 PBS TV stations in smaller communities and secondary PBS affiliates and public stations in large ones are ending their free, over-the-air television broadcasts after decades of service because of politics, budget cuts and repacking the TV dial to give up more spectrum for wireless providers.
PBS TV stations in smaller communities and secondary PBS affiliates and public stations in large ones are ending their free, over-the-air television broadcasts after decades of service because of politics, budget cuts and repacking the TV dial to give up more spectrum for wireless providers.
The most significant trigger for the impending closedown of several stations, especially those run from universities, is the FCC’s spectrum auction and reallocation plan, repacking UHF stations into a much smaller number of available channels, requiring stations to buy new transmitting equipment many cannot afford.
The original plan to repack television stations reassured affected broadcasters that the auction proceeds from the wireless industry auctions would cover the costs of the necessary new equipment.
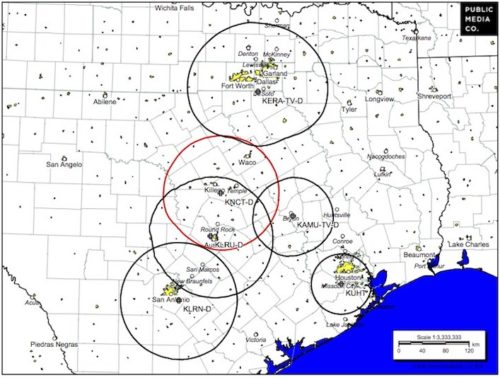
KNCT’s coverage partly overlaps other nearby public stations.
Then Central Texas College, which owns and operates PBS affiliate KNCT in Belton, Tex., learned Republicans in Congress might appropriate only enough funding to cover 60% of the transition costs. The trustees that oversee KNCT, which serves central Texas, realized they would have to find roughly half of the $4.5 million needed to change their channel from 46 to 17 as part of the “station repack” and hope Congress would change its mind and reimburse the station.
That was money the trustees ultimately decided could not be found, especially as annual deficits at the station now average $500,000 — costs covered by the college.
KNCT general manager Max Rudolph, who has been in charge of KNCT for most of its 38 year history, said the station will now have to leave the airwaves.
“The board had to make a tough decision, but repacking was only the tip of the iceberg,” Rudolph said. “It’s economics — dollars and cents.”
KNCT operates with a staff of 15 — including five part-time employees, that take care of both the PBS TV station and KNCT-FM, which will continue on the air. The annual budget for the TV station was about $1 million, half spent on PBS membership and programming. Donors also provided around $160,000 a year.
 KNCT-TV serves the Belton/Killeen/Temple/Waco, Tex. market, although KNCT’s signal struggles to reach into the northeastern part of its service area near Waco, where public TV station KAMU-TV in more distant College Station strangely provides a better signal.
KNCT-TV serves the Belton/Killeen/Temple/Waco, Tex. market, although KNCT’s signal struggles to reach into the northeastern part of its service area near Waco, where public TV station KAMU-TV in more distant College Station strangely provides a better signal.
The station hopes to continue operations through online streaming and on-demand shows kept on its website, but both require a subscription to internet service. For parts of central Texas, it represents the end of free PBS over-the-air programming.
Last year, Central Michigan University decided to accept a $14 million offer for satellite PBS station WCMZ-TV in Flint to vacate its current UHF channel and close down for good April 23, 2018. WCMZ-TV’s signal reaches as far away as Port Huron, Detroit and Lansing. But its intended market was Flint, which lacked local PBS service when the station signed on more than 30 years ago. Today, Central Michigan University still operates its primary station WCMU in Mount Pleasant, along with WCMV, which serves Cadillac and Traverse City, WCML, serving Alpena, Petoskey, Cheboygan and the Straits of Mackinac, and WCMW, which broadcasts to the Lake Michigan communities of Manistee, Ludington and Pentwater.
CMU officials are pulling the plug on WCMZ because, they claim, 99 percent of viewers live in areas that are now served by other public broadcasting stations. While cord cutters may miss WCMZ, cable and other pay television customers likely won’t because the service is expected to continue uninterrupted on cable and possibly satellite.
 KMTP, San Francisco’s youngest multicultural public television station, is looking for a new home after selling its spectrum for $87.8 million in last year’s FCC auction. KMTP is licensed to Minority Television Project, Inc., a not-for-profit corporation, and serves the San Francisco Bay Area with non-commercial public television. KMTP broadcasts international programming in multiple languages including English and is not affiliated with PBS.
KMTP, San Francisco’s youngest multicultural public television station, is looking for a new home after selling its spectrum for $87.8 million in last year’s FCC auction. KMTP is licensed to Minority Television Project, Inc., a not-for-profit corporation, and serves the San Francisco Bay Area with non-commercial public television. KMTP broadcasts international programming in multiple languages including English and is not affiliated with PBS.
 Its best chance to survive is dependent on an acquisition or arrangement with Poquito Mas Communications LLC, the licensee of low-power KCNZ in San Francisco, which is best known for carrying Creation TV, a Chinese language religious network. KMTP can either occupy several of KCNZ’s subchannels, or potentially buy the station outright. As a low power outlet, KMTP can hope to keep carriage on cable television, giving it perfect reception in areas where KCNZ’s low-power UHF transmitter cannot reach. But that means cord-cutters may have no access to the channel unless they live near the transmitter.
Its best chance to survive is dependent on an acquisition or arrangement with Poquito Mas Communications LLC, the licensee of low-power KCNZ in San Francisco, which is best known for carrying Creation TV, a Chinese language religious network. KMTP can either occupy several of KCNZ’s subchannels, or potentially buy the station outright. As a low power outlet, KMTP can hope to keep carriage on cable television, giving it perfect reception in areas where KCNZ’s low-power UHF transmitter cannot reach. But that means cord-cutters may have no access to the channel unless they live near the transmitter.
WUSF-TV, on the air in Tampa for 51 years, signed off late last year after the University of South Florida decided to liquidate the station for $18.8 million in auction proceeds from the FCC’s spectrum auction. The area’s larger PBS station, WEDU, has absorbed most of the programming that used to appear on WUSF, which now appears as a virtual subchannel on WEDU — unofficially called WEDQ.
Today, WEDU carries six different signals on its over the air digital channel: WEDU/PBS HD, PBS World, PBS Kids, WEDU+, Florida Channel, and Create TV. Many of these services are also available on cable television. But the original competing voice from WUSF is now gone.
 WYCC in Chicago was the city’s second PBS affiliate, behind the larger and better known WTTW. Licensed by City Colleges of Chicago, the trustees decided to liquidate WYCC last year for cash as part of the FCC’s spectrum auction.
WYCC in Chicago was the city’s second PBS affiliate, behind the larger and better known WTTW. Licensed by City Colleges of Chicago, the trustees decided to liquidate WYCC last year for cash as part of the FCC’s spectrum auction.
WYCC began its operations in 1983 with a message from President Ronald Reagan, congratulating the station for producing adult learning programming lacking on commercial television. WYCC first ended its PBS affiliation in 2017 and had one sole program provider, MHz Networks’ WorldView, when it ceased broadcasting on Nov. 27, 2017.
WTTW has sought to claim WYCC’s remaining assets and intends to place WorldView on one of its subchannels in the future. It already grabbed two Australian shows WYCC used to air: “Miss Fisher’s Murder Mysteries” and “The Doctor Blake Mysteries.” All that will remain of WYCC are its “call letters,” which could possibly reappear when WTTW launches WorldView.


