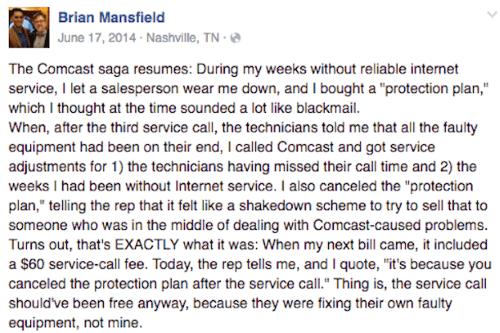
6 A group of five men representing Bell, Rogers, and Vidéotron burst into the private home of a Montreal man at 8 a.m. on June 12 without notice and interrogated him for nine hours about his involvement in a search engine that helps Canadian viewers circumvent geographic restrictions on online TV shows and movies.
A group of five men representing Bell, Rogers, and Vidéotron burst into the private home of a Montreal man at 8 a.m. on June 12 without notice and interrogated him for nine hours about his involvement in a search engine that helps Canadian viewers circumvent geographic restrictions on online TV shows and movies.
The lawyer representing Canadian telephone company Bell and two of the country’s largest cable companies — Rogers and Vidéotron, was backed by a bailiff and independent counsel who informed Montreal software developer Adam Lackman, founder of TVAddons and a current defendant in a copyright infringement lawsuit filed by the telecom companies, that he was “not permitted to refuse to answer questions” posed by the companies under threat of additional criminal and civil penalties.
Lackman was instructed he had one hour to locate an attorney, but was forbidden to use any electronic or telecommunications device to contact one. He was also not allowed to leave the designated room in his home where he was held unless accompanied by a corporate lawyer or court official. The men also warned Lackman’s attorney he could not counsel Lackman on his answers to their questions and had to remain silent.
“I had to sit there and not leave their sight. I was denied access to medication,” Lackman told TorrentFreak. “I had a doctor’s appointment I was forced to miss. I wasn’t even allowed to call and cancel.”
Lackman was eventually placed in a room in his home and interrogated almost continuously for nine hours, but was given a brief break for dinner and time to finally talk privately with his attorney. By the time the bailiff, two computer technicians, the independent counsel and the corporate attorney left, it was 16 hours later and after midnight. The men left with Lackman’s personal computer and phone, along with a full list of usernames and passwords to access his email and social media accounts.
“The whole experience was horrifying,” Lackman told CBC News. “It felt like the kind of thing you would have expected to have happened in the Soviet Union.”

Lackman
The telecom giants gained access to Lackman’s home with the use of a Anton Piller order, a type of civil search warrant that gives private individuals and companies acting as plaintiffs in a lawsuit full access to a defendant’s home with no warning. The order was designed to allow searches and seizure of relevant evidence at high risk of being destroyed by a defendant.
The Canadian companies were upset because of Lackman’s involvement in Kodi, an open source home theater platform that allows viewers to access stored and online streaming media. Lackman produces apps, known as add-ons, that help Kodi users access live TV streams and recorded content. Unfortunately, that sometimes occurs in contravention of geographic and copyright restrictions imposed by the Canadian companies on Canadian viewers. As a result, several large telecom companies filed suit against Lackman for copyright infringement.
“Approximately 40 million unique users located around the world are actively using infringing add-ons hosted by TVAddons every month, and approximately 900,000 Canadian households use infringing add-ons to access television content,” claims the lawsuit. “The amount of users of infringing add-ons hosted TVAddons is constantly increasing.”

