AT&T’s Supreme Court: senior executives sitting together in judgment of landlines at Wednesday’s analyst conference.
Yesterday, at least a half-dozen AT&T senior executives sat lined up in a perfect row to present Wall Street with the company’s vision for the future.
There were no consumers in attendance, just a group of Wall Street investors and analysts that braved the latest nor’easter to attend.
At issue: what to do about AT&T’s landline network, particularly in rural areas. Earlier this year, AT&T CEO Randall Stephenson, still smarting from a regulatory slap-down of his plan to acquire T-Mobile USA, ranted his disapproval of federal regulators for nixing the deal and then reflected on AT&T’s rural customers who still cannot buy broadband service from AT&T.
One of Stephenson’s strongest arguments in favor of merging with T-Mobile was it would facilitate a rural broadband solution. With that off the table, Stephenson seemed at a loss:
“We have been apprehensive on moving, doing anything on rural access lines because the issue here is, do you have a broadband product for rural America?,” Stephenson said. “And we’ve all been trying to find a broadband solution that was economically viable to get out to rural America and we’re not finding one to be quite candid. That having been set aside, now we’re looking at rural America and asking, what’s the broadband solution? We don’t have one right now.”
Now AT&T claims they do, and miracle of miracles, it turns out they never needed the buyout deal with T-Mobile after all.
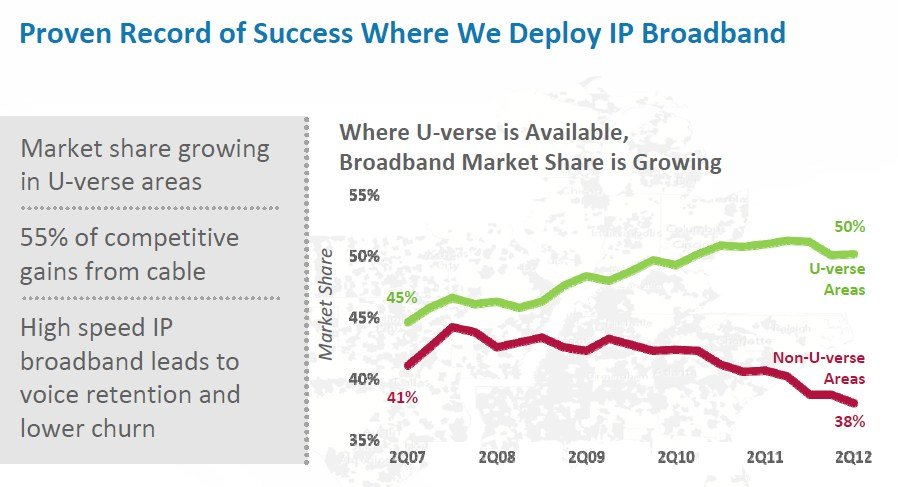
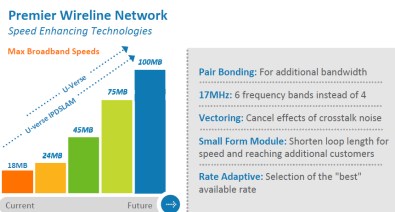
AT&T’s solution is good news for urban, suburban, and exurban customers who will benefit from billions in additional investments to beef up the company’s U-verse platform. Those with access to U-verse TV, broadband, and phone service will soon find maximum speeds available up to 75Mbps — important at a time when cable companies are moving to 50-100Mbps premium service tiers. Those without access to U-verse, bypassed by its recently completed initial buildout, now will have a chance to see the service in their communities.
 For more exurban and near-rural areas, AT&T has a positive plan to rid customers of the scourge of painfully slow ADSL service, better known simply as “DSL,” which AT&T pitches at speeds typically 10Mbps or less. In more rural areas, it is often much less.
For more exurban and near-rural areas, AT&T has a positive plan to rid customers of the scourge of painfully slow ADSL service, better known simply as “DSL,” which AT&T pitches at speeds typically 10Mbps or less. In more rural areas, it is often much less.
By using additional fiber and using D-SLAM technology to reduce the amount of copper wiring between the phone company and you, AT&T’s IPDSLAM service will dramatically improve speeds for customers languishing with 3Mbps service to upwards of 45Mbps. But for now, AT&T won’t roll this out as a full-scale U-verse service. Because maximum speeds are lower and network variability is expected to be greater, AT&T will instead pitch this as a broadband and landline phone service package. Customers will be marketed satellite dishes if they want television service bundled in.
Although not as robust of a platform as U-verse will soon be, it still represents a major improvement over DSL, which is now barely tolerable for today’s online multimedia experience.
