 Frontier Communications has revealed to investors what many probably realized long ago — the independent phone company chronically underinvested in network upgrades and repairs for years, giving customers an excuse to switch providers.
Frontier Communications has revealed to investors what many probably realized long ago — the independent phone company chronically underinvested in network upgrades and repairs for years, giving customers an excuse to switch providers.
Remarkably, the phone company did not just underperform for its remaining voice and DSL internet customers. In a sprawling confidential “Presentation to Unsecured Bondholders” report produced by Frontier’s top executives, the company admits it was even unable to achieve significant growth in its fiber territories, where Frontier-acquired high-speed FiOS and U-verse fiber networks held out a promise to deliver urgently needed revenue.
Frontier’s bondholders were told the company’s ongoing losses and poor overall performance were unsustainable, despite years of executive “happy talk” about Frontier’s various rescue and upgrade plans. In sobering language, Frontier admitted its capital structure and efforts to deleverage the company’s massive debts were likely to cut the company off from future borrowing opportunities and deter future investment.
The presentation found multiple points of weakness in Frontier’s current business plan:
Voice landline service remains in perpetual decline. Like other companies, Frontier’s residential landline customers left first, but now business customers are also increasingly disconnecting traditional phone service.
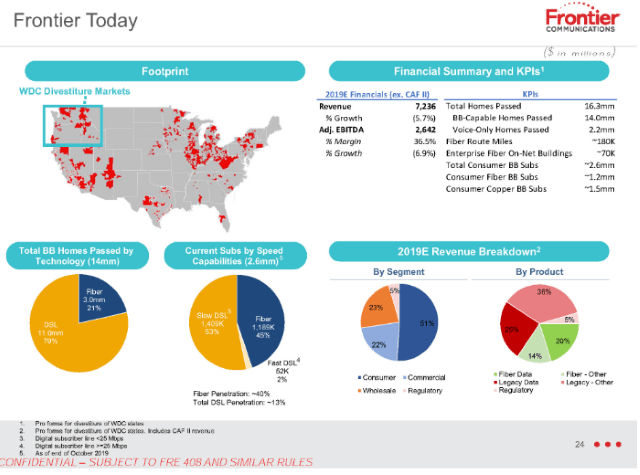
 About 51% of Frontier’s revenue comes from its residential customers. That number has been declining about 5% annually, year over year as customers leave. Frontier’s internet products are now crucial to the company’s ability to stay in business. Less than 30% of Frontier’s revenue comes from selling home phone lines. For Frontier to remain viable, the company must attract and keep internet customers. For the last several years, it has failed to do either.
About 51% of Frontier’s revenue comes from its residential customers. That number has been declining about 5% annually, year over year as customers leave. Frontier’s internet products are now crucial to the company’s ability to stay in business. Less than 30% of Frontier’s revenue comes from selling home phone lines. For Frontier to remain viable, the company must attract and keep internet customers. For the last several years, it has failed to do either.
Frontier customers are disconnecting the company’s low-speed DSL service in growing numbers, usually leaving for its biggest residential competitor: Charter Spectrum. Frontier remains saddled with a massive and rapidly deteriorating copper wire network. The company disclosed that 79% of its footprint is still served with copper-based DSL. Only 21% of Frontier’s service area is served by fiber optics, after more than a decade of promised upgrades. Frontier’s own numbers prove that where the company still relies on selling DSL, it is losing ground fast. Only its fiber service areas stand a chance. Just consider these numbers:
- Out of 11 million homes in Frontier’s DSL service area, only 1.5 million customers subscribe. That’s a market share of just 13 percent, and that number declines every quarter.
- Where Frontier customers can sign up for fiber to the home service, 1.2 million customers have done so, delivering Frontier a respectable 40 percent market share.
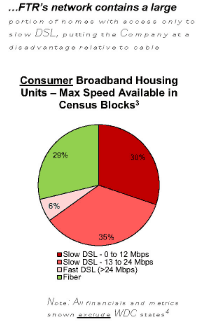
Frontier has been promising DSL speed upgrades for over a decade, but the company’s own numbers show a consistent failure to deliver speeds that can meet the FCC’s definition of “broadband,” currently 25 Mbps.

