 After 44 years in the cable television business, the Dolan family has agreed to part with its prize possession, Cablevision Systems Corp. in a $17.7 billion dollar deal with Patrick “The Slasher” Drahi’s Altice NV.
After 44 years in the cable television business, the Dolan family has agreed to part with its prize possession, Cablevision Systems Corp. in a $17.7 billion dollar deal with Patrick “The Slasher” Drahi’s Altice NV.
The transaction will profoundly impact Cablevision’s employees, customers, and potentially the cable business in general in the New York City metropolitan area, where Cablevision’s 3.1. million customers live.
Who is Patrick Drahi?
Although few Americans have heard of the self-made billionaire Patrick Drahi, most of French-speaking Europe knows Mr. Drahi only too well, regularly criticized in the French press for surrounding himself with debt-laden acquisitions, stiffing vendors and suppliers, and paying rock-bottom wages to the employees that remain after constant campaigns of ruthless cost cutting.
Drahi’s idol is none other than cable magnate billionaire John Malone, the man pulling the strings at Charter Communications. In the 1970s and 1980s, Malone ran America’s largest cable conglomerate – Tele-Communications, Inc. (TCI), a company castigated by customers for high rates and poor service about as much as Comcast is today.
 Malone’s reputation with the U.S. Congress reached its lowest point in the 1980s when then-Sen. Al Gore, Jr. (D-Tenn.) alternately accused Malone of heading a monopolistic cable “Cosa Nostra” that extorted his constituents with rate increases that exceeded 180% in less than five years and the “Darth Vader of Cable.” Malone taught Drahi that massive sums of money could be made buying and selling cable television (and later broadband) over systems that are usually de facto monopolies. Although entertainment is always in high demand, few governments treat the cable systems that offer it as an “essential utility,” allowing them to charge whatever they want for service.
Malone’s reputation with the U.S. Congress reached its lowest point in the 1980s when then-Sen. Al Gore, Jr. (D-Tenn.) alternately accused Malone of heading a monopolistic cable “Cosa Nostra” that extorted his constituents with rate increases that exceeded 180% in less than five years and the “Darth Vader of Cable.” Malone taught Drahi that massive sums of money could be made buying and selling cable television (and later broadband) over systems that are usually de facto monopolies. Although entertainment is always in high demand, few governments treat the cable systems that offer it as an “essential utility,” allowing them to charge whatever they want for service.
From his earliest days working for a small cable operator, Drahi dreamed of building a cable empire buying and selling cable systems, extracting whatever he could from subscribers. One of his earliest techniques was flouting a French telecommunications law that, at the time, forbade the carriage of non-French language channels. His cable systems quietly added Arabic language networks to entice the large North African immigrant community in France to sign up for service. Drahi did not directly promote the networks, relying on word-of-mouth to deliver sales in the Arabic speaking community.
The Sacred Monster
While very conservative about spending money on wages, service upgrades, and technology, customers of Drahi-owned cable companies report he had no problem raising their rates. Numericable’s customer satisfaction rating rivals that of Comcast — a one-star cable company charging five-star prices.

