Drahi (center) surrounded by executives.
The billionaire owner of France’s largest cable operator has acquired St. Louis-based Suddenlink in a surprise $9.1 billion deal, and it is likely only the first move for the Altice Group in the U.S. cable business. But it may not be a welcome one for customers, employees, and suppliers of America’s seventh largest cable company about to be introduced to the notorious “Drahi Method” of conducting business that French newspaper La Parisien calls “brutal.”
The acquisition of Suddenlink represents a modest first step for a company that hopes to divide its business half in Europe and half in the United States. Incorporated in Luxembourg for tax-savings purposes, most of Altice’s interests in the cable business are in France and its overseas territories. Numericable is Altice’s cable brand in Luxembourg, France, and parts of Portugal and recently acquired SFR is Altice’s fiber broadband and mobile brand in French-speaking Europe.
 Moroccan-born billionaire businessman Patrick Drahi sees investing in cable as a great opportunity to build needed cash flow from America’s pervasive broadband duopoly. Altice is heavily in debt, financing a whirlwind of acquisitions including Israeli cable and mobile providers, Portugal’s largest telecom company, a mobile carrier in the Dominican Republic, in addition to SFR, France’s second largest wireless company, all mostly paid for with debt and junk bonds. That’s a long way from Drahi’s early days in cable, when he sold service door to door for his small regional Internet and cable-TV company in France’s Alsace region.
Moroccan-born billionaire businessman Patrick Drahi sees investing in cable as a great opportunity to build needed cash flow from America’s pervasive broadband duopoly. Altice is heavily in debt, financing a whirlwind of acquisitions including Israeli cable and mobile providers, Portugal’s largest telecom company, a mobile carrier in the Dominican Republic, in addition to SFR, France’s second largest wireless company, all mostly paid for with debt and junk bonds. That’s a long way from Drahi’s early days in cable, when he sold service door to door for his small regional Internet and cable-TV company in France’s Alsace region.
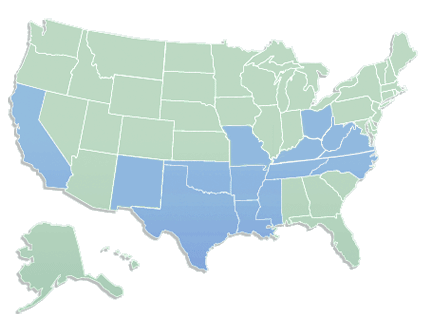
Suddenlink’s national service area
His mentor is Dr. John Malone, America’s former cable magnate, who followed a similar pattern of buying up cable companies across the United States in the 1970s and 80s to create Tele-Communications, Inc. (TCI), then America’s largest cable company (it was later sold to Comcast). Drahi shares Malone’s philosophy for cash flow-generating acquisitions: “Always start with cable.” He has plenty of opportunities in the United States, which unlike Europe is largely a cable broadband duopoly in big cities and a monopoly everywhere else. While Drahi confronts revenue erosion from European telecom price wars among phone, broadband, and television companies, he has plenty of room to raise the rates on captive customers on the other side of the Atlantic.
The average Suddenlink customer lives in a small to medium-sized city in West Virginia, Texas, Arkansas, Louisiana or Arizona. Suddenlink is well-positioned to sell its 1.5 million customers broadband service, because the alternative is usually low-speed DSL from companies like Frontier, Windstream, CenturyLink or AT&T. Drahi will sell all the services Suddenlink traditionally has, but customers can expect to pay a higher price.
Drahi has decided to focus on his high-end customers and has stopped competing to win customer volume based on price. The customers that pay the most for service also get the best customer service. If lower-end customers feel ignored and decide to leave, that is increasingly an accepted fact of life by Altice management. As a result, Numericable-SFR continues to lose mobile and market share in Francophone markets because customers have found better deals elsewhere. But the company is still keeping its best customers well-pampered and they have stayed, so far.
Life will be anything but pampered for Suddenlink employees and suppliers, who will soon be targeted for Drahi’s traditional culling of the herd and vicious cost cutting. European capitalists look in awe at “the Drahi Method,” a program of ruthless cost controls, job cuts, and threats visited on every acquired company. The French press is buzzing about Drahi’s latest acquisition in the United States, and wonder if Drahi’s slash and burn management style was better suited to America’s greed era of the 1980s and not the Obama’s ‘we are better than that’ era of the 2010s. But they know the story of how Drahi takes over is always the same.

Suppliers complain Drahi’s companies don’t pay their bills.
After each acquisition is complete, Altice flies in a small team of executives who live to slash costs. It’s what Le Echos calls “helicopter management.” Many middle and upper management at the acquired companies are terminated instantly, replaced with relocated Drahi loyalists. Salary freezes are imposed on those remaining and are indefinite. Job cuts in customer service are frequently next and are sometimes severe. In fact, the company’s relationship with its employees is so bad, the French trade union CFDT has taken several actions against Altice-owned SFR-Numericable over pay freezes and terminations they call unjust for a company collecting a profit margin of more than 25%, even during a price war.
