 States and communities across the country are warning the Federal Communications Commission its proposal to limit local authority over wireless infrastructure siting will create chaos and open the door to public safety and aesthetics nightmares.
States and communities across the country are warning the Federal Communications Commission its proposal to limit local authority over wireless infrastructure siting will create chaos and open the door to public safety and aesthetics nightmares.
The FCC’s proposal would allegedly accelerate wireless infrastructure deployment by removing or pre-empting what some on the Commission feel are improper zoning barriers, unjustified fees meant to deter providers from adding new towers, and various other bureaucratic impediments. It would modify current “shot clock” rules that set time limits on applications and deem them automatically granted if a local or state authority failed to reach a decision in as little as 60 days.
While the wireless industry has expressed strong support for the proposed changes introduced by FCC Chairman Ajit Pai in March during the FCC’s “Infrastructure Month,” many states and localities are fiercely opposed to what some are calling a federal government takeover of local zoning and permitting. States as diverse as Illinois, Utah, and Maine have submitted comments objecting to the proposal, noting it will turn the FCC into a national zoning agency that could allow the installation of new cell towers and monopole antennas just about anywhere if the clock for consideration has run out.
Several communities have also submitted comments to the FCC reminding the agency its existing rules have allowed some providers to abuse the system, with further easing of regulatory oversight on the local level only increasing the potential for more abuse.
Communities have complained some providers have intentionally overwhelmed local authorities by submitting “bulk applications” that attempt to win approval for dozens of new sites with incomplete or missing paperwork. Others report providers using the public rights-of-way have placed large pieces of infrastructure in direct line with residents’ front doors, have created public safety problems with equipment that blocks drivers’ views at intersections, and had to contend with requests to place 120-200 foot monopole antennas on the edge of public highways and abandoned retired infrastructure providers fail to maintain or remove.
The Utah Department of Transportation, among others, calls the FCC’s proposal “detrimental to public safety” and warns the FCC could end up creating a new loophole allowing providers to submit defective applications and then stalling required corrections until the shot clock runs out.
“No decisions are made on incomplete applications because the requested information is necessary for a decision to be issued,” Utah’s DOT writes. “This information may include, but is not limited to, when and where the work will be performed, type of installation, impacts to the traffic of the state highway. All safety issues must be addressed. Any shot clock start considerations by the Federal Communications Commission must be based upon completed applications. Otherwise the telecommunications company may fail to submit a completed application and continue to not submit all the requested information until the shot clock time period has run out. Such an approach would have detrimental impacts to safety of the traveling public on state highways because the Federal Communications Commission seeks to remove any authority from the states and local governments to address safety and placement after the shot clock has run out.”
Utah also fears the FCC’s decision to set uniform fees for applications could end up subsidizing large telecom companies with taxpayer dollars.
“Any requirement mandating lower fees than the actual costs will require the states to subsidize the telecommunications industry,” Utah’s DOT warned.
Maine’s Department of Transportation worries the FCC is putting the interests of multi-billion dollar telecom corporations ahead of the citizens of the state and their own needs. By allowing telecommunications companies to win irrevocable rights to place wireless towers where they want by running out the clock, the interests of those companies overshadow the public interest.
 “The only ‘right’ that any entity receives to locate within Maine’s highway corridors is a revocable permit,” the DOT wrote. “To minimize overall expense and downtime, it is essential that facilities are appropriately located the first time around and there should not be any rules stating that it is in any way appropriate for an entity to construct facilities in a location that has not been explicitly approved by the applicable licensing authority, property owner or facility owner.”
“The only ‘right’ that any entity receives to locate within Maine’s highway corridors is a revocable permit,” the DOT wrote. “To minimize overall expense and downtime, it is essential that facilities are appropriately located the first time around and there should not be any rules stating that it is in any way appropriate for an entity to construct facilities in a location that has not been explicitly approved by the applicable licensing authority, property owner or facility owner.”
Because the FCC’s proposal is so wide-ranging and skewed in favor of telecom companies, several state and local agencies are asking the FCC to clearly affirm that a company’s business interests should never come before public safety, future transportation needs, or at the public’s expense.
“Any new or revised rules should clearly affirm a state or local highway agencies’ authority to properly manage the highway corridor in the interest of highway safety, operations, and right of way preservation for future highway purposes,” offers Maine’s DOT, adding that after the state’s experience with financially troubled telecom companies abandoning outdated or damaged infrastructure, the public should not have to pay to clean it up.
“Accommodation of wireless towers or other monopole structures within the highway corridor also present hidden public expense when relocation of those facilities cause construction delays or when such facilities are abandoned by a [company] that declares bankruptcy,” the agency noted.
 The Illinois Department of Transportation echoed Utah and Maine, noting the telecom industry needed to work with local and state officials to ensure timely permitting.
The Illinois Department of Transportation echoed Utah and Maine, noting the telecom industry needed to work with local and state officials to ensure timely permitting.