Drahi
The announced acquisition of Cablevision (and earlier Suddenlink) by Drahi’s company — Altice NV, came with glowing coverage from the American media, particularly cable business news channels, the Wall Street press, and the New York Times. A Sept. 7, 2015 piece by Nicola Clark in the Times presented Drahi as a classic “rags to riches” success story, noting he loathes being interviewed and allegedly leads a humble existence:
Despite a personal fortune estimated at close to €17 billion, Mr. Drahi indulges in few of the trappings of great wealth, friends and colleagues said. Although he keeps several elegant homes — in Geneva, Paris and Tel Aviv — his personal tastes and habits hew to the mundane. He wears a plastic Swatch instead of a Rolex and often arrives at business meetings on foot or a bicycle, instead of by chauffeured car.
Clark only mentions in passing she relied almost entirely on a series of interviews with “a half-dozen friends and colleagues” to paint what turned out to be a one-sided picture of Mr. Drahi for American readers. That story had eyes rolling among staffers in the offices of French newspaper Les Echos, incredulous at the American infatuation with a man the newspaper calls the “sacré monstre” — sacred monster. In New York, reporter Lucie Robequain, foreign business correspondent for the French daily, tried to share the scene at the Goldman Sachs-organized Communacopia conference where the deal was personally announced by Mr. Drahi for her French readers.
 “Newspapers [in America] devote entire pages [about Drahi], emphasizing his self-made-man side which Americans love so much,” Robequain noted. She added the New York Times painted Drahi an almost romantic figure, proposing to his wife one hour after meeting her and then putting everything between them at risk to build his personal fortune.
“Newspapers [in America] devote entire pages [about Drahi], emphasizing his self-made-man side which Americans love so much,” Robequain noted. She added the New York Times painted Drahi an almost romantic figure, proposing to his wife one hour after meeting her and then putting everything between them at risk to build his personal fortune.
A later piece in the Times on Sept. 17 by Emily Steel and Mark Scott also was the subject of derision in the European press. Steel and Scott called Altice a “bold new player” in the American cable market and gave Dexter Goei, one of Drahi’s lieutenants (some in the French press prefer ‘minion’) space to gush about the game-changing deal. Goei joined Altice in 2009, having worked for 15 years in investment banking with JP Morgan and Morgan Stanley until the Great Recession arrived.
“There’s a new sheriff in town, and we’re probably going to run it a little differently,” Goei said during the investor conference in New York on Thursday that unveiled the deal.
Phantom Fiber
The Times piece also relied on unnamed “analysts” dangling the promise of fiber optics to appease subscribers concerned about a legendary cost-cutter taking the helm of the cable company.
[…] Analysts said Altice invests heavily in new infrastructure — with a focus on upgrading fixed-line networks with the latest fiber-optic technology. The priority, analysts said, is to provide subscribers with faster Internet connection speeds at competitive prices.
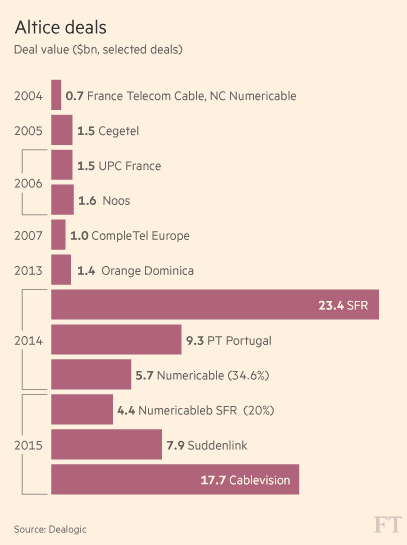
Previous deals involving Altice (Image: Financial Times)
In Europe, the press is skeptical about promised upgrades, noting Altice is “an empire built on a mountain of debt” largely made possible by quantitative easing and record low interest rates, which permit companies to finance buyouts on the cheap. Drahi says he can save money through synergy — sharing operations and minimizing the need for customers to reach out for customer service. Altice officials claim just by simplifying Cablevision’s bills, the company can save $14 million annually.
Drahi’s success story with Wall Street and other investors comes from his ability to cut costs at acquired companies, often dramatically. It is part of the informal deal with investors that has allowed the company generous credit to continue its buying spree. The Cablevision deal promises the Dolans and other investors only $3.3 billion in cash. The rest of the purchase price will come from raising $8.6 billion in new debt, saddled on Cablevision’s books inside Altice.
So while unnamed analysts are promising fiber upgrades for Cablevision customers, the Financial Times and CNBC report only one thing will be on Cablevision’s menu post-merger: spending a lot less, not more. Drahi seems to agree.
In a slide presentation to investors, Altice compares Cablevision’s $49 a month in operating expenses per customer against what its Numericable operation in France spends on its customers: $14 a month.
So how does Numericable spend three times less on subscribers than Cablevision?
Cost Cutting Specialists
Say hello to Michel Combes, former CEO of Alcatel-Lucent. Two years ago, he took leadership of the company that was better known by many as Bell Labs. Known as a cost-cutter, Combes quickly announced plans to strip the company of less profitable business units and fired about 10,000 workers while also holding the line on salaries (except for his) of the remaining employees. After two years in the leadership position, Combes engineered the sale of the company to Nokia, putting himself out of a job. But he won’t be hurting. A breathtaking golden parachute package approved by his colleagues on Alcatel Lucent’s board caused a political furor in France.