At least 30% of Frontier DSL customers receive between 0-12 Mbps download speed. Another 35% receive between 13-24 Mbps. Only 6% of Frontier customers get the “fast” DSL capable of exceeding 24 Mbps that is touted repeatedly by Frontier executives on quarterly conference calls.
Despite the obvious case for fiber to the home service, Frontier systematically “under-invested in fiber upgrades” in copper service areas at the same time consumers were upgrading broadband to acquire more download speed. Frontier’s report discloses that nearly 40% of consumers in its service area subscribe to internet plans offering 100 Mbps or faster service. Another 40% subscribe to plans offering 25-100 Mbps. In copper service areas, Frontier is speed-competitive in just 6% of its footprint. That leaves most speed-craving customers with only one path to faster speed: switching to another provider, typically the local cable company.
 So why would a company like Frontier not immediately hit the upgrade button and start a massive copper retirement-fiber upgrade plan to keep the company in the black? In short, Frontier has survived chronic underinvestment because of a lack of broadband competition. Nearly two million Frontier customers have only one choice for internet access: Frontier. For another 11.3 million, there is only one other choice – a cable company that many detest. Frontier has enjoyed its broadband monopoly/duopoly for at least two decades. So long as its customers have fewer options, Frontier is under less pressure to invest in upgrades.
So why would a company like Frontier not immediately hit the upgrade button and start a massive copper retirement-fiber upgrade plan to keep the company in the black? In short, Frontier has survived chronic underinvestment because of a lack of broadband competition. Nearly two million Frontier customers have only one choice for internet access: Frontier. For another 11.3 million, there is only one other choice – a cable company that many detest. Frontier has enjoyed its broadband monopoly/duopoly for at least two decades. So long as its customers have fewer options, Frontier is under less pressure to invest in upgrades.
For years Frontier’s stock was primarily known for its generous dividend payouts to shareholders — money that could have been spent on network upgrades. But what hurt Frontier even more was an aggressive merger and acquisition strategy that acquired castoff landline customers from Verizon and AT&T in several states. In its most recent multi-billion dollar acquisition of Verizon customers in California, Texas, and Florida, Frontier did not achieve the desired financial results after alienating customers with persistent service and billing problems. The longer term legacy of these acquisitions is a huge amount of unpaid debt.
Frontier’s notorious customer service problems are now legendary. Frontier’s new CEO Bernie Han promises that customer service improvements are among his top four priorities. Improving the morale of employees that have been forced to disappoint customers on an ongoing basis is another.
Frontier executives are proposing to fix the company by deleveraging the company’s debt and restructuring it, freeing up capital that can be spent on long overdue network upgrades. Executives claim the first priority will be to scrap more of Frontier’s copper wire network in favor of fiber upgrades. That would be measurable progress for Frontier, which has traditionally relied on acquiring fiber networks from other companies instead of building their own.
But the company will also continue to benefit from a chronic lack of competition and Wall Street’s inherent dislike of large capital spending projects. The proposal does not come close to advocating the scrapping of all of Frontier’s copper service in favor of fiber. In fact, a rebooted Frontier would only incrementally spend $1.4 billion on fiber upgrades until 2024, $1.9 billion in all over the next decade. That would bring fiber to only three million additional Frontier customers, those the company is confident would bring the highest revenue returns. The remaining eight million copper customers would be stuck relying on Frontier’s existing DSL or potentially be sold off to another company.
Frontier seems more attracted to the prospect of introducing or upgrading service to approximately one million unserved or underserved rural customers where it can leverage broadband subsidy funding from the U.S. government. To quote from the presentation: Frontier plans to “invest in areas that are most appropriate and profitable and limit or cease investments in areas that are not.”
Another chronic problem for Frontier’s current business is its cable TV product, sold to fiber customers.
“High content/acquisition costs have made adding new customers to the Company’s video product no longer a profitable exercise,” the company presentation admits. If the company cannot raise prices on its video packages or successfully renegotiate expensive video contracts to a lower price, customers can expect a slimmed down video package, likely dispensing with regional sports networks and other high cost channels. Frontier may even eventually scrap its video packages altogether.
To successfully achieve its goals, Frontier is likely to put itself into Chapter 11 bankruptcy reorganization no later than April 14, 2020. The company’s earlier plans may have been impacted by the current economic crisis caused by the coronavirus pandemic, so the exact date of a bankruptcy declaration is not yet known.