Instead, the telecom industry has spent millions lobbying state and federal legislators to curtail or eliminate local oversight and control. While many telecom companies are honest and accommodating, especially when they are considering major infrastructure expansion, some are not and work to game the system.
IDOT notes it is willing to manage the burden of processing applications on a timely basis, but utilities should not be rewarded with a right to run out the clock with an incomplete application.
“The burden of timely issuance of permits is shared by both the state and the industry,” IDOT wrote. “It is important that the utility fulfill its duties and meet their obligations.”
In one instance, a large telecom company submitted a very large number of permit applications across Illinois for a network upgrade it had no plans to commence in the near future, overwhelming permit offices. If the FCC’s reforms were in place, many of those applications would have been automatically approved after the deadline for consideration ran out, even though the provider was in no hurry to start work.
“The concept behind this is […] if a government authority doesn’t respond in a timely manner, the permit is automatically granted,” the filing said. “The [proposal] is attempting to shift the burden of court appeal to the [local permitting authority] as opposed to the permit applicant.”
Columbia, S.C. mayor Steve Benjamin believes the FCC is trying to solve a non-existent problem.
“Simply put, local rights-of-way management does not discourage wireless deployment,” Mayor Benjamin said in March. “Instead, it serves numerous public policy goals and ensures that rights-of-ways are managed in a manner that allows for all users to safely and efficiently use public rights-of-way. The city is deeply concerned […] the Commission is simply seeking to preempt local authority and to dictate how local governments should manage public property, all in an effort to marginally increase the profits of an already profitable industry at the expense of important and legitimate public interest goals.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe






 An
An  Consolidated Communications will inherit residential FairPoint phone and broadband customers in 17 states, most notably those in Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont. But press releases from Consolidated showed little interest in the residential telecommunications business. Instead, Consolidated executives are looking at FairPoint’s business and enterprise customers, and the benefits of owning FairPoint’s 17,000 fiber route mile network.
Consolidated Communications will inherit residential FairPoint phone and broadband customers in 17 states, most notably those in Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont. But press releases from Consolidated showed little interest in the residential telecommunications business. Instead, Consolidated executives are looking at FairPoint’s business and enterprise customers, and the benefits of owning FairPoint’s 17,000 fiber route mile network.
 “Not as patient as FairPoint’s own customers that spent several years of hell dealing with Verizon’s sale of its landlines in Vermont, New Hampshire, and Maine,” said FairPoint customer Sally Jackman, who lives in Maine. “It looks like the hedge funds want their pound of profits from another sale, exactly what FairPoint customers don’t need right now.”
“Not as patient as FairPoint’s own customers that spent several years of hell dealing with Verizon’s sale of its landlines in Vermont, New Hampshire, and Maine,” said FairPoint customer Sally Jackman, who lives in Maine. “It looks like the hedge funds want their pound of profits from another sale, exactly what FairPoint customers don’t need right now.”

 Such legislation strips consumers of any assumption they can get affordable, high quality landline service and would allow FairPoint to mothball significant segments of its network (and the customers that depend on it), telling the disconnected to use a cell phone provider instead.
Such legislation strips consumers of any assumption they can get affordable, high quality landline service and would allow FairPoint to mothball significant segments of its network (and the customers that depend on it), telling the disconnected to use a cell phone provider instead. Last week, even FairPoint’s CEO Paul Sunu appeared to undercut his company’s own arguments for the need of such legislation, just as the company renewed its efforts in Portland to get a new 2016 version of the deregulation bill through the Maine legislature.
Last week, even FairPoint’s CEO Paul Sunu appeared to undercut his company’s own arguments for the need of such legislation, just as the company renewed its efforts in Portland to get a new 2016 version of the deregulation bill through the Maine legislature.
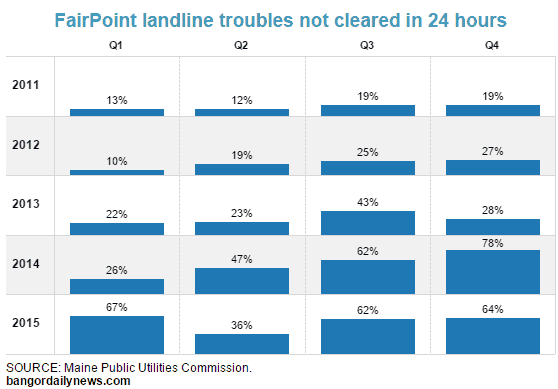 “The market determines the service quality criteria of importance to customers and the service quality levels they find acceptable,” Sarah Davis, the company’s senior director of government affairs, wrote. “To the extent service quality is deficient from the perspective of consumers, the competitive marketplace imposes its own serious penalties.”
“The market determines the service quality criteria of importance to customers and the service quality levels they find acceptable,” Sarah Davis, the company’s senior director of government affairs, wrote. “To the extent service quality is deficient from the perspective of consumers, the competitive marketplace imposes its own serious penalties.”