Combes
Combes’ departure bonus was originally planned to amount to $15 million in stock after completing the company’s sale to Nokia, an amount Emmanuel Macron, France’s economic minister, called shocking and irresponsible. Under pressure, the board has since cut the payoff roughly in half. But according to L’Observateur, Drahi has offered his friend an even more lucrative “golden hello” — stock options awarded as a signing bonus worth up to $100 million. Combes’ first role will be to serve as Altice’s chief operating officer, presiding over new rounds of cost-cutting at the company’s various acquisitions. One item spared from review is Combes’ own compensation package. Those under him are not so lucky.
Wages and Jobs
“I do not like to pay salaries, I pay as little as I can,” Drahi told investors at the Goldman Sachs event last week. Drahi complained more than 300 employees at Cablevision were being paid more than $300,000 a year. “This we will change.“
In addition to a large number of expected layoffs at Cablevision, widespread salary reductions are also likely to be forthcoming. Drahi’s cable companies have some of the smallest compensation packages in the industry, except at the top executive level.
Cablevision’s already testy relationship with some of its union employees will likely grow much worse under Drahi’s leadership. But that battle may have to wait until another day. In February, the union ratified a two-year agreement with Cablevision. In Europe, Drahi’s reputation among public unions is so poor many of the opinions expressed by unionized workers cannot be printed in a family newspaper.

Suppliers complain Drahi’s companies don’t pay their bills.
In Lisbon, Jorge Felix – a representative of the trade union organization of workers at PT (Portugal Telecom) warns U.S. unions should get everything from Altice and Mr. Drahi in writing.
“There are commitments made by Altice before our union and are written,” Felix said, adding that he was disturbed by Drahi’s attitude toward his middle class employees. Felix notes Drahi has already created tremendous controversy in Portugal by stonewalling payment of suppliers and vendors’ outstanding invoices until the company secures written agreements promising enormous discounts, often amounting to 30-40% off current prices. That, in turn, can cause layoffs and salary reductions at suppliers, enriching Altice but hurting just about everyone else.
Drahi: Looking to run faster than the music
France’s Economic Minister Macron seems to agree, lashing out at Drahi’s now familiar business model.
“Is it good for the economy? The answer is no,” he said. “Is it good for investment? The answer is no. Is it good for employment? The answer is no.”
Macron also expressed concern that Drahi’s telecom empire was growing too fast — and taking on too much debt too quickly.
“I have a big concern in terms of leverage on Drahi due to its size and its place in our economy,” he said. “That’s my responsibility to look at it. He is looking to run faster than the music.”

Macron
Macron and his staff are concerned many of Drahi’s top executives and advisers come from New York’s financial markets and investment banks who either left or were pushed out in the turmoil of the Great Recession. Macron worries Drahi could be constructing the world’s first “too big to fail” cable operator that could cost nearly 100,000 jobs and require a government bailout if things turn sour.
Promised Service Improvement & Upgrades
With each cable consolidation merger, companies routinely promise subscribers will benefit from improved service. As mentioned earlier, unnamed analysts predict Drahi could invest up to $30 billion to improve the cable companies he buys in the United States.
“Which Altice are they talking about,” asks Stop the Cap! reader François Ribaud. “Altice owns Numericable, the largest cable company in metropolitan France, and if they are spending money it certainly was not on us.”
Ribaud’s original cable company Noos was acquired by Numericable in a massive acquisition effort in the early 2000s which today leaves almost all of France served by a single cable operator — Numericable.
“Things stagnated after that because Patrick Drahi does not spend money unless he has to,” Ribaud said. “The set-top boxes are outdated, the broadband service is often oversold, and heaven help you if there are service problems. The North African call center customer service help is an example for Numericable of getting what you pay for. They are awful.”

