With many cable operators reporting a need to double network capacity every 18-24 months to keep up with customer traffic demands, the industry is spending time and money contemplating how to meet future needs while also finding ways to cut costs and make networks more efficient.
Top technology executives from five major cable operators answered questions (sub. req’d.) from Multichannel News about their current broadband networks and their plans for the future. Some, like Mediacom, are aggressively adopting DOCSIS 3.1 cable broadband upgrades for their customers while companies like Cox and Comcast are deploying multiple solutions that use both traditional hybrid fiber-coax network technology and, on occasion, fiber-to-the-home to boost speed and performance. But at least one cable company — Charter Communications — thinks it can continue operating its existing DOCSIS 3 network without major upgrades for several years to come.
Cable Broadband Traffic Can Be Handled
“We’ve been on a pretty steady path of doubling our network capacity every 18-24 months for several years, and I don’t see anything that makes me think that will change,” said Tony Werner, president of technology and product at Comcast. “We’ve been strategically extending fiber further into our network to meet customer demand, and that effort, combined with our commitment to deploying DOCSIS 3.1 has given us a network that’s powerful, flexible, and ready for what’s next.”
J.R. Walden, senior vice president of technology at Mediacom was more aggressive.
“We have completed the removal of all the analog channels. That was the big step one,” Walden said. “Step two was to start transitioning high-speed data over to DOCSIS 3.1, so we’re not adding any more 3.0 channels, and reuse spectrum for 3.1, which is a bit more efficient. The whole company is 3.1, all the modems we’re buying since June have been 3.1, so we’ve begun that next transition.”
Walden added Mediacom is also trying to improve broadband performance by reducing the number of customers sharing the same connection.
“We average about 285 homes to 290 homes per node as an average,” he said.
Mediacom is also scrapping older technology on the TV side to open new bandwidth. The cable company is getting rid of MPEG-2-only set-top boxes so the company can transition its video lineup to MPEG-4. But even that won’t last long. Walden admits the company will then quickly start moving less-viewed channels and some premium networks to IP delivery.
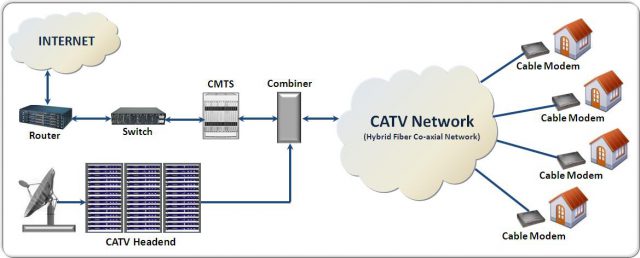
Traditional cable broadband service relies on a hybrid fiber-coax network.
In its European markets, Liberty Global has adopted Converged Cable Access Platform (CCAP) equipment across its footprint. CCAP technology saves cable operators space and operates more efficiently, and supports future convergence of technologies that cable operators want to adopt in the future. CCAP has helped Liberty Global deal with its 45% traffic growth by making upgrades easier. The company is also using advanced features of CCAP to better balance how many customers are sharing a connection. The next step is adopting DOCSIS 3.1.
“Seventy to 80% of our plant will be DOCSIS 3.1 ready by the end of next year, giving us a path to even greater capacity expansion allowing us to continue to increase the available capacity across our access network, upstream and downstream,” said Dan Hennessy, chief architect of network architecture for Liberty.
Charter is prioritizing maximizing performance on the network it already has.
“Our priority is to constantly balance capacity against demand. It’s a never-ending quest,” said Jay Rolls, Charter’s chief technology officer. “We watch it very closely, and we’re very pragmatic about it — the volume of tools, metrics and ways to see what’s really happening, and invest accordingly, is really deepening in ways that matter.”
Is Fiber-to-the-Home in Your Future?
While some cable operators like Altice’s Cablevision are scrapping their existing hybrid fiber-coax networks in favor of fiber-to-the-home (FTTH), America’s largest cable operators are not in any hurry to follow Altice.
Comcast has expanded its fiber network closer to customers in the last few years, but sees no need to convert customers to FTTH service.
“I feel pretty strongly that the best path ahead is to leverage the existing coaxial network and DOCSIS resources to the fullest, then inch towards FTTH, over time Why? Because we can. We don’t have to build an entire network just to turn up one customer.”
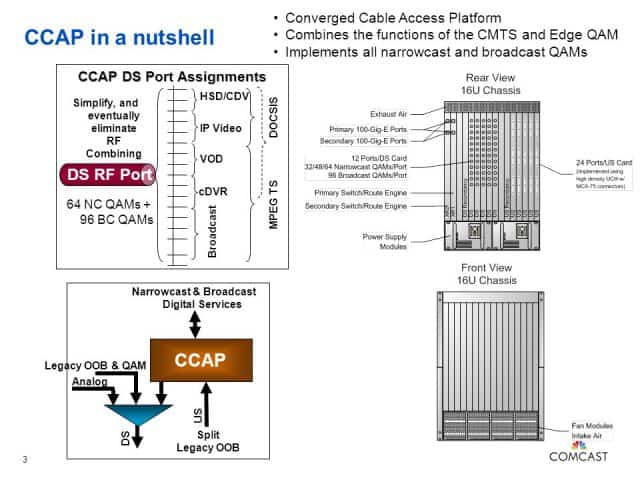
The next generation of cable broadband service may depend on CCAP – technology that will cut operator costs and lay the foundation for changing the way video and other services are delivered to customers.
Cox has a 10-year Network 2.0 plan that will bring fiber closer to customers, but not directly to every home. More important to Cox is having the option to support symmetrical speeds, which means delivering upload speeds as fast as download speeds. In the meantime, network cabling Greensboro can improve your current connectivity and reliability, preparing your network for high-speed internet.
“We’re also thinking about the fiber investment and fiber deep as it relates to our wireless strategy, enabling some of our customers with a small cell strategy but also positioning ourselves to take advantage of that in the future, as well as thinking about fiber deep to benefit both residential and our commercial customers simultaneously,” said Kevin Hart, Cox’s executive vice president and chief product and technology officer.

Liberty/Virgin Media’s Project Lightning is bringing cable broadband and TV service to places in the UK that never had cable service before.
In Europe, Liberty Global’s “Project Lightning” network expansion initiative is building out traditional cable service in the United Kingdom. Most of the UK never adopted cable service, favoring small satellite dish service instead. Now Liberty Global is putting cable expansion on its priority list. But decades after most North Americans got cable service for the first time, today’s new buildouts are based largely on fiber optics — either fiber to the home or fiber to the neighborhood, where coaxial cable completes the journey to a customer’s home.
Charter admits the technology it will use in the future partly depends on what the competition is offering. Rolls says the company can eventually roll out DOCSIS 3.1, take fiber deeper, or offer symmetrical download/upload speeds presumably targeted towards its commercial customers. But he also suggested Charter’s existing network can continue to deliver acceptable levels of service without spending a lot on major upgrades.
“It’s a rational approach, where we’re trying to balance the needs, the available technologies, and the costs,” Rolls said. But he also suggested DOCSIS 3.1 isn’t always the answer to upgrades. “DOCSIS 3.1 has some pretty remarkable capabilities, but it’s not necessarily a hard-and-fast reason to not take fiber deeper, for instance [allowing for additional DOCSIS 3 node splits]. Different situations drive different capacity decisions.”
Walden agreed, and Mediacom customers should not expect more than DOCSIS 3.1 upgrades for the near future.
“[Fiber deep] is a bit further out, at least as a large-scale type of project,” Walden told Multichannel News. “I think fiber deep for multi-dwelling units, high-density areas and some planned higher end communities doing deeper fiber or fiber-to-the-home [is happening]. But as a wholesale [change] and going to node+0 kind of architecture, I don’t see that in the next two years.”
Are Symmetrical Speeds Important for Customers?

Verizon’s fiber to the home service FiOS uses symmetrical broadband speeds to its advantage in the marketplace.
Many fiber to the home networks offer customers identical upload and download speeds, but cable broadband was designed to favor downstream speeds over upstream. That decision was based on the premise the majority of users will receive much more traffic than they send. But as the internet evolves, some are wondering if cable broadband’s asymmetric design is now outdated and some competitors like Verizon’s FiOS fiber to the home service now use its symmetrical speed advantage as a selling point.
Cox Communications does not think most customers care, even though its network upgrades are laying the foundation to deliver symmetrical speeds.
“It’s a little but further out on the horizon,” said Hart. “The upstream growth rate is ticking up a couple of notches, but not to the tune that we would need significant additional capacity and/or a complementary need for symmetrical bandwidth. [A]t this stage, the symmetrical is a nice-to-have for residential and definitely will be a good option for our commercial customers.”
Rolls isn’t sure if symmetrical speeds are important to customers either and Charter has no specific plans to move towards upload speed upgrades.
“The world of applications and services continues to evolve, obviously, but so far we’ve been able to meet those needs with an asymmetrical topology,” Rolls said. “That said, things like real-time gaming, augmented and virtual reality, and the Internet of Things — some of those will likely drive more symmetry in the network. It remains to be seen.”
 Exurban communities in northern Illinois bypassed for upgrades from second-rate cable companies and considered too-small-for-fiber by AT&T are clamoring for a third option that will deliver fiber optic broadband.
Exurban communities in northern Illinois bypassed for upgrades from second-rate cable companies and considered too-small-for-fiber by AT&T are clamoring for a third option that will deliver fiber optic broadband. Sugar Grove is just one of several exploding exurban communities in the far western suburbs of Chicago. As residents migrate further away from the city center, they expect services to migrate with them. But when essential utilities are in the hands of private companies, smaller towns and villages are often frustrated to hear there is not enough Return On Investment to provide 21st century quality service.
Sugar Grove is just one of several exploding exurban communities in the far western suburbs of Chicago. As residents migrate further away from the city center, they expect services to migrate with them. But when essential utilities are in the hands of private companies, smaller towns and villages are often frustrated to hear there is not enough Return On Investment to provide 21st century quality service. “The MetroZone opportunity is a milestone in that we are able to track those who are interested in us coming to the village of Sugar Grove,” said Kathy Scheller, business development manager for MetroNet. “Our goal is to have 25 percent of the village pre-signed by Feb. 28.”
“The MetroZone opportunity is a milestone in that we are able to track those who are interested in us coming to the village of Sugar Grove,” said Kathy Scheller, business development manager for MetroNet. “Our goal is to have 25 percent of the village pre-signed by Feb. 28.”

 Subscribe
Subscribe While giant cable company mergers unexpectedly took a breather in 2017, Fierce Cable predicts this year isn’t likely to be a repeat of last year.
While giant cable company mergers unexpectedly took a breather in 2017, Fierce Cable predicts this year isn’t likely to be a repeat of last year.