The Honourable B. Richard Bell (Image: Keith Minchin)
On June 9, a Canadian Federal Court judge handed the telecom companies a victory in the form of an interim injunction and restraining order against Lackman prohibiting him from engaging in any activity that could further violate the companies’ interpretation of copyright law. The ruling also included an Anton Piller order, which critics contend often allows private companies to engage in extended fishing expeditions looking for additional evidence to further their case.
The order included the right to seize any and all data surrounding the alleged offense, including equipment, paper records, bank accounts, and anything else in Lackman’s possession that plaintiffs could argue was connected to the lawsuit. It also permitted a bailiff and computer forensics experts to assume control of many of Lackman’s internet domains including TVAddons.ag and Offshoregit.com, as well as his social media and web hosting accounts for a period of two weeks. Since the case was handled ex parte (open to only one side) by the Federal Court, Lackman was not informed or given the opportunity to present a defense.
The ruling evidently allowed the companies to believe they had carte blanche to question Lackman.
When the corporate attorney was not grilling Lackman about his own involvement in Kodi add-ons, he demanded Lackman disclose any and all information he had on an additional 30 individuals that might also be involved in services like TVAddons. That demand fell squarely outside of the range of the court order, which is designed to protect existing evidence, not permit plaintiffs to fish for new evidence to bolster their case.
After the search ended, Lackman and his attorney went to court to challenge what they believed to be one of the most shocking instances of corporate intimidation and legal abuse ever seen in a copyright case. Lackman’s attorney had little trouble convincing the Honourable B. Richard Bell, who presided over a Federal Court hearing on the matter.
Bell found multiple egregious violations of the court order, including a limit on any search to between 8 a.m. and 8 p.m. but instead lasted until at least midnight. The judge also found ample evidence Lackman’s rights were violated and he was subjected to an intimidation campaign designed to destroy his software business, leave him financially unable to mount any defense against the lawsuit, and get him to both incriminate himself and others against his will.

A court transcript reveals the real motives of Canadian telecom companies: to “neutralize the guy” that is hurting their businesses.
“It is important to note that the Defendant was not permitted to refuse to answer questions under fear of contempt proceedings, and his counsel was not permitted to clarify the answers to questions. I conclude unhesitatingly that the Defendant was subjected to an examination for discovery without any of the protections normally afforded to litigants in such circumstances,” the judge said. “Here, I would add that the ‘questions’ were not really questions at all. They took the form of orders or directions. For example, the Defendant was told to ‘provide to the bailiff’ or ‘disclose to the Plaintiffs’ solicitors’.”
Bell also saw through the plaintiffs’ questioning of Lackman about 30 other individuals that might also be allegedly involved in copyright infringement.

Lose in one venue, win in another.
“I conclude that those questions, posed by Plaintiffs’ counsel, were solely made in furtherance of their investigation and constituted a hunt for further evidence, as opposed to the preservation of then existing evidence,” he wrote in a June 29 order. “I am of the view that [the order’s] true purpose was to destroy the livelihood of the Defendant, deny him the financial resources to finance a defense to the claim made against him, and to provide an opportunity for discovery of the Defendant in circumstances where none of the procedural safeguards of our civil justice system could be engaged.”
The judge ruled the Anton Piller order be declared null and void and ordered all of Lackman’s possessions to be returned to him.
To all observers, it was a withering repudiation of the tactics used by the Canadian telecom companies suing Lackman. But deep pockets always allow lawyers the luxury of a change of venue and the telecom companies promptly appealed Bell’s ruling to the Federal Court of Appeal, requesting a stay of execution of Judge Bell’s order. The court granted the appeal on behalf of the telecom companies and allowed the plaintiffs to keep possession of all seized items, domains, and social media accounts until a full appeal of the case can be heard this fall. However, the court found defects in the execution of the Anton Piller order, and ordered the telecom companies to post a security bond of $140,000 CDN and continue the $50,000 CDN bond in case sanctions are later warranted.
Lackman intends to continue his legal fight and is raising money to cover legal expenses on the fundraising site Indiegogo. He has also set up a new TVAddons website and Twitter account and has resumed the add-on development that got him embroiled in the copyright infringement lawsuit in the first place. But Lackman seems to have at least one judge on his side.
“The defendant has demonstrated that he has an arguable case that he is not violating the [Copyright] Act,” wrote Judge Bell, adding that by the plaintiffs’ own estimate, only about one per cent of Lackman’s add-ons were allegedly used to pirate content.
Updated 8/16: The website is now back under this new URL: https://www.tvaddons.co/

 The Daily News reports the MirRam Group represents the mayor, City Council Speaker Melissa Mark-Viverito and Public Advocate Letitia James. James has been a client since 2013 while Mayor deBlasio hired the company in April to assist him with his re-election campaign. The lobbying firm has collected $150,000 from Charter and its predecessor Time Warner Cable in the last 12 months.
The Daily News reports the MirRam Group represents the mayor, City Council Speaker Melissa Mark-Viverito and Public Advocate Letitia James. James has been a client since 2013 while Mayor deBlasio hired the company in April to assist him with his re-election campaign. The lobbying firm has collected $150,000 from Charter and its predecessor Time Warner Cable in the last 12 months.

 Subscribe
Subscribe