The New York Public Service Commission on Thursday approved its final settlement proposal with Charter Communications in a 3-1 vote, allowing Spectrum to continue as the dominant cable operator in New York State.
The New York Public Service Commission on Thursday approved its final settlement proposal with Charter Communications in a 3-1 vote, allowing Spectrum to continue as the dominant cable operator in New York State.
The Commission rejected all recommended changes from consumer groups (including Stop the Cap!), industry trade associations, and service providers, preferring its own Settlement Agreement.
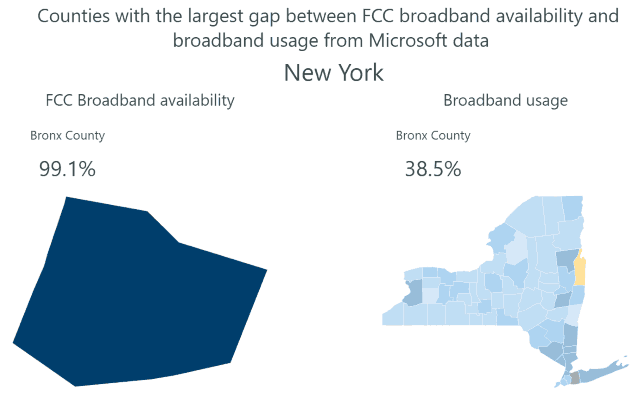
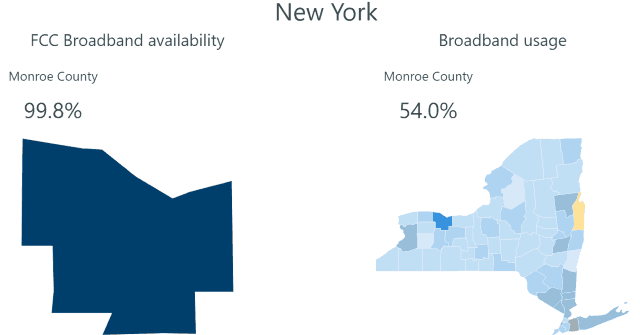
In July 2018, the PSC voted to rescind approval of the 2016 Merger Order that allowed Charter to assume control of Time Warner Cable franchise areas in New York. The Commission found that Charter had violated a key merger condition requiring the cable operator to expand its service area on a timely basis to reach 145,000 rural homes and businesses that lack broadband service. The Commission found Charter was attempting to count newly constructed condos and multi-dwelling units in the New York City area towards that commitment, which the Commission claimed violated the terms of the agreement. After Charter argued it had the legal standing to define its network buildout more broadly and on its own terms, the Commission held an emergency meeting where it took the unprecedented step of voting to de-certify the merger and throw the cable company out of New York.
The Commission and Charter’s lawyers began private negotiations almost immediately after the vote, signaling the Commission was amenable to settlement talks.
The final settlement approved last week, nearly one year after the vote, narrowly focuses on Charter’s rural broadband commitment, reaffirms and expands it with a new $12 million rural broadband fund paid for by Charter. The cable company also agreed to stop counting addresses in the New York City area towards it broadband expansion commitment, and will deposit a $2,800 payment to escrow for each address where Charter misses its target construction deadline.
“We’re pleased the PSC has approved the agreement, and we look forward to continuing to serve our customers and expanding the availability of high-speed broadband in New York State,” Andrew Russell, Charter spokesman told the (Albany) Times-Union. “We thank the PSC, Chairman Rhodes, the commissioners and staff for working with us throughout this process.”
The settlement details:
- Charter will complete the expansion of its existing network to pass 145,000 addresses entirely in Upstate New York. This expansion will not include New York City addresses, which the company had previously planned to include in an earlier buildout plan. To date, Charter has passed approximately 65,000 of the required 145,000 addresses. To comply with the settlement, the Department estimates that the company will invest more than $600 million, more than double the public benefit value estimated by the Commission in its 2016 merger approval.
- Charter’s expansion will be completed by September 30, 2021, in accordance with a schedule providing frequent interim enforceable milestone requirements, with corresponding reporting and accountability.
- Charter will also pay $12 million for additional broadband expansion projects at locations to be selected by the Department of Public Service and the New York State Broadband Program Office. Of the $12 million payments, $6 million will be administered by the New York State Broadband Program Office and $6 million will be paid into an escrow fund for work that will be completed by Charter at the State’s direction.
 In Rochester, Stop the Cap! was disappointed to learn the PSC had rejected recommendations on improving the settlement.
In Rochester, Stop the Cap! was disappointed to learn the PSC had rejected recommendations on improving the settlement.
“We feel all New Yorkers have paid a price for this bad merger, including skyrocketing cable bills and a yet to be determined number of rural residents that will fall through the cracks and end up serviced by no one,” said Phillip Dampier, the group’s founder and president. “We applaud the PSC requiring Charter to serve additional rural households, but every customer should get better service from Charter, including the 200 Mbps download speed that customers in many other states receive, and there must be a better solution for low-income residents that don’t qualify for Spectrum’s restrictive Internet Assist program and cannot afford $65 a month for internet access.”
Stop the Cap! today also filed a clarification request with the PSC about Charter’s internet speed commitment.
“There seems to be confusion about exactly what internet speed Spectrum should be offering its New York customers,” Dampier added. “The PSC seems to imply Charter has not yet met its obligation to increase internet speed to 300 Mbps by the end of 2019, while Charter considers the fact it offers gigabit service as evidence it has completed all of its speed obligations to New York State regulators. We want the PSC to clarify if it still expects Charter to offer 300 Mbps as a base speed to customers by the end of this year or whether the mere availability of speeds at or above 300 Mbps (which Time Warner Cable was already offering a significant part of New York a year before the Charter merger) has satisfied this merger condition.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe Frontier Communications has publicly admitted its residential telephone service in rural and “high-cost” service areas is “
Frontier Communications has publicly admitted its residential telephone service in rural and “high-cost” service areas is “

 CenturyLink’s stock is being pummeled after the company announced a cut in divided payouts to shareholders earlier this year, preferring to keep the money in-house to reduce debt and increase spending on necessary broadband upgrades.
CenturyLink’s stock is being pummeled after the company announced a cut in divided payouts to shareholders earlier this year, preferring to keep the money in-house to reduce debt and increase spending on necessary broadband upgrades. Investors were not impressed with those plans, and CenturyLink’s share price cratered.
Investors were not impressed with those plans, and CenturyLink’s share price cratered.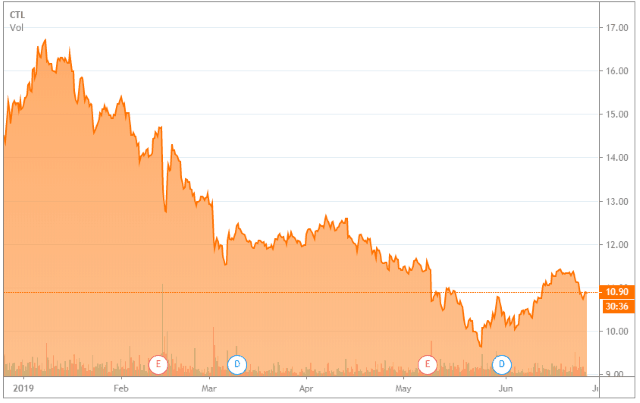

 States with large urban poor communities are particularly sensitive to the merger, because both T-Mobile and Sprint focus their coverage on urban areas. With the average U.S. household spending $1,100 annually on wireless phone service, even small rate increases can dramatically increase service suspensions or disconnections due to late or non-payment.
States with large urban poor communities are particularly sensitive to the merger, because both T-Mobile and Sprint focus their coverage on urban areas. With the average U.S. household spending $1,100 annually on wireless phone service, even small rate increases can dramatically increase service suspensions or disconnections due to late or non-payment.