 Internet access in rural states like Idaho is mostly a mixture of cable internet in larger cities and towns and DSL service in suburban areas. Rural communities often have to rely on wireless internet, where available, or satellite internet access. A few communities have a co-op utility that doubles as a broadband provider, but in most cases rural Idaho only gets what CenturyLink, Frontier, and other telephone companies are willing to provide.
Internet access in rural states like Idaho is mostly a mixture of cable internet in larger cities and towns and DSL service in suburban areas. Rural communities often have to rely on wireless internet, where available, or satellite internet access. A few communities have a co-op utility that doubles as a broadband provider, but in most cases rural Idaho only gets what CenturyLink, Frontier, and other telephone companies are willing to provide.

 Subscribe
Subscribe With an estimated 90,000 New Yorkers stranded without broadband service, a proposal from Charter Communications to block funding for future projects is coming under fire from a bipartisan group of rural legislators.
With an estimated 90,000 New Yorkers stranded without broadband service, a proposal from Charter Communications to block funding for future projects is coming under fire from a bipartisan group of rural legislators.
 Frontier Communications filed for bankruptcy reorganization protection this week with more than $10 billion in debts and departing customers, despite retention efforts that cost the company more than $5 million a month.
Frontier Communications filed for bankruptcy reorganization protection this week with more than $10 billion in debts and departing customers, despite retention efforts that cost the company more than $5 million a month.


 Frontier Communications has revealed to investors what many probably realized long ago — the independent phone company chronically underinvested in network upgrades and repairs for years, giving customers an excuse to switch providers.
Frontier Communications has revealed to investors what many probably realized long ago — the independent phone company chronically underinvested in network upgrades and repairs for years, giving customers an excuse to switch providers. About 51% of Frontier’s revenue comes from its residential customers. That number has been declining about 5% annually, year over year as customers leave. Frontier’s internet products are now crucial to the company’s ability to stay in business. Less than 30% of Frontier’s revenue comes from selling home phone lines. For Frontier to remain viable, the company must attract and keep internet customers. For the last several years, it has failed to do either.
About 51% of Frontier’s revenue comes from its residential customers. That number has been declining about 5% annually, year over year as customers leave. Frontier’s internet products are now crucial to the company’s ability to stay in business. Less than 30% of Frontier’s revenue comes from selling home phone lines. For Frontier to remain viable, the company must attract and keep internet customers. For the last several years, it has failed to do either.

 So why would a company like Frontier not immediately hit the upgrade button and start a massive copper retirement-fiber upgrade plan to keep the company in the black? In short, Frontier has survived chronic underinvestment because of a lack of broadband competition. Nearly two million Frontier customers have only one choice for internet access: Frontier. For another 11.3 million, there is only one other choice – a cable company that many detest. Frontier has enjoyed its broadband monopoly/duopoly for at least two decades. So long as its customers have fewer options, Frontier is under less pressure to invest in upgrades.
So why would a company like Frontier not immediately hit the upgrade button and start a massive copper retirement-fiber upgrade plan to keep the company in the black? In short, Frontier has survived chronic underinvestment because of a lack of broadband competition. Nearly two million Frontier customers have only one choice for internet access: Frontier. For another 11.3 million, there is only one other choice – a cable company that many detest. Frontier has enjoyed its broadband monopoly/duopoly for at least two decades. So long as its customers have fewer options, Frontier is under less pressure to invest in upgrades.