 Subscribe
Subscribe

 The loss was devastating to residents, especially at the nursing home.
The loss was devastating to residents, especially at the nursing home.
 Of the 64 properties he manages, Scally told Habitat fewer than a dozen have signed up for a bulk rate, and those deals were signed years ago.
Of the 64 properties he manages, Scally told Habitat fewer than a dozen have signed up for a bulk rate, and those deals were signed years ago.
 Spectrum ignores her complaints, she claims, transferring her from call center to call center in search of a solution. She finally took her complaint to the FCC, something she does not think should be required after paying the company $1,600 a month for cable television.
Spectrum ignores her complaints, she claims, transferring her from call center to call center in search of a solution. She finally took her complaint to the FCC, something she does not think should be required after paying the company $1,600 a month for cable television. Charter Communications is raising rates for its dwindling number of Earthlink customers still subscribed to Earthlink’s legacy internet plans in an effort to avoid Spectrum’s entry-level $65 internet service.
Charter Communications is raising rates for its dwindling number of Earthlink customers still subscribed to Earthlink’s legacy internet plans in an effort to avoid Spectrum’s entry-level $65 internet service.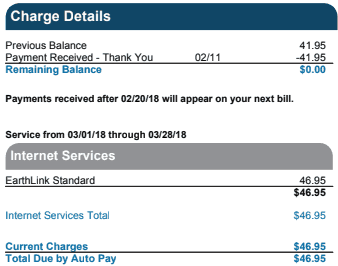 This last loophole allowed some customers to avoid switching to Spectrum’s more costly $65 entry-level 100/10 Mbps plan (200 Mbps in select areas). But now Spectrum is gradually taking away Earthlink’s price advantage. The new rate is $46.95 a month, and is likely to continue increasing in similar increments at least twice a year, until its price reaches about $60.
This last loophole allowed some customers to avoid switching to Spectrum’s more costly $65 entry-level 100/10 Mbps plan (200 Mbps in select areas). But now Spectrum is gradually taking away Earthlink’s price advantage. The new rate is $46.95 a month, and is likely to continue increasing in similar increments at least twice a year, until its price reaches about $60. The Chair of the New York State Public Service Commission announced today that the Commission is
The Chair of the New York State Public Service Commission announced today that the Commission is  In two instances, the staff found Charter was claiming new service expansion in buildings clearly already covered by the city’s existing franchise agreement.
In two instances, the staff found Charter was claiming new service expansion in buildings clearly already covered by the city’s existing franchise agreement.

 Other top Charter executives all made in excess of $1 million in 2017:
Other top Charter executives all made in excess of $1 million in 2017: