AT&T launched its U-verse service in parts of the Memphis area Monday, promising competition for Comcast, the dominant cable company in southwest Tennessee. But some area residents expected much more to come from last year’s controversial industry-friendly statewide franchising law that promoters promised would bring lower prices for service across the state.
AT&T plans to offer U-verse within the next two years to subscribers in Arlington, Bartlett, Collierville, Covington, Dyersburg, Germantown, Lakeland, Memphis, Piperton and Ripley. Monday’s launch only covers a portion of Memphis, and doesn’t cover large portions of downtown.
[flv width=”552″ height=”294″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/U-verse overview.flv[/flv]
An Overview of AT&T U-verse television service
Unlike traditional cable services, AT&T’s U-verse is typically delivered on a copper wire and fiber optic based Internet Protocol network. Not as advanced as Verizon FiOS, which provides a fiber optic connection straight into the home, AT&T’s system still relies in part on traditional copper phone wire that runs from the pole to your home. AT&T uses this approach to save money — company officials claim 100% fiber networks are too costly to build, and Wall Street investors balk at the up front costs.
AT&T uses its fiber network from the phone company office to individual neighborhoods to reduce the distance between the homeowner and the company’s equipment, which delivers a digital signal across the customer’s existing phone line. Just like DSL, the shorter the distance between the customer and the telephone company equipment, the faster the speeds. AT&T U-verse requires fast speeds to handle the video channels, digital phone, and broadband components that are part of the U-verse product line.
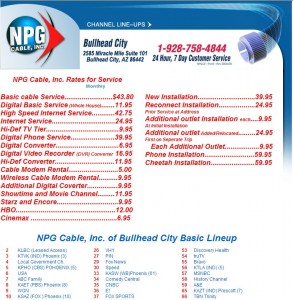
AT&T’s U-verse pricing ranges from $49 a month for an enhanced basic service package of 130 channels to $109 for 390 channels. Premium channels are extra. Plans include one AT&T set top box. AT&T’s system will require a set top box for each television, at a monthly rental of $7 for each additional set, which can increase costs significantly for houses with several televisions. An HD package runs $10 per month. AT&T specials often include discounted or free installation, which takes between four to seven hours to complete and is only done on weekdays. No contracts are required and customers can cancel at any time.
AT&T claims that 70% of their customers choose a bundled package that includes television, broadband, and/or telephone service.
Company officials credited the passage of the Competitive Cable and Video Services Act, which became effective in July 2008, for paving the way for AT&T U-verse in the city. AT&T’s praise also included crediting elected officials by name who supported the company’s lobbying efforts towards passage of that bill, which stripped cable franchising authority from local communities and adopted a statewide franchise system.
“We are thrilled to offer this innovative video choice to customers in the Memphis metropolitan area. As we celebrate this Memphis launch, I want to remember the contributions of the Tennessee General Assembly to open Tennessee’s video services marketplace to competition which is truly benefiting consumers. I would like to again thank Memphis area legislators including Speaker Emeritus Jimmy Naifeh, Senator Mark Norris, House Speaker Pro Tem Lois DeBerry, Chairman Ulysses Jones and the many others who supported competition and choice for consumers,” said Gregg Morton, president, AT&T Tennessee.
In turn, elected officials were quoted in AT&T’s press release:
“As Tennessee policymakers, our goal was to increase investment throughout the state and give consumers more choices and innovative new services,” said Senator Norris. “AT&T has been a great community citizen and the launch of AT&T U-verse also supports economic growth in Memphis.”
“We are excited that AT&T has brought their 100 percent Internet Protocol-based television service to Memphis,” said Chairman Jones. “Consumers in Memphis have asked for this and today, AT&T has delivered.”
<
p style=”text-align: center;”>AT&T Group President for Operations Support John Stankey discusses the company’s fiber strategy and provides an update on its progress in deploying its groundbreaking IPTV service, AT&T U-verse TV. (11 minutes)
You must remain on this page to hear the clip, or you can download the clip and listen later.
<
p style=”text-align: center;”>
The Municipal Technical Advisory Service, in association with the Tennessee Municipal League, noted that the lobbying effort to pass the Act was among the most expensive lobbying campaigns in state history.
This legislation is part of the national trend to diminish or eliminate the franchising authority of cities by granting cable companies the right to provide services without negotiating agreements with local governments.
In recent years, several cable companies operating in Tennessee permitted local franchise agreements to expire and refused to negotiate contracts with cities in anticipation that legislation would be adopted that would give cable companies great advantages in negotiating new agreements.
This tactic has paid off, as this law essentially grants a statewide franchise to these companies. Current franchise holders may now terminate their local agreements and seek a state franchise. A city that has previously negotiated a franchise agreement with one cable provider may be forced to permit other cable companies to serve its area under the same terms and conditions of the existing agreement
Such legislation has traditionally been advocated by telephone companies like AT&T and Verizon who are introducing video services in a bid to remain competitive with cable, which now offers its own telephone service. Seen as a shortcut to negotiating with each individual municipality, the statewide franchise advocates claims it reduces the time and expense of bring needed competition to communities.
In addition to an expensive lobbying campaign, astroturfer FreedomWorks coincidentally showed up to promote their “Choose Your Cable” campaign, which in fact mirrors AT&T’s public policy advocacy of statewide franchising.
FreedomWorks Chairman Dick Armey commented, “FreedomWorks and our thousands of Tennessee members were proud to take part in the grassroots battle in Tennessee that finally saw this ground-breaking legislation through. We salute the Tennessee state legislature for its leadership in giving Tennessee consumers the advantages of increased competition in the video services market. The Competitive Cable and Video Services Act will offer cable consumers more choices and more innovation. And when businesses are forced to compete for customers, the customers win.”
Incumbent cable operators have had mixed reactions to such proposals, generally opposing them in areas where they would likely face the entry of AT&T or Verizon into their markets, and taking a more favorable approach in areas where they are unlikely to face a strong telephone company competitor.
In Tennessee, with AT&T itching to bring U-verse to state residents, cable operators launched a major opposition effort.
Local municipalities and many consumer advocates strongly oppose statewide franchising legislation, noting such laws remove local oversight over operators that do not perform responsibly and reasonably in their communities. Additionally, in many states where statewide franchise bills have become law, local communities find franchise fees paid into state bodies that do not always pass on the full amount of that revenue to towns and cities.
Other common problems include:
- Threatened loss of local Public, Educational, and Governmental (PEG) local access channels;
- Reduced control over zoning regulations prohibiting digging and construction without permits;
- Loss of “free service” provisions that deliver cable programming to public schools, community centers, and town, police and fire halls at no charge;
- Loss of authority to help manage customer complaints.
In Tennessee, those opposing the legislation managed to get rid of statewide franchise fee administration, retained control over their existing PEG channels, and kept existing “free service” provisions, as well as reasonable zoning requirements. However, the telecommunications industry did manage to include language banning municipally owned broadband networks in any area where an incumbent provider exists:
Broadband joint venture authority.
The law creates the “Tennessee broadband deployment fund” to be used to promote the deployment of broadband service to rural areas. Guidelines will be developed to govern use of the funds, and grants will be available to local governments, cable companies, and telecommunications companies.
Cities now have the authority to enter into joint ventures with one or more third parties to provide broadband services. Joint ventures will be authorized only in areas that are historically unserved. City electric companies and electric cooperatives that participate in these joint ventures must still comply with other applicable statutes, and no revenues from utility operations may be used to subsidize the joint venture.
Cable operators also managed some concessions, and after the bill was signed into law, the state cable television association said they could live with the result.
Stacey Briggs, executive director of Tennessee Cable Telecommunications Association:
“This has been a good process – not easy, but good – and Speaker Naifeh should be commended for managing this outcome on a highly complex policy.
The cable industry, including Comcast and Charter, stood firm to make sure that our members were treated fairly and that AT&T and other companies were not granted advantages in the law. And, most important for consumers, Tennessee’s cable companies will continue making substantial and meaningful investment in Tennessee. Cable companies will continue to be the leader in bringing the most advanced products, services and newest technologies to consumers across the state.
AT&T and other companies have had the right to compete under local franchising rules for more than a dozen years. This new policy streamlines the franchise process, but it remains to be seen whether new entrants will compete in Tennessee.”
After all of the lobbying was done, the bill was signed into law, and the competition FreedomWorks was touting did arrive, the only thing missing from the consumer perspective was lower pricing.
Comcast, the local cable operator serving Memphis, seemed unfazed by AT&T’s entry into the area.
“We have competed successfully against satellite TV and other competitors for many years,” said Trevor Yant, vice president and general manager of Comcast of Memphis. “AT&T will become another player in the market with the services they choose to offer.”
One of the possible reasons for Comcast’s apparent lack of concern may stem from the reaction of many Memphis residents, who note AT&T’s prices are often higher than those charged by Comcast.
Among the mostly unimpressed reactions on local message boards:
mrhmeisme:
“$109.00 for 390 channels doesn’t sound like a very competitive price for a yet untested product. That’s some 20 percent higher than my current package that has all the channels that interest me. I suppose the proof will be in the pudding.”Not_Chicken_Little:
“The website for U-verse presents the packages very poorly, and the prices don’t seem to be any bargain. But I am glad to see some competition, even though I don’t think they’ll make much headway. They need to show what they’ve got in a more attractive and understandable way, and cut prices – they don’t make me even think of switching with the lame sales pitch they have now.”dmat7777:
“I just did a comparison of cost between my current Comcast and the U-verse. For comparable services, U-verse would be about $15 more per month for me. Some of the packaging/options might look better. For example, the Flickr photo being included, but I’m more concerned about how much $$$ per month. I don’t see AT&T taking this seriously. They seem to be doing the typical huge corporate thing, and not addressing the customers real concerns. No surprise there.”ChickPea:
“$49 a month is too rich for my blood. When someone offers a decent package available for $25-$30 a month, I’ll be in.”
Oddly, the most common requests and complaints among Memphis area residents continue to be unanswered by Tennessee officials who were eager to support the Competitive Cable and Video Services Act, but left out a few things:
umbluegray:
“I want a plan where I can pick and choose the channels I want. I hate paying money to some of the basic channels like MTV, etc.”ladydonald:
“I would be a big fan of a-la carte programming if it were ever enacted.A-la carte channels are a niche that all of the providers are totally ignoring. Just think what would or could happen if those options were available.”
Hogs2009:
“It would be nice if you could pick out what cable channels you want and skip the rest. 90% of cable channels I do not want but am charged for. I mainly have cable for sports broadcasting channels, like ESPN, ESPN2, and ESPN Classic. I also like having local on cable because it is more clear, again because some games are on local channels. A-la carte is a great idea!”
Many residents were also suspicious of just how good a local competitor AT&T will be against Comcast, which itself took over providing cable service formerly provided by Time Warner Cable:
DanWesson:.
“Since Comcast bought out service from Time Warner locally, our service has been sub-par. I have had technicians out the house multiple times due to inexplicably losing certain HD channels and internet service that continually drops or can be agonizingly slow, on par with dial-up some days (particularly the hot ones, which is very strange). Their technicians on the phone and who come to the house have been polite and friendly, but they aren’t exactly going out of their way to fix the problem.Comcast also charges me more than Time Warner did in addition to charging a “modem-rental” fee when the cable modem was free from Time Warner and I haven’t exchanged it since the change.
All that said, I’m not sure AT&T is the way to go as their corporate practices are the worst in the Telecom industry. Customer service has always been non-existent as the customer is merely a cash-cow. I’m all for competition in the marketplace, though. If Direct TV didn’t require a contract that might would be the route I went, but I’d still be reliant on one of these other worthless companies for internet.”
Not_Chicken_Little:
“On the website trying to check availability, U-verse tells me it cannot find my address! It suggests I try again using my AT&T phone number instead and directs me to continue to another screen. That screen, however, has no option to enter a phone number – only the address.So I already see the level of competence I would have to endure if I choose U-verse. And like dmat7777, I see that the price for comparable service would be considerably higher than what I have now.”
apollo1377:
“AT&T can’t handle phone service. Do you think they can take on more? I think NOT.”ima_cracker:
“If AT&T could deliver a more reliable package some would pay more to get it.Instead they are mortgaging the company’s reputation for wireline services, which they continually deride, to try and emulate the cable companies financial model, which has produced a reputation for reliability that is the envy of nobody.
If instead of trying to destroy the value in wireline AT&T decided to pursue a higher quality, more reliable service for cable, they could at some point expect to capture a substantial amount of market share. But they assume the consumer is too stupid to make the distinction between one service and another.”
ChickPea:
“AT&T websites are a perennial problem. Ever since BellSouth was taken over by AT&T, getting any information on local service online has been a struggle. A site map would probably look like a birds nest.
That said, I’m loving my AT&T DSL lite! Cheap and plenty fast for a non-gamer.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe