Last week, Verizon’s Tom Maguire responded to some of our earlier coverage about Verizon’s decision to abandon landline service on portions of Fire Island devastated by last fall’s Hurricane Sandy. We have received several complaints from readers about our decision to grant space to Verizon to present their views without reciprocation. While we understand those concerns, Stop the Cap! believes readers deserve both sides of a discussion that AT&T and Verizon will soon seek to have with customers across many of their rural service areas. For that reason, we invited Verizon’s participation. This is our response:

Phillip Dampier
Raise your hand if you want Verizon’s Voice Link to replace your traditional telephone service and lose your only wired broadband connection.
Almost no one has. Despite the arguments from Verizon Communications and AT&T that wireless is the answer to troublesome copper wiring and maintaining rural telephone service, dozens of Fire Island, N.Y. customers have been sufficiently provoked to file comments with state regulators, making it clear they want no part of the loss of their landline and its accompanying, affordable broadband service. In more than 135 public comments with the Public Service Commission at press time, Stop the Cap! could only find one comment from a Fire Island resident who had no issues with Verizon’s wireless landline replacement. He was upset Verizon had not wired a nearby yacht club for broadband service.
Both AT&T and Verizon have publicly advocated that rural customers would be better served moving from traditional wired landline service to their respective wireless 4G LTE networks. AT&T characterizes it as “an upgrade” that switches customers to an “all IP” 21st century network. Verizon has been less bold in its public policy statements, framing its position mostly in economic terms — does it make sense to invest large sums to upgrade or repair damaged infrastructure that serves a relatively small number of customers?
Until recently, customers have been free to make the choice between a landline and wireless service themselves. Now, the residents of Fire Island and some barrier islands off the coast of New Jersey have a very different choice: They can accept Verizon’s Voice Link landline replacement, sign up for cell service that has proved troublesome in both areas, or give up phone service altogether. Verizon has made it clear it is not prepared to replace the destroyed infrastructure on portions of the islands, it will not invest in major upkeep and repairs to network facilities that may have been compromised but are still functioning for now, and will likely never offer its fiber FiOS network in the affected areas.
Stop the Cap! has expressed repeated concern that the decision to abandon wired infrastructure in favor of wireless is based primarily on profit motives, is short-sighted, and represents a downgrade in the quality of an important, regulated utility service, particularly in rural and out-of-the-way places that have few, if any alternatives. Fire Island is shaping up to argue our case, based on the testimony of those actually living and working on the island.
Customers Don’t Want the ‘Solution’ Verizon is Offering
Voice Link is not proving a welcome permanent resident on Fire Island for many customers.
The reasons are clear: inadequate wireless service is common on the island, Voice Link does not perform or sound as good as the landline it replaces, and Verizon’s wireless broadband alternative will cost many residents their unlimited-use DSL service in favor of a wireless capped option that could cost more than $100 a month.

Letter to affected Verizon customers on Fire Island.
Verizon’s strongest argument is that landline service has fallen out of favor in the United States, with customers increasingly disconnecting home phones in favor of cell phones. If Verizon’s statistics are correct, 80 percent of the voice traffic on the island is already handled by Verizon Wireless. (Verizon does not specify if that traffic comes from permanent residents or temporary visitors, a point of contention with residents.)
 Maguire was very careful to limit Verizon’s advocacy of Voice Link in terms of its capacity to handle voice calls. That is because Voice Link is currently incompatible with a whole range of important services that have worked fine with traditional landlines for years.
Maguire was very careful to limit Verizon’s advocacy of Voice Link in terms of its capacity to handle voice calls. That is because Voice Link is currently incompatible with a whole range of important services that have worked fine with traditional landlines for years.
Maguire’s words are important: “Verizon’s commitment is to provide our customers with voice service,” — the kind you had in the late 70s. Voice Link fails faxing, home medical monitoring, home alarm systems, dial-up service, credit card transactions, and home satellite equipment that connects to the telephone network.
Voice Link is no upgrade for Fire Island. It represents turning back the clock, especially for broadband customers.
Maguire claimed in his editorial the company was only considering Voice Link for the universe of customers where the copper network was not supporting their requirements, with the exception of Sandy-impacted Fire Island and some New Jersey barrier islands. But that does not tell the whole story. In a filing with the New York State Public Service Commission, Verizon makes it clear it intends to introduce the same solution in other parts of New York:
It also seeks to deploy Voice Link in other parts of the State, both as an optional service in areas where the company also offers tariffed wireline local exchange service, and (subject to the Commission’s approval) as a sole service offering in particular locations and circumstances.
While Verizon has sought to appease regulators by volunteering to offer an equal level of service for the same or less money, there are questions about whether a regulator has any oversight authority over Voice Link.
“It is a remarkable concept in utility regulation that a regulated utility may determine that costs are unreasonable and as a result choose to provide alternative, and potentially unregulated service to affected customers,” said Louis Barash of Ocean Beach. “Verizon proposes to permit the PSC to regulate that activity, but it is not clear that the Commission has such authority. And it certainly isn’t clear that the Commission would have any authority to reverse its decision, or otherwise to sanction the company, if Verizon failed to comply with its undertakings.”
Broadband & Competition Matters: Forcing Customers Off Unlimited DSL in Favor of Near-Exclusive, Usage-Capped, Verizon Wireless Broadband
Offering broadband is a vital part of any telephone company’s strategy to add and keep customers. Yet Verizon’s DSL customers on the western half of Fire Island will have their broadband service canceled unless wired service (copper or fiber) is available. Verizon’s only alternative is a usage-capped, prohibitively expensive Verizon Wireless mobile data plan that may or may not perform well on the signal-challenged island. There is literally nowhere else for customers to go.
Verizon’s own statistics confirm none of its wireless competitors handle significant traffic on and off the island.
Maguire: “A multimillion dollar investment with no guarantee that residents of the island will even subscribe to our services makes no economic sense. In fact, that’s probably why Verizon is the sole provider on the island. None of the companies we compete with in other parts of New York offer services on the island.”
Maguire’s evidence:
“The company discovered that 80 percent of the voice traffic was already wireless. If other wireless providers were factored in, it is likely that the percentage is closer to 90 percent.”
That means Verizon’s wireless competitors collectively have a traffic share of less than 10%.
Verizon’s Plan & Public Safety
 Residents advise visitors they better have Verizon Wireless and a robust phone that works well in challenging reception areas if they expect to use it while on the island. AT&T, Sprint, and T-Mobile customers are often out of luck. That poses an immediate and direct threat to public safety, according to public safety officials.
Residents advise visitors they better have Verizon Wireless and a robust phone that works well in challenging reception areas if they expect to use it while on the island. AT&T, Sprint, and T-Mobile customers are often out of luck. That poses an immediate and direct threat to public safety, according to public safety officials.
“The cellphone service on Fire Island progressively gets worse every year as more and more people are bringing smartphones out there,” explained Dominic Bertucci, chief of the Kismet Fire Department. “There are some days where you can barely get a signal.”
The Brookhaven Town Fire Chiefs Council, which represents the leadership of 39 fire departments and fire companies in the region is vehemently opposed to Voice Link and considers it a safety menace, especially during frequent summer power outages when the island’s population is at its peak.
“Without a copper wire phone service, a service that still functions even during a power failure, how can we insure that the residents can call for help?” asks president John Cronin. “How will they call for the lifesaving services that are provided by the fire and EMS units of Fire Island? The corporate desire for greater profit cannot be made at the expense of the safety of the residents of Fire Island.”
“Wireless service is not reliable,” adds Fair Harbor resident Meredith Davis. “Imagine being in an emergency and having ‘spotty’ reception which happens out there all the time on cell phones. That is not safe and not okay.”