But AT&T’s “good news” may not be so great for its most rural customers, who either have the slowest DSL service or more likely no broadband at all. Those customers have waited years for AT&T to invest in upgrades to finally connect them to the Internet, but AT&T’s plans have gone in a very different direction.
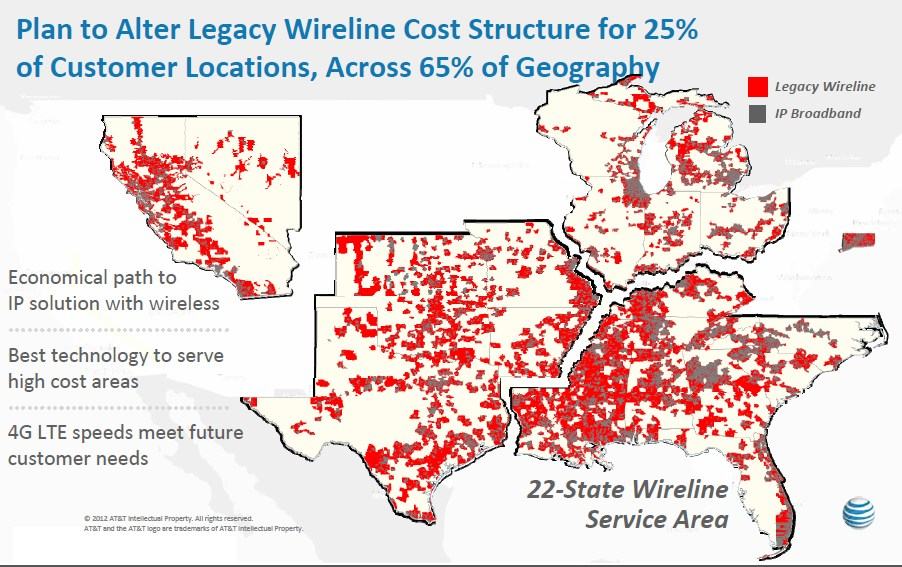
AT&T’s rural solution is to take down the existing landline network and move everyone to its wireless cell phone service. To implement this proposed solution, AT&T will aggressively invest in rural cell sites within the 22 states where it supplies landline service. The company claims 99% of its customers will be able to access a 4G LTE signal within a few years.
But here is where things begin to get dicey. AT&T told investors it has no current plans to differentiate rural wireless customers from their urban counterparts. In larger cities, a smartphone and data plan is not necessarily a necessity — customers can still access a landline to place urgent calls or find a home broadband plan that does not carry the kinds of restrictive data caps wireless plans deliver.
Rural landline customers often pay low rates for their home phones, primarily because their local calling areas are generally far more restricted than in larger communities. The base rate for rural phone customers can be around $10 (before taxes and fees) in some areas. The base rate for AT&T’s wireless service starts at around $40 for 450 talk minutes or $19.99 for anchored, wireless unlimited calling home phone service (with a $36 activation fee and a two-year contract) that works with your existing home phones. Both represent rate increases.
Wireless data plans are notoriously expensive and limited. Verizon’s plan for home broadband users is priced at $60 a month with a 10GB limit. Less expensive plans with limits 25 times greater (or unlimited) are available from wired broadband providers. If the customer wants a smartphone for their data and home voice calling, bundled plans start at $85 a month with a 1GB usage limit.
With these prices, it is no surprise AT&T is promoting this as great news for the company. But we’re not so sure the average rural American is going to be pleased treated like a second class citizen with high priced, usage-capped Internet access.
As victims of Hurricane Sandy also found out last week, the venerable landline also enjoys a reputation of working after disasters strike. Unlike a fallen tree knocking down a phone line in the backyard, should AT&T’s wireless network fail in a storm, it would potentially leave hundreds, if not thousands of customers without service. Repair crews could take days to reach damaged facilities. That actually happened to Frontier Communications in some parts of West Virginia where heavy snows and tree damage made travel nearly impossible.
But there are important clues to what AT&T is really up to in regulatory filings that accompanied the showy presentation AT&T put on in New York Wednesday.
AT&T Has a Plan — Move Customers Away from Low Profit, Low Growth Landlines to High Profit Wireless/Deregulated Broadband
After the two hour presentation ended, AT&T posted a copy of its proposal sent to the Federal Communications Commission.
Reviewing the 24-page document is a classic case of déjà vu. Once again, after the rhetoric is set aside, AT&T is back, peddling the same case to retire landline service and the regulatory obligations that accompany it. Only now, it has a carrot to dangle in front of regulators — significant investments in broadband expansion.
Although the private sector has invested well over $1 trillion in broadband networks, much remains to be done. As of 2010, roughly 14 million Americans, residing in rural and other high cost areas where the broadband business case is tenuous at best, still lacked access….
