 By the year 2022, 60% of the world’s population will be connected to the internet and 82% of online traffic will come from streaming video.
By the year 2022, 60% of the world’s population will be connected to the internet and 82% of online traffic will come from streaming video.
Those are the conclusions found in Cisco’s newest Visual Networking Index (VNI), based on independent analyst forecasts and real-world network usage data tracked by the networking equipment manufacturer.
“By 2022, more IP traffic will cross global networks than in all prior ‘internet years’ combined up to the end of 2016,” Cisco predicts. “In other words, more traffic will be created in 2022 than in the 32 years since the internet started.”
Key predictions for 2022
Cisco’s VNI looks at the impact that users, devices and other trends will have on global IP networks over a five-year period. From 2017 to 2022, Cisco predicts:
- Global IP traffic will more than triple
- Global IP traffic is expected to reach 396 exabytes per month by 2022, up from 122 exabytes per month in 2017. That’s 4.8 zettabytes of traffic per year by 2022.
- By 2022, the busiest hour of internet traffic will be six times more active than the average. Busy hour internet traffic will grow by nearly five times (37 percent CAGR) from 2017 to 2022, reaching 7.2 petabytes1 per second by 2022. In comparison, average internet traffic will grow by nearly four times (30 percent CAGR) over the same period to reach 1 petabyte by 2022.
1 A petabyte is equal to 1,000 terabytes or one million gigabytes.
- Global internet users will make up 60 percent of the world’s population
- There will be 4.8 billion internet users by 2022. That’s up from 3.4 billion in 2017 or 45 percent of the world’s population.
- Global networked devices and connections will reach 28.5 billion
- By 2022, there will be 28.5 billion fixed and mobile personal devices and connections, up from 18 billion in 2017—or 3.6 networked devices/connections per person, from 2.4 per person.
- More than half of all devices and connections will be machine-to-machine by 2022, up from 34 percent in 2017. That’s 14.6 billion connections from smart speakers, fixtures, devices and everything else, up from 6.1 billion.
- Global broadband, Wi-Fi and mobile speeds will double or more
- Average global fixed broadband speeds will nearly double from 39.0 Mbps to 75.4 Mbps.
- Average global Wi-Fi connection speeds will more than double from 24.4 Mbps to 54.0 Mbps.
- Average global mobile connection speeds will more than triple from 8.7 Mbps to 28.5 Mbps.
- Video, gaming and multimedia will make up more than 85 percent of all traffic
- IP video traffic will quadruple by 2022. As a result, it will make up an even larger percentage of total IP traffic than before—up to 82 percent from 75 percent.
- Gaming traffic is expected to grow nine-fold from 2017 to 2022. It will represent four percent of overall IP traffic in 2022.
- Virtual and augmented reality traffic will skyrocket as more consumers and businesses use the technologies. By 2022, virtual and augmented reality traffic will reach 4.02 exabytes/month, up from 0.33 exabytes/month in 2017.
Regionally, Asian-Pacific internet users are expected to use far more internet data than North Americans — 173 exabytes a month by 2022 vs. 108 exabytes in North America. Usage caps, usage-based pricing, and overall slower internet speeds in the U.S. and Canada have slowed growth in new high-bandwidth internet applications. The prevalence of low-speed DSL in rural areas also restricts potential traffic growth. Large parts of the Asia-Pacific region use very high-speed fiber to the home technology.
The slowest growing regions — Latin America and the Middle East/Africa, which lag behind in internet penetration, often apply low usage caps or bandwidth restrictions and often do not have the ability to financially scale growth to meet demand. Even by 2022, Latin America will generate only 19 exabytes of traffic per month.


 Subscribe
Subscribe A snowstorm, in winter, in Upstate New York, was the excuse Frontier Communications gave for leaving scores of residents in the Minerva-Johnsburg area without phone or internet service for as long as 10 days this month.
A snowstorm, in winter, in Upstate New York, was the excuse Frontier Communications gave for leaving scores of residents in the Minerva-Johnsburg area without phone or internet service for as long as 10 days this month.
 Pearsall pays Frontier for internet speeds advertised at 6-10+ Mbps, but receives 0.69 Mbps for downloads and 0.08 Mbps for uploads at his home in Garnet Lake. A typical Microsoft Office software update takes approximately 48 hours to arrive, assuming one of many frequent service outages does not force the upgrade to start anew.
Pearsall pays Frontier for internet speeds advertised at 6-10+ Mbps, but receives 0.69 Mbps for downloads and 0.08 Mbps for uploads at his home in Garnet Lake. A typical Microsoft Office software update takes approximately 48 hours to arrive, assuming one of many frequent service outages does not force the upgrade to start anew.