Charles Dolan
Drahi’s competitors in the fixed line and wireless markets eventually forced his wallet open, requiring an investment in fiber optics to help it remain a player in one of Europe’s most contentious telecommunications price wars. Drahi’s company in France lost subscribers as its network suffered from a lack of needed upgrades to manage demand.
“Now that I live in New York, I can say it is completely different than in France,” Ribaud said. “There is certainly no price war here, so there is no need to spend more money. The only people spending money will be customers I assure you.”
The Creator of Home Box Office Signs Off
Cablevision has been rumored “for sale” for so long without a deal, many analysts predicted the founding family would never let go of the company founded by 88-year old Charles Dolan, who helped transform what used to be a rural service to help customers receive distant over the air stations over a shared antenna into an urban and suburban subscription television business. Dolan made cable television something more.
Dolan founded Home Box Office (HBO), a commercial-free premium movie and entertainment channel free from the network “standards and practices” divisions that removed profanity and edited out violence from movies originally shown intact in theaters.
Cablevision systems used to cover 2.9 million subscribers in 19 states, many in small and medium-sized communities. By the 1990s, cable systems were swapped or sold to build regional empire-like service areas. Cablevision was no different, retreating to just three large service areas in New York, Cleveland and Boston. Soon thereafter, Cablevision would only serve metropolitan New York, particularly in Brooklyn, the Bronx, Long Island, parts of northern New Jersey and Connecticut, while exiting Cleveland and Boston.
The New York Post reported secret talks for the sale began in June, and a deal was complete at the end of August. Some of the discussions took place on a yacht floating around the Mediterranean. The Post reports the sale of Cablevision was an emotional experience for Dolan and he still thinks of the people who work there as family. But in the end, the Dolan family’s proceeds from the sale will reinforce their already well-established wealth and prominence. The same is unlikely to be true for Cablevision’s employees and customers under Drahi’s cost-conscious leadership.


 Subscribe
Subscribe



 AT&T today announced it was selling off its residential wireline network in Connecticut to Stamford-based Frontier Communications for $2 billion in a deal that includes an expanded license for U-verse TV that could eventually be available to Frontier customers nationwide.
AT&T today announced it was selling off its residential wireline network in Connecticut to Stamford-based Frontier Communications for $2 billion in a deal that includes an expanded license for U-verse TV that could eventually be available to Frontier customers nationwide. Frontier’s acquisition will give the company hands-on experience with AT&T’s U-verse network in Connecticut and offer a path to bring improved service to Frontier customers elsewhere. Company officials also acknowledged a key reason for the transaction was boosting Frontier’s lagging dividend, a critical part of its share price. By taking on nearly 1,000,000 new customers, Frontier will boost its cash flow, returning some of that new revenue in a higher dividend payout to shareholders. But the company will take on an extra $2 billion in debt to manage higher dividend payouts.
Frontier’s acquisition will give the company hands-on experience with AT&T’s U-verse network in Connecticut and offer a path to bring improved service to Frontier customers elsewhere. Company officials also acknowledged a key reason for the transaction was boosting Frontier’s lagging dividend, a critical part of its share price. By taking on nearly 1,000,000 new customers, Frontier will boost its cash flow, returning some of that new revenue in a higher dividend payout to shareholders. But the company will take on an extra $2 billion in debt to manage higher dividend payouts. SNET began operations in 1878 as the District Telephone Company of New Haven and pre-dated the Bell System. The company founded the first exchange and printed the world’s first telephone directory. It remained independent of Bell System ownership until 1998, when SBC Communications (formerly Southwestern Bell) acquired the company. In late 2005, SBC purchased AT&T and AT&T Connecticut was born.
SNET began operations in 1878 as the District Telephone Company of New Haven and pre-dated the Bell System. The company founded the first exchange and printed the world’s first telephone directory. It remained independent of Bell System ownership until 1998, when SBC Communications (formerly Southwestern Bell) acquired the company. In late 2005, SBC purchased AT&T and AT&T Connecticut was born. CWA’s Local 3902 chapter, which represents AT&T workers in the Triad,
CWA’s Local 3902 chapter, which represents AT&T workers in the Triad, 