Verizon disclaims legal responsibility for failed wireless 911 calls in its terms and conditions. The most Verizon owes you is a refund of a portion of your monthly service charges.
“If you are unfamiliar with Fire Island, there is very little medical service and the only way off the island is a scheduled ferry service or, for some people who have permits and trucks, a very long drive,” explains lifelong Fire Island resident Nora Olsen. “When someone needs to be rushed to the hospital, they are evacuated by helicopter, which makes timely emergency calls of the essence to save lives. So you can imagine how important it is to have reliable phone service. It should be up to the individual to decide if they want to switch to a wireless service. They should not be forced into it by Verizon. The people who are most likely to want to stick with the phone service they have been used to all their life — senior citizens — are the most likely to need to use the phone to call for help.”
A number of residents also claim Verizon has overblown the real extent of damage on the island and is not operating in good faith.
“In the larger communities of Ocean Beach and Seaview, I have met no one yet that has their connectivity lost,” said resident Karen Warren. “So for Verizon to assert that the infrastructure is largely destroyed and to repair it would be an enormous expense is simply not true. To add insult to injury, before coming out and finding out that our lines were in fact intact, Verizon offered to ‘replace’ our existing DSL data service with LTE Jetpak wireless broadband. The performance and reliability with only a single device connected was horrendous.”
“[Verizon is] pushing us toward a higher-cost and lower-value solution,” Warren concluded.
Getting specific information about the current state of Verizon’s network on Fire Island and repair/replacement costs are hard to come by. Verizon filed an application with the PSC declaring much of the information confidential or a trade secret, refusing to share it with the public. The company was concerned some might access the Public Service Commission website, find the case number about Fire Island, navigate to the specific Verizon filing containing information about their infrastructure… and then vandalize it.
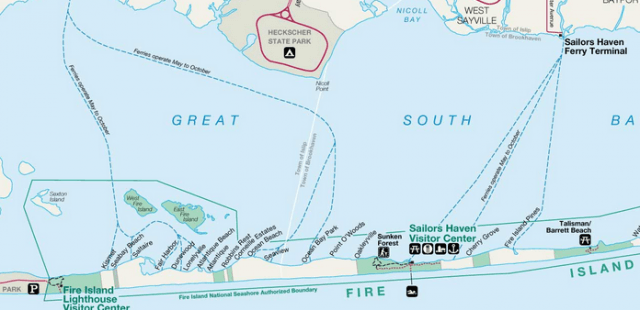
The worst affected communities on Fire Island.
Barash suspects Verizon might be hiding something, especially considering the company requested to bypass usual waiting periods and public notification requirements:
Verizon asserts that it would cost “$4.8 million for a voice-only digital loop carrier system comparable to the networking serving the eastern part of the island.” It is by no means clear, however, that such a system is the minimum required to restore/repair the western part of the system to the service it had pre-storm. Certainly Verizon’s application makes no representation to that effect. This estimate apparently contemplates an entire new system for the western portion of Fire Island, notwithstanding that a meaningful percentage of the copper wire system is still operational.
Moreover, Verizon’s position on the required scope of repairs has been a constantly shifting target. Verizon apparently advised Commission Staff, and Staff repeated at the April 18 Commission Hearing, that the western Fire Island telephone system was “damaged beyond repair by the storm.” Verizon apparently has abandoned that claim; this application indeed is premised on the assumption that the system can be repaired. Furthermore, in its first (May 3) submission to the Commission, Verizon stated that “five of the six cables that run between Fire Island and the mainland – the five that serve the western portion of the Island – were also badly damaged by the storm.” Just a week later, it has abandoned that claim as well, and instead in its amended Certification asserts “Five of the six cables that run throughout Fire Island were badly damaged by the storm.” It is hard to accept at face value Verizon’s estimated repair costs when even at this late date it does not seem to have a handle on exactly the damage that needs repair.
A full Hearing, with notice to affected customers, is necessary to develop facts sufficient to make such determinations and to be reasonably certain the Commission is acting based on reasonably verifiable facts.
Residents deserve a full voice and full disclosure in discussions that will directly impact their vital telecommunications services for years to come. Verizon’s corporate officials will not have to live with the results. Neither will the staff at the PSC.
Stop the Cap! has chosen to directly participate in the New York State Public Service Commission regulatory process and has filed two formal comments thus far. The first outlines Verizon’s greater strategy to abandon landline service in rural areas outlined by Verizon CEO Lowell McAdam in 2012. We also provided the Commission the prices Verizon Wireless intends to charge Verizon DSL customers switching to wireless broadband service. The second objects to Verizon’s excessive request for secrecy and exposes cell coverage issues on Fire Island.

 Despite every effort by Verizon, Fire Island residents that lost landline service are increasingly opposed to Voice Link, if the public comments filed with the Commission are any indication.
Despite every effort by Verizon, Fire Island residents that lost landline service are increasingly opposed to Voice Link, if the public comments filed with the Commission are any indication.

 Subscribe
Subscribe

 Maguire was very careful to limit Verizon’s advocacy of Voice Link in terms of its capacity to handle voice calls. That is because Voice Link is currently incompatible with a whole range of important services that have worked fine with traditional landlines for years.
Maguire was very careful to limit Verizon’s advocacy of Voice Link in terms of its capacity to handle voice calls. That is because Voice Link is currently incompatible with a whole range of important services that have worked fine with traditional landlines for years. Residents advise visitors they better have Verizon Wireless and a robust phone that works well in challenging reception areas if they expect to use it while on the island. AT&T, Sprint, and T-Mobile customers are often out of luck. That poses an immediate and direct threat to public safety, according to public safety officials.
Residents advise visitors they better have Verizon Wireless and a robust phone that works well in challenging reception areas if they expect to use it while on the island. AT&T, Sprint, and T-Mobile customers are often out of luck. That poses an immediate and direct threat to public safety, according to public safety officials.