 A dispute is emerging in New York between Sprint and T-Mobile and the Communications Workers of America (CWA) and pro-consumer group the Public Utility Law Project (PULP) over the wireless companies’ attempt to argue for their merger deal in a partly secretive filing not open to review by the public.
A dispute is emerging in New York between Sprint and T-Mobile and the Communications Workers of America (CWA) and pro-consumer group the Public Utility Law Project (PULP) over the wireless companies’ attempt to argue for their merger deal in a partly secretive filing not open to review by the public.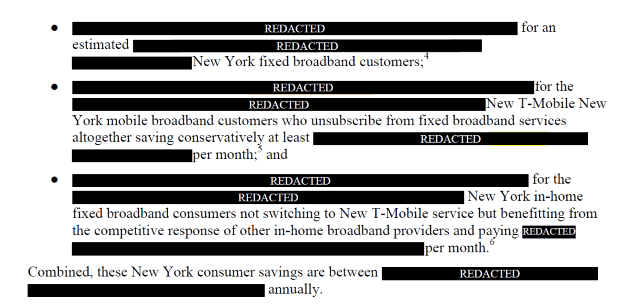
 The merger of the two wireless companies requires state and federal approval. Alaska, Colorado, Delaware, Georgia, Louisiana, Maryland, Minnesota, Nevada, Texas, Utah, West Virginia and the District of Columbia have already essentially “rubber-stamped” approval of the merger deal with little comment. Pennsylvania regulators submitted a series of questions that the two companies answered earlier this week.
The merger of the two wireless companies requires state and federal approval. Alaska, Colorado, Delaware, Georgia, Louisiana, Maryland, Minnesota, Nevada, Texas, Utah, West Virginia and the District of Columbia have already essentially “rubber-stamped” approval of the merger deal with little comment. Pennsylvania regulators submitted a series of questions that the two companies answered earlier this week.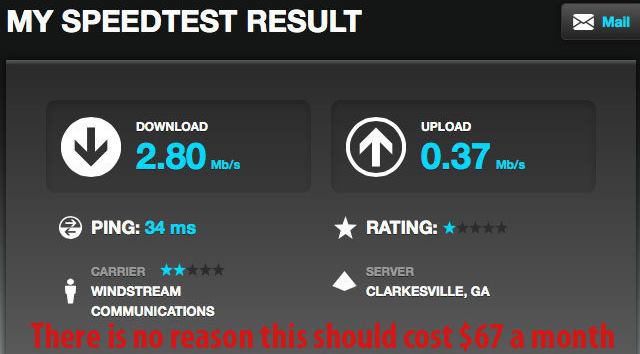
 “It took a service technician coming out to make it clear to us there was no way we would ever get faster speed because there was too much copper wiring between their office and our homes,” Brown said. “The technician felt for us, and about half of his service calls were disappointing customers like us.”
“It took a service technician coming out to make it clear to us there was no way we would ever get faster speed because there was too much copper wiring between their office and our homes,” Brown said. “The technician felt for us, and about half of his service calls were disappointing customers like us.” “We are paying for internet speed that we aren’t receiving,” Ruth complained. “It is so slow that we have a hard time getting a short 50 second video to load. Forget watching a YouTube video, it’s not going to happen.”
“We are paying for internet speed that we aren’t receiving,” Ruth complained. “It is so slow that we have a hard time getting a short 50 second video to load. Forget watching a YouTube video, it’s not going to happen.” Wall Street balks at the dollar amounts it would take for Windstream to fully update its network to offer broadband speeds that were common for cable subscribers a decade ago. That kind of network investment would likely drive down the share price, impact shareholder dividends or stock buyback plans, and increase debt. Instead, many phone companies are hoping the federal government will come to the rescue and subsidize rural network improvements through the FCC’s Connect America Fund or government grants. But many of those grants won’t deliver service improvements to existing customers. Instead it will allow rural phone companies to bring broadband to customers who never had it before.
Wall Street balks at the dollar amounts it would take for Windstream to fully update its network to offer broadband speeds that were common for cable subscribers a decade ago. That kind of network investment would likely drive down the share price, impact shareholder dividends or stock buyback plans, and increase debt. Instead, many phone companies are hoping the federal government will come to the rescue and subsidize rural network improvements through the FCC’s Connect America Fund or government grants. But many of those grants won’t deliver service improvements to existing customers. Instead it will allow rural phone companies to bring broadband to customers who never had it before.