[…] Carriers such as AT&T are stepping up to do their part. In fact, just today, AT&T announced a $6 billion investment plan to expand and upgrade its wireline network to bring robust IP broadband services to millions of additional locations in its legacy footprint.
[…] AT&T makes this announcement with full confidence that the Commission will continue to implement the National Broadband Plan’s vision of removing regulatory impediments to efficient, all-IP networks, including obligations that could require carriers to maintain legacy facilities and services even after they have deployed new, IP-based alternatives.
Translation: We used to bypass 14 million Americans, leaving them behind because it was unprofitable to serve them. But now we’re going to invest some additional money. But before you get that investment, we need you to agree the landline is a relic and (largely unregulated) IP-based networks are the future. We are not going to run both, so if you want all of this investment, you have to let us abandon our regulatory responsibilities and commitments to rural customers.
AT&T even tried to calm investor fears about capital spending increases, arguing the potential payoff of discarding landline service opens up a new era of earnings, both from shifting customers to AT&T’s highly profitable wireless service at a cost of double, triple, or more what customers used to pay the phone company, and a platform to sell them even more services later.
A number of Wall Street analysts disagreed, panning AT&T’s wireline investments as unproven.
The Broadband Coalition, a group of competing telecom providers, called the entire affair a smokescreen:
AT&T’s announcement today that it needs regulatory intervention from the FCC in order to invest in IP technology is a re-run of a tired ploy to leverage the company’s dominance. AT&T only invests in order to respond to competition, and competition is made possible by the very pro-competitive policies that AT&T seeks to eliminate. The Broadband Coalition members have invested billions of dollars to bring the benefits of IP to American consumers from coast to coast. But if AT&T gets its way, competition will largely disappear, investments will dry up and consumers will suffer.
Former Congressman Chip Pickering, coalition spokesman, stated, “AT&T is simply trying to use its belated roll out of IP technology as an excuse to rewrite the telecom rules to its advantage. We already know that AT&T’s claim that IP will somehow alter the laws of economics and lessen its dominance is patently false. Clearly, AT&T’s proposed changes are not necessary to achieve widespread IP deployment, but the retention of competition policy is.”
Consumer groups accused AT&T of lying to federal regulators when the company argued the T-Mobile acquisition was essential to accomplish their plan to expand wireless service to 96% of the U.S. population. A year later, the company now claims it can deliver 4G wireless service to 300 million Americans and 99% of its landline service area without breaking much of a sweat.
CNN:
AT&T insists that it wasn’t being disingenuous with the regulators. Things changed, the company says, pointing to the 40 new spectrum deals it signed over the past year. The FCC recently made available some spectrum that wasn’t on the table when AT&T was negotiating its T-Mobile takeover.
“We chartered a new path,” AT&T spokeswoman Roberta Thomson told CNNMoney on Wednesday.
That’s precisely what the FCC — and industry analysts — believed would happen.
Now What
For now, rural customers need not worry AT&T will put their entire rural landline operation up for sale, potentially selling off a large number of customers to companies like CenturyLink, Frontier, Windstream or FairPoint.
But AT&T’s lobbying machine will soon descend on state legislatures to win regulatory approval of their “abandon landlines” agenda. AT&T has a carrot for those legislators as well — a promise that states that hurry to rubber stamp AT&T’s wish list will be first in line for “investments.”
“We are going to have to see 21st-century regulation for 21st-century investments like this,” said AT&T CEO Randall Stephenson. “I think what you’re going to see is that these investments will go first to those states where you have good line of sight to good regulatory authority to do some of the things we’re talking about here.”
The implications for rural customers are profound if AT&T wins permission to scrap the landline network. Despite assurances from AT&T this is a technology argument, in fact it is more of a campaign to rid themselves of regulatory and consumer protection rules that have been around for decades. The type of technology used makes all the difference. Landline providers are usually compelled to provide reasonable, affordable, universal service for all Americans. Broadband, IP-based, and wireless networks now exist largely in a deregulation free-for-all where AT&T can do as it pleases, serve who it likes, and charge whatever it wants.
Considering AT&T’s current business plans, that sets the stage to worsen the newest digital divide — one pitting urban areas with faster, advanced, and more competitively priced networks against rural America, consigned to expensive, usage capped wireless service that may or may not work when a natural disaster strikes.
The only way this plan works for consumers is if common-sense service obligations, consumer protection, open access for competitors, and mandated equivalence of service is part of the package. Without it, AT&T will get exactly what it wants: a regulation free lifestyle, an expensive wireless network that rural residents will be forced to use for basic telecommunications, and cost savings and revenue opportunities AT&T will use to bolster its own profits, while cementing its monopoly position in the rural communities of 22 states where it operates.


 Subscribe
Subscribe