event. U.S. viewers see coverage of those games over Jewish Life TV, a cable network that reaches Time Warner Cable and Bright House customers, but not Charter Cable customers. A takeover of Time Warner and Bright House by Charter Communications could risk the end of that carriage agreement. Supporting Charter at its time of need may establish enough goodwill to guarantee JLTV will be a part of the “New Charter” lineup.
Sheridan’s research also discovered, as of Oct. 9, 2015:
- With a total of 31 letters from politicians in the state of Texas, not one came from a local official. Eighteen Chambers of Commerce in Texas sent letters in support of the deal;
- No state-level representatives weighed in on the deal in New York either, although 30 local and county leaders gave their support;
- One third of the 28 states where Charter provides service had no comment on the merger, pro or con, hardly representing a nationwide groundswell of support;
- Charter Communications’ corporate headquarters, formerly in Missouri and now in Connecticut, also drew little hometown interest. Just one letter from a state-level politician in Missouri reached the FCC. There were no letters from Connecticut at all;
- Of 258 unique commenters sending letters in support of the merger, 211 (82%) claimed to represent the interests of their members and affiliates without providing supporting evidence that was true. Most of those organizations received direct financial support or in-kind contributions from one or more of the involved cable operators or counted them as dues-paying members;
- Not counting Time Warner Cable or Bright House’s combined 13+ million customers, only about 30 unique consumers submitted a comment to the FCC regarding the merger, representing 0.000005% of Charter’s six million customers.
 On Monday, Stop the Cap! joined 21 other public interest organizations in sending a joint letter urging the Federal Communications Commission to deny Charter’s bid to take over Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks. Late last week, the Wall Street Journal reported that FCC Chairman Tom Wheeler may be planning to circulate a draft order approving the $90 billion merger.
On Monday, Stop the Cap! joined 21 other public interest organizations in sending a joint letter urging the Federal Communications Commission to deny Charter’s bid to take over Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks. Late last week, the Wall Street Journal reported that FCC Chairman Tom Wheeler may be planning to circulate a draft order approving the $90 billion merger.

 Subscribe
Subscribe If the Federal Communications Commission weighed comments for and against the merger of Charter-Time Warner Cable-Bright House Networks based on volume, it would likely be a done deal.
If the Federal Communications Commission weighed comments for and against the merger of Charter-Time Warner Cable-Bright House Networks based on volume, it would likely be a done deal.






 Altice will pay $34.90 in cash per share, a 22 percent premium to Wednesday’s closing price of $28.54, giving Cablevision an equity value of $10 billion.
Altice will pay $34.90 in cash per share, a 22 percent premium to Wednesday’s closing price of $28.54, giving Cablevision an equity value of $10 billion. Drahi has said Altice may look at properties to be sold under Charter Communications Inc’s takeover of Time Warner Cable Inc. Another target could be Cox Communications, but the closely held company has repeatedly said it is not for sale.
Drahi has said Altice may look at properties to be sold under Charter Communications Inc’s takeover of Time Warner Cable Inc. Another target could be Cox Communications, but the closely held company has repeatedly said it is not for sale.
 To complete an acquisition of landline assets in California, Florida, and Texas from Verizon Communications, Frontier Communications is hoping to raise
To complete an acquisition of landline assets in California, Florida, and Texas from Verizon Communications, Frontier Communications is hoping to raise  Californian consumers are among those most concerned about a Frontier takeover of landline and FiOS service. Verizon ventured far beyond its original service area extending from Maine to Virginia after it acquired independent telephone networks operated by General Telephone (GTE) and Continental Telephone (Contel) in 2000. In 2015, the company wants to return to its core landline service area in the northeast.
Californian consumers are among those most concerned about a Frontier takeover of landline and FiOS service. Verizon ventured far beyond its original service area extending from Maine to Virginia after it acquired independent telephone networks operated by General Telephone (GTE) and Continental Telephone (Contel) in 2000. In 2015, the company wants to return to its core landline service area in the northeast. David Lazarus, a consumer reporter for the Los Angeles Times,
David Lazarus, a consumer reporter for the Los Angeles Times,  As AT&T and Verizon ponder ditching high-cost landline customers, so long as there are companies like Frontier willing to buy, the deal works for both. Verizon gets a tax-free transaction that benefits both executives and shareholders. An already debt-laden Frontier satisfies shareholders by growing the business, which usually makes the balance sheet look good each quarter.
As AT&T and Verizon ponder ditching high-cost landline customers, so long as there are companies like Frontier willing to buy, the deal works for both. Verizon gets a tax-free transaction that benefits both executives and shareholders. An already debt-laden Frontier satisfies shareholders by growing the business, which usually makes the balance sheet look good each quarter. Those losses have to be reflected somewhere, and customers complain they are paying the highest price.
Those losses have to be reflected somewhere, and customers complain they are paying the highest price. 
 With the move, Drahi can embark on a breathtaking acquisition spree without diluting the control he has over his growing cable empire. Going forward, Altice will apply different voting rights to various classes of stock offered to investors. Drahi now holds 58.5% of Altice stock. But his shares are special because they grant him 92% of the voting power. Other shareholders will find they are not entitled to an equal say in how the public company is run.
With the move, Drahi can embark on a breathtaking acquisition spree without diluting the control he has over his growing cable empire. Going forward, Altice will apply different voting rights to various classes of stock offered to investors. Drahi now holds 58.5% of Altice stock. But his shares are special because they grant him 92% of the voting power. Other shareholders will find they are not entitled to an equal say in how the public company is run. With generous grants of authority like these passing muster, it’s no wonder executives of corporations around the world are urging consideration to move the corporate headquarters to the land of tulips and windmills. Fiat Chrysler already did, at the behest of Italy’s Agnelli family, which controls the Italian-American car company with a tight grip. Mylan, a producer of generic pharmaceutical drugs, managed to fend off Israeli rival Teva Pharmaceuticals, using Holland’s tolerance of executive-friendly poison pill maneuvers to keep unfriendly takeover artists away.
With generous grants of authority like these passing muster, it’s no wonder executives of corporations around the world are urging consideration to move the corporate headquarters to the land of tulips and windmills. Fiat Chrysler already did, at the behest of Italy’s Agnelli family, which controls the Italian-American car company with a tight grip. Mylan, a producer of generic pharmaceutical drugs, managed to fend off Israeli rival Teva Pharmaceuticals, using Holland’s tolerance of executive-friendly poison pill maneuvers to keep unfriendly takeover artists away. Keeping that newly privatized and deregulated wealth requires ruthlessness for others but protection for your allies and yourself. Drahi followed the teachings of American cable magnate John Malone (who is Charter Communications’ biggest shareholder today) and began a debt-fueled buying spree of independent cable systems, quickly followed by ruthless cost-cutting at the acquired companies, earning him the nickname “The Slasher,” among others less charitable. His critics say he has a lot of nerve, because in many instances Drahi billed the companies he acquired for consulting and management fees. BFM Business
Keeping that newly privatized and deregulated wealth requires ruthlessness for others but protection for your allies and yourself. Drahi followed the teachings of American cable magnate John Malone (who is Charter Communications’ biggest shareholder today) and began a debt-fueled buying spree of independent cable systems, quickly followed by ruthless cost-cutting at the acquired companies, earning him the nickname “The Slasher,” among others less charitable. His critics say he has a lot of nerve, because in many instances Drahi billed the companies he acquired for consulting and management fees. BFM Business 