But the worst is reserved for the suppliers that provide everything from coaxial cable to paper for the office printer.
“Suppliers are fifth wheel,” complained one French company that considered itself extorted to hand over a 40% discount just to get their past due invoices paid. One told Le Monde the best a supplier can hope for from an Altice-run company is to barely survive. Many more die than live.
Sometimes, the hardball tactics against suppliers and vendors seem to backfire on the company. Les Echos shares the embarrassing story of the major SFR-owned mobile store that had a big problem. This past January, the demonstration display where customers can sample the latest tablets and smartphones was curiously empty, except for a few employees milling around a coffee machine placed there to take up some of the empty space. Where were the phones and tablets to show off to make the sale? The distributor who supplies SFR had not been paid. No payment, no phones.
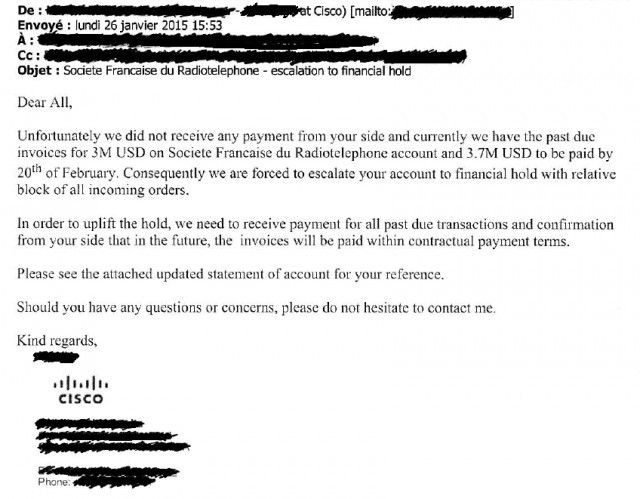
Drahi’s company even stiffed Cisco, which sent this warning note suspending shipments pending payment.
Just a few months before announcing his deal to acquire Suddenlink, a large group of French suppliers went to French authorities to seek a broad-based mediation to stop Drahi’s promises of payment in return for future discounts.
Les Echos reports Drahi spared no one from the cut.
“Cleaning companies, network equipment manufacturers, call centers, manufacturers of smartphones, TV, everybody goes,” it reported. Drahi’s managers even dared to challenge the local power company, Dalkia, threatening to cancel their energy services contract unless the company was granted an immediate 80 percent discount. Le Figaro reported the company ignored the contracts it had already signed with the energy company.

An empty bag: No phones at the SFR store.
“It’s vicious,” one supplier told Les Echo. “For them, everything can be renegotiated, even contracts already signed and running.”
An IT company also accused Drahi’s company of refusing to pay for past work unless it received a 30% discount. The firm said no and threatened to sue. It is now facing bankruptcy because its business overwhelmingly depends on Numericable and SFR.
The cuts can also seem petty.
Last December, office workers in Saint-Denis found themselves without paper for the office printers. Numericable SFR management had not bothered to pay its office suppliers and they cut the company off. This year, employees report they often have to bring their own toilet paper to work as the company has stopped stocking employee restrooms, apparently part of another cost-cutting measure.
The problem of unpaid invoices has grown so bad the cable operator is increasingly responsible for suppliers clogging the only Commercial Court in Paris with cases large and small, including those from Pace – the company that provides set-top boxes for Drahi’s cable companies, M6 – a television channel not paid for its programming, STS – a major software company, Orange – a major telecom operator, and even the workers who solicit customers to buy cable service going door to door, who say they have not been paid either. In fact, Numericable-SFR has been hauled into court with stunning regularity, losing almost every case, and forced to pay costs, including court fees and interest. The company has already been convicted 12 times for unpaid bills and in several other cases, it only agreed to settle minutes before a trial began.
Altice’s willingness to put itself deeply in debt just to make more acquisitions was enough for Moody’s to throw a caution flag in February, warning investors the company was under review for a credit downgrade.
 “Today’s rating action is prompted by significant uncertainties about the funding of the envisaged €1.95 billion share repurchase program and its impact on Numericable-SFR’s liquidity, leverage and operational flexibility. Moody’s views the potential transaction as aggressive given that the company closed the large acquisition of SFR only recently and is still in the early stage of integrating the acquired asset,” the ratings agency said.
“Today’s rating action is prompted by significant uncertainties about the funding of the envisaged €1.95 billion share repurchase program and its impact on Numericable-SFR’s liquidity, leverage and operational flexibility. Moody’s views the potential transaction as aggressive given that the company closed the large acquisition of SFR only recently and is still in the early stage of integrating the acquired asset,” the ratings agency said.
One might forgive Drahi’s desire to economize, considering his recent acquisition of SFR left Altice in debt for more than $12 billion and owing $55 million in interest payments a month. But Drahi continues his acquisitions unabated by those economic realities.
Another problem is Drahi’s crackdown on who is authorized to pay suppliers and other vendors. Under SFR’s old owner, about fifty employees were authorized to sign checks over €100,000 across all of France. Today, any check over €10,000 must be signed by at least one of just three employees. Silicon reports the crackdown became even more severe last winter.
“Since December, any investment must be approved by the investment committee,” a source told Silicon. “All projects are blocked, all expenses must be justified, even 50 Euros. It is set to ‘stop and go’.“
The inherent delays and austerity measures eventually also reach customers, according to ex-employees who say getting a replacement box or new cable strung can be a major problem when suppliers stop shipping and the company stops buying. It can also annoy customers that discover calling customer service no longer means talking to an employee in France. Drahi found call centers in Tunisia and Morocco that would do the same work for a fraction of the price.
Drahi said his Suddenlink acquisition is only the start. He has reportedly also shown an interest in acquiring Time Warner Cable, and shares of Cablevision stock were also increasing this afternoon suspecting that company could also be a target.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
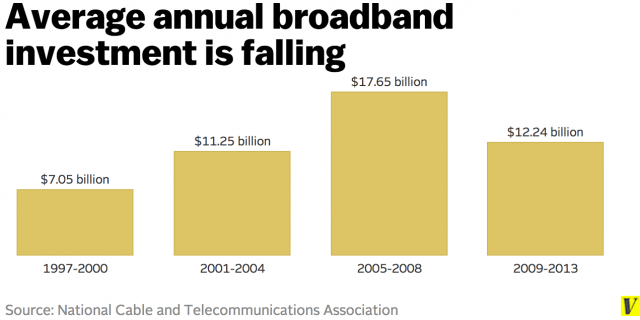
 Most of the same telecom companies that want to create Internet paid fast lanes, drag their feet on delivering 21st century broadband speeds, refuse t0 wire rural areas for broadband without government compensation, and have cut investment in broadband expansion are warning that any attempt by the FCC to enact strong Net Neutrality policies will “threaten new investment in broadband infrastructure and jeopardize the spread of broadband technology across America, holding back Internet speeds and ultimately deepening the digital divide.”
Most of the same telecom companies that want to create Internet paid fast lanes, drag their feet on delivering 21st century broadband speeds, refuse t0 wire rural areas for broadband without government compensation, and have cut investment in broadband expansion are warning that any attempt by the FCC to enact strong Net Neutrality policies will “threaten new investment in broadband infrastructure and jeopardize the spread of broadband technology across America, holding back Internet speeds and ultimately deepening the digital divide.”


 So Google spending $11 billion to reach 20 million new homes is business malpractice while spending $18 billion for three million Time Warner Cable customers is confirmation of the cable industry’s robust health and valuation?
So Google spending $11 billion to reach 20 million new homes is business malpractice while spending $18 billion for three million Time Warner Cable customers is confirmation of the cable industry’s robust health and valuation?
 But Forbes’ Peter Cohan called Google’s much less investment into fiber broadband
But Forbes’ Peter Cohan called Google’s much less investment into fiber broadband 

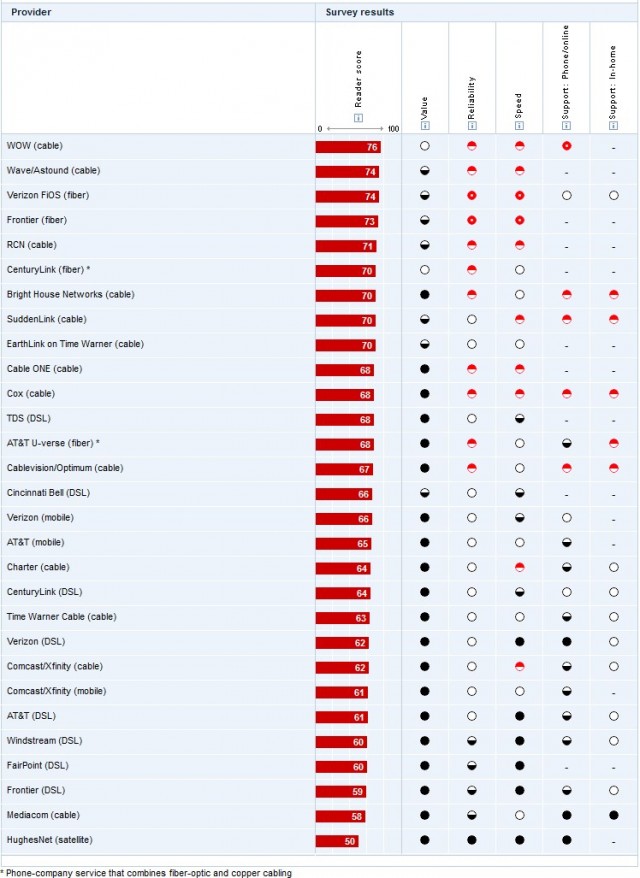
 Despite claims of improved customer service and better broadband, Comcast and Time Warner Cable’s customer satisfaction scores are in near-free fall in the latest Consumer Reports National Research Center’s survey of consumers about their experiences with television and Internet services.
Despite claims of improved customer service and better broadband, Comcast and Time Warner Cable’s customer satisfaction scores are in near-free fall in the latest Consumer Reports National Research Center’s survey of consumers about their experiences with television